【java】Stream的使用
首先,给大家推荐一个好的地方:http://ifeve.com/stream/ 可以好好学一下
接下来,今天要删除数组中的某些元素,想到了之前用过的这个JDK8的Stream
https://www.cnblogs.com/hhhshct/p/11275516.html
https://developer.ibm.com/zh/articles/j-lo-java8streamapi/
================================
1.Array转化为Stream并进行筛选
【有个坑】:数组转化为Stream有两种方式
1.Stream.of(数组)
2.Arrays.stream(数组)
区别:两种都支持引用数据类型,但是如果是基本数据类型的话,请选择第二种,所以妥善期间使用第二种比较合适。
【注意】:
使用stream进行任何操作,并不会因此而改变原数据的任何地方。因此想要获取到处理后的数据,需要你接收下来。
【代码展示】:
①filter中一行代码如下:
@org.junit.Test
public void test() throws IOException{
String [] str = "2.1.1&2.1.2&2.1.5&2.1.6&3.1.1&3.2.2&3.3.3&4.1.1&4.1.2&4.1.4&5.1.2&7.1.2&7.2.1&7.3.1.1&7.3.3.1&7.3.4.3&7.3.5.2&7.3.6.2&7.3.6.3".split("&");
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(str);
Object[] o1 = stream.filter(s -> s.contains("2.1.")).toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < o1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str[i].toString());
}
}
②filter中写代码块的代码如下:
【注意】:filter中写代码块,需要true或者false都要返回,否则要报错!
@org.junit.Test
public void test() throws IOException{
String [] str = "2.1.1&2.1.2&2.1.5&2.1.6&3.1.1&3.2.2&3.3.3&4.1.1&4.1.2&4.1.4&5.1.2&7.1.2&7.2.1&7.3.1.1&7.3.3.1&7.3.4.3&7.3.5.2&7.3.6.2&7.3.6.3".split("&");
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(str);
Object[] o1 = stream.filter(s -> {if(s.contains("3.1.")&& ! s.contains("7.")){
return true;
}return false;
}).toArray();
//输出原数据
System.out.println("输出原数据");
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str[i]);
}
System.out.println("输出处理后数据");
for (int i = 0; i < o1.length; i++) {
System.out.println(o1[i]);
}
}
2.List集合转化为Stream
【集合.stream()即可】
3.使用count()计数
计算List中对象的某个属性值为一个特定值的 对象有多少个
Long shanghaiNum = comList.stream().filter(i->"上海所属产品".equals(i.getBelong())).count();
先把list转化为stream(),然后filter中写出需要满足的筛选条件,最后count()计数。
4.List进行filter筛选后获取到新的List
List<ComPriceSet> xianList = comList.stream().filter(i-> "西安所属产品".equals(i.getBelong())).collect(Collectors.toList());
5.List按照对象的某个字段进行去重 distinct()
【需要进行去重操作的对象,重新equals()方法】
例如下面:

package net.shopxx.controller.admin;
/**
* 产品工具类 内部结算销量统计表
* @author SXD
*
*/
public class ProCom {
private Long productId;
private String productName;
public Long getProductId() {
return productId;
}
public void setProductId(Long productId) {
this.productId = productId;
}
public String getProductName() {
return productName;
}
public void setProductName(String productName) {
this.productName = productName;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result
+ ((productId == null) ? 0 : productId.hashCode());
result = prime * result
+ ((productName == null) ? 0 : productName.hashCode());
return result;
}
//规定如果productId一致,则代表两个equals() 为true
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
ProCom other = (ProCom) obj;
if (productId == null) {
if (other.productId != null)
return false;
} else if (!productId.equals(other.productId))
return false;
return true;
}
}
List<ProCom> xianProList = xianProList.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList())
6.List中有需要按照某个字段进行分组,可以使用Collectors.groupingBy()分组器实现
例如:
按照ComLabSet实体中productId进行分组,Collectors.groupingBy(ComLabSet::getProductId)中::后面跟的是你要分组的字段的get方法名

package net.shopxx.controller.admin;
/**
* 导出实验室对账单 工具类
* @author SXD
*
*/
public class ComLabSet implements Comparable<ComLabSet>{
private Long orderId; //订单ID
private Boolean by_credit_card;//是否赠送 1true 0false
private Long productId; //产品ID
private String productName; //产品名称
private String product_belong;//产品所属公司
private String cybbm; //采样包编码
private Long sysId; //实验室ID
private String sysName; //实验室名称
public Long getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public void setOrderId(Long orderId) {
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public Boolean getBy_credit_card() {
return by_credit_card;
}
public void setBy_credit_card(Boolean by_credit_card) {
this.by_credit_card = by_credit_card;
}
public Long getProductId() {
return productId;
}
public void setProductId(Long productId) {
this.productId = productId;
}
public String getProductName() {
return productName;
}
public void setProductName(String productName) {
this.productName = productName;
}
public String getProduct_belong() {
return product_belong;
}
public void setProduct_belong(String product_belong) {
this.product_belong = product_belong;
}
public String getCybbm() {
return cybbm;
}
public void setCybbm(String cybbm) {
this.cybbm = cybbm;
}
public Long getSysId() {
return sysId;
}
public void setSysId(Long sysId) {
this.sysId = sysId;
}
public String getSysName() {
return sysName;
}
public void setSysName(String sysName) {
this.sysName = sysName;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(ComLabSet s) {
Long productId1 = this.getProductId();
Long productId2 = s.getProductId();
return productId1>productId2 ? 1 : productId1 == productId2 ? 0 : -1;
}
}
Map<Long,List<ComLabSet>> xianTypeMap = xianList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(ComLabSet::getProductId));
结果类似于下面:Map的键是分组字段productId ,值是一组的list

7.按照实体的某个字段 转换类型后再分组
例如:将student的 String字段name 转换成 Long类型。将name按照Long类型进行分组
student实体

package com.sxd.streamTest;
/**
* @ClassName Student
* @Description TODO
* @Author sxd
* @Date 2019/9/26 21:06
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Long getNameToLong(){
return Long.valueOf(name);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Student(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
转化:
//name按照String类型分组
Map<String, List<Student>> collect = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getName));
//name按照Long类型分组 Map<Long, List<Student>> collect1 = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getNameToLong));
8.mapToInt 的使用之 字符串数组转化成整型数组
String[] stringArr = new String[]{"111","222","333"};
int [] intArr = Arrays.stream(stringArr).mapToInt(s->Integer.parseInt(s)).toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < intArr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(intArr[i]);
}
效果:

9.List转化为数组
专刊:http://www.cnblogs.com/sxdcgaq8080/p/8269877.html
10.将对象数组转化为String数组
这里演示,就将反射对象转化为String[],主要是看怎么转化为String[],任意对象数组都可以【注意最后toArray(String[]::new)才是转化为String数组的关键】
User user = new User();
user.setPassword("adsas");
user.setUserName("德玛西亚");
String [] strs = Arrays.stream(user.getClass().getDeclaredFields()).map((field) ->{
return field.getName().toString();
}).toArray(String[]::new);
System.out.println(strs[0] instanceof String);
11.List去重
List<String> unique = list.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
12.List<GoodsMsg>按照集合中实体GoodsMsg 中的floor字段进行升序排序和降序排序【本方法 不需要GoodsMsg实体实现Comparable接口】
升序:
list = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(GoodsMsg::getFloor)).collect(Collectors.toList());
降序:
list = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(GoodsMsg::getFloor).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
13.List<实体>获取List<String>其中一个字段
List<String> toIds = mappers.stream().map(i->i.getToUid()).collect(Collectors.toList());
14.List<Dealer> dealer实体按照id字段去重 List集合实体按照某个字段去重 不用更改实体的做法【效率一定比自己做去重要快很多】【可以尝试ArrayList和LinkedList两种】
list = list.parallelStream().filter(distinctByKey(Dealer::getId)).collect(Collectors.toList());
public static <T> Predicate<T> distinctByKey(Function<? super T, ?> keyExtractor) {
Set<Object> seen = ConcurrentHashMap.newKeySet();
return t -> seen.add(keyExtractor.apply(t));
}
15.List<Student> Student实体 按照 id和name 两个字段或多个字段 去重
List<Student> distinctResult = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toCollection(() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(o -> o.getId() + ";" + o.getAge()))), ArrayList::new));
16.字符串逗号切割,字符串数组转化成Long类型的List或Set
String str = "123,456,789,220,,";
try {
List<Long> collect = Arrays.asList(str.split(",")).stream().map(a -> Long.parseLong(a)).collect(Collectors.toList());
Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>(collect);
System.out.println(set.size());
}catch (Exception e){
throw new Exception("搞一下?");
}
17.List转Map【根据ID做为key,对象做value】
List<WareExtVO> list;
list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(WareExtVO::getSkuId, wareExtVO -> wareExtVO));
18.List转Map【ID做key,另一个字段做value】
Map<Integer, String> collect = wmStores.stream().filter(i -> difference.contains(i.getId().toString())).collect(Collectors.toMap(WmStore::getId, WmStore::getSap_id));
解决重复key问题(异常:java.lang.IllegalStateException: Duplicate key)
第一种,如果有重复key,以后面的value覆盖前面的value
Map<String, String> map = xxxList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e.getCode(), e -> e.getName() , (key1, key2) -> key2));
第二种,如果有重复key,以之前的value和这个value拼接,作为新的value
Map<String, String> map = xxxList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(e -> e.getCode(), e -> e.getName() , (key1, key2) -> key1 + "~" + key2));
19.List转Map【ID做key,List<对象>做value】
Map<Integer, List<Student>> sexKeyMap = stuList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getSex));
Map<Integer, List<Student>> map = list.stream().collect(
Collectors.toMap(
Student::getId,
stu -> Lists.newArrayList(stu),
(List<Student> newList, List<Student> oldList) -> {
oldList.addAll(newList);
return oldList;
}
)
);
20.对封装类List集合进行排序,升序或降序
List<Long> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(12L);
list.add(10L);
list.add(17L);
list.add(7L);
//升序
List<Long> collect = list.stream().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Long aLong : collect) {
System.out.println(aLong);
}
//降序
List<Long> collect1 = list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Long::longValue).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (Long aLong : collect1) {
System.out.println(aLong);
}
21.stream过程中加入代码段,处理一些逻辑map方法内
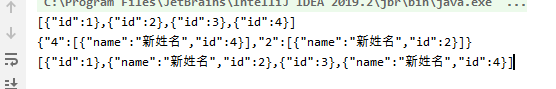
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<StuA> list = new ArrayList<>();
StuA a = new StuA();
a.setId(1);
list.add(a);
StuA b = new StuA();
b.setId(2);
list.add(b);
StuA c = new StuA();
c.setId(3);
list.add(c);
StuA d = new StuA();
d.setId(4);
list.add(d);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(list));
Map<Integer, List<StuA>> map = list.stream().filter(i -> i.getId() % 2 == 0)
.map(x -> {
x.setName("新姓名");
return x;
}).collect(Collectors.toMap(StuA::getId,
stuA -> Lists.newArrayList(stuA),
(List<StuA> newList, List<StuA> oldList) -> {
oldList.addAll(newList);
return oldList;
}));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(map));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSON(list));
}
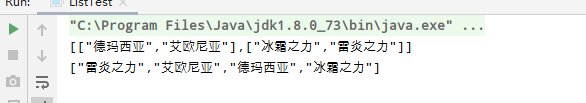
22. flatMap 铺平 平铺 套层集合为一层集合
List<List<String>> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(Arrays.asList("德玛西亚","艾欧尼亚")); list.add(Arrays.asList("冰霜之力","雷炎之力")); System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(list)); //铺平 平铺 套层集合为一层集合 Set<String> collect = list.stream().flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toSet()); System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(collect));
23.
24.





