20162330 第六周 蓝墨云班课 队列课下作业
作业要求
- 1 补充课上没有完成的作业
2 参考15.3节,用自己完成的队列(链队,循环数组队列)实现模拟票务柜台排队功能
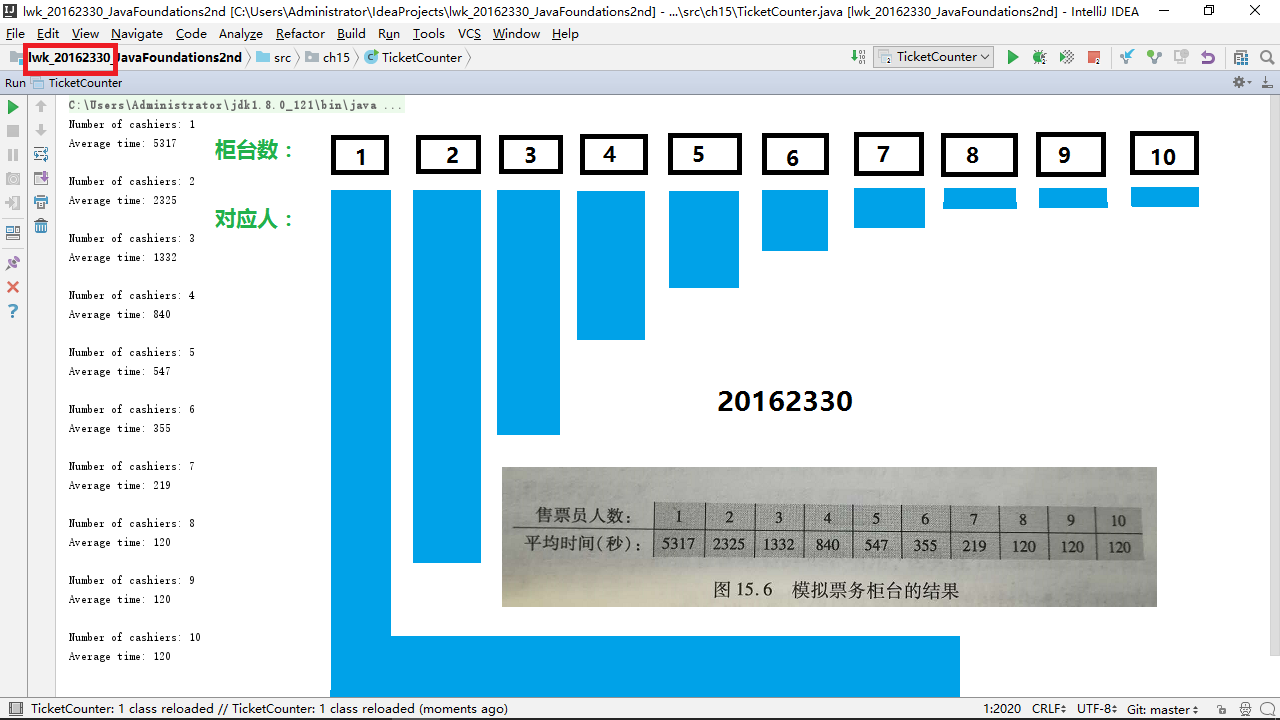
3 用JDB或IDEA单步跟踪排队情况,画出队列变化图,包含自己的学号信息
4 把代码推送到代码托管平台
5 把完成过程写一篇博客:重点是单步跟踪过程和遇到的问题及解决过程
6 提交博客链接
模拟票务柜台排队的实现
- 使用链表实现队列只需补充程序15.5即可:
public class LinkedQueue<T> implements Queue<T> {
private int count;
private LinearNode<T> front,rear;
/*
Creates an empty queue.
*/
public LinkedQueue(){
count = 0;
front = rear = null;
}
/*
Adds the specified element to the rear of this queue.
*/
public void enqueue(T element) {
LinearNode<T> node = new LinearNode<>(element);
if(count == 0) {
front = node;
}
else {
rear.setNext(node);
}
rear = node;
count++;
}
/*
Removes the rear element from the front of the queue.
*/
public T dequeue() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("The queue is empty.");
}
T result = front.getElement();
front = front.getNext();
count--;
if (isEmpty()) {
rear = null;
}
return result;
}
/*
Examines the element at the front of the queue.
*/
public T first() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
if (isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyCollectionException ("The queue is empty.");
}
return front.getElement();
}
/*
Determines if the queue is empty.
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
/*
Determines the number of elements on the queue.
*/
public int size() {
return count;
}
/*
Returns the representation of the queue.
*/
public String toString(){
String result = "";
LinearNode<T> current = front;
while (current != null)
{
result += current.getElement().toString() + "\n";
current = current.getNext();
}
return result;
}
}
-
和实现栈相同的是,可以使用上一章中的 LinearNode类 创建的对象实现队列;和实现栈不同的是,这里必须在链表的两端进行操作。
-
由于实现的是单链表,所以要将新元素放在表尾。如果队列为空,那么front和rear都指向表头结点。实现表头出队和检测对头元素操作时,注意空队列要抛出异常。还要注意出队操作时要判断两次队列是否为空,第一次为空则抛出异常,第二次为空则(在删除前面的元素之后)将rear置为null。
- 使用数组实现队列只需补充程序15.6即可:
public class CircularArrayQueue<T> implements Queue<T> {
private final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
private int front, rear, count;
private T[] queue;
/*
Creates an empty queue using the default capacity.
*/
public CircularArrayQueue() {
front = rear = count = 0;
queue = (T[]) (new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY]);
}
/*
Adds the specified element to the rear of this queue,expanding
the capacity of the queue array if necessary.
*/
public void enqueue(T element) {
if (count == queue.length) {
expandCapacity();
}
queue[rear] = element;
rear = (rear + 1) % queue.length; //取余赋值确定下一个可用位置
count++;
}
/*
Creates a new array to store the contents of this queue with
twice the capacity of the old one.
*/
public void expandCapacity() {
T[] larger = (T[]) (new Object[queue.length * 2]);
for (int index = 0; index < count; index++) {
larger[index] = queue[(front + index) % queue.length]; //按相对次序复制数组
}
front = 0;
rear = count;
queue = larger;
}
/*
Removes the rear element from the queue.
*/
public T dequeue() throws EmptyCollectionException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("queue");
}
T result = queue[front];
queue[front] = null;
front = (front + 1) % queue.length; //取余赋值确定下一个出队位置
count--;
return result;
}
/*
Examines the element at the front of the queue.
*/
public T first() throws EmptyCollectionException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new EmptyCollectionException("queue");
}
return queue[front];
}
/*
Determines if the queue is empty.
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (count == 0);
}
/*
Determines the number of elements on the queue.
*/
public int size() {
return count;
}
/*
Returns the representation of the queue.
*/
public String toString() {
String result = "";
int scan = 0;
while (scan < count) {
if (queue[scan] != null) {
result += queue[scan].toString() + "\n";
}
scan++;
}
return result;
}
}
-
和使用数组实现栈不同的是,这里使用了“取余赋值”的方式确定入队和出队位置,不论是扩容前还是扩容后都适用,同时也包含了队列为空的情况(出队操作不需要第二次判空赋值)。比如入队操作中的
rear = (rear + 1) % queue.length,就可以通过取余赋值确定下一个可用位置。 -
这里的扩容方法比实现栈复杂一些,要求按照相对次序复制原数组,在扩容后更新,front需要置为0,rear需要置为count。这里的toString方法由于遍历不会影响其他操作所以不用像链表一样使用另外创建的临时变量代替front引用。
-
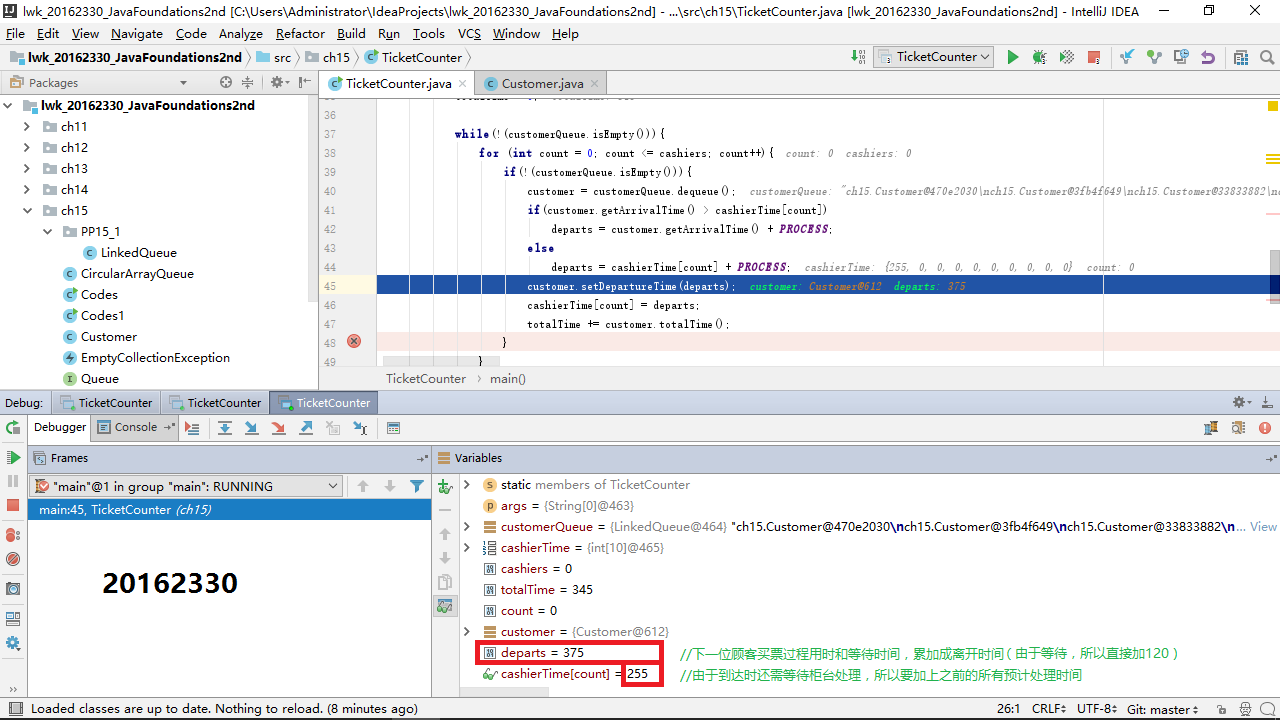
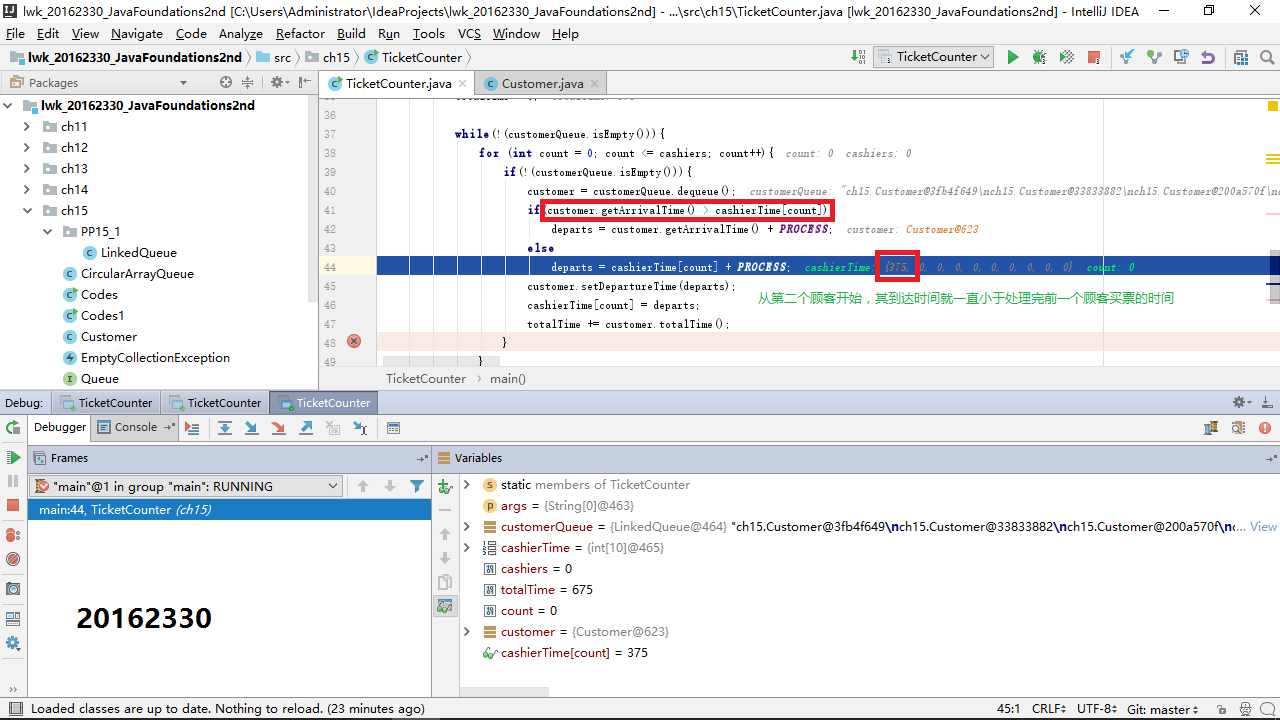
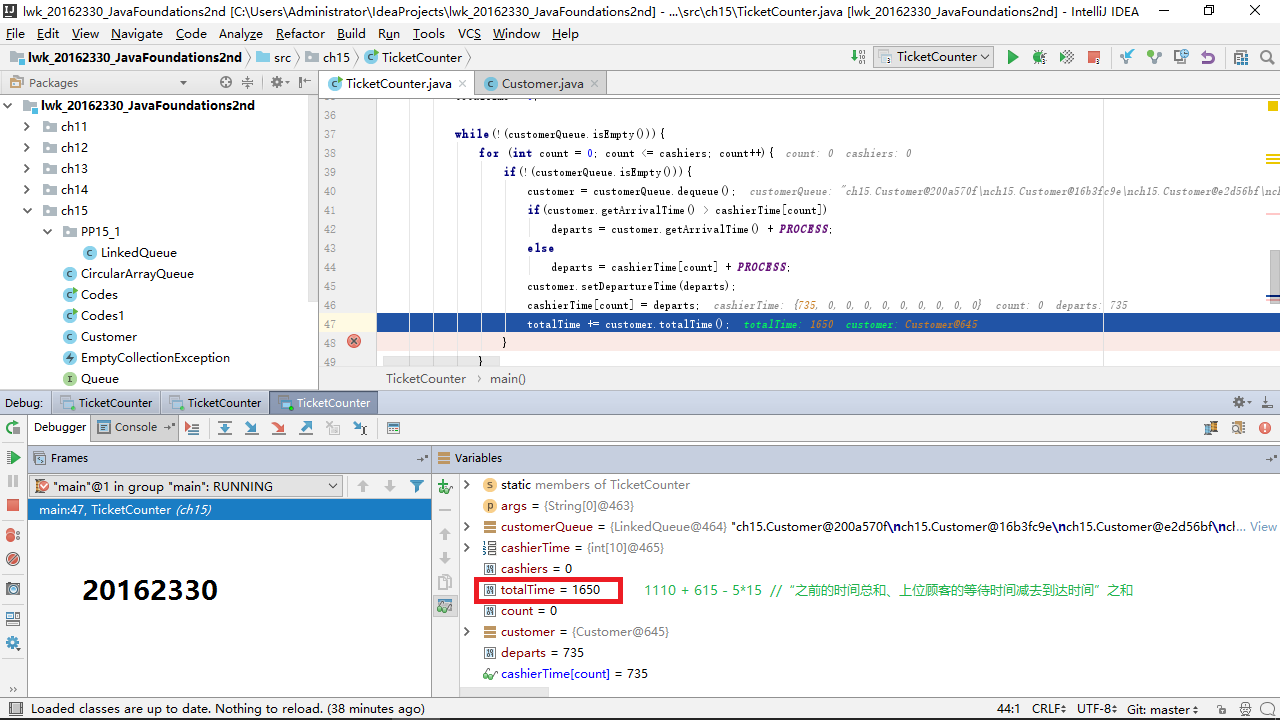
关于实现模拟票务柜台的Customer顾客队列和TicketCounter类,要求如下:
- 只排一个队,并且先来先服务。
- 平均15秒来一位顾客。
- 如果增加一位售票员,立即投入工作。
- 从顾客来到售票员跟前买票到买完离开,平均需要2分钟(120秒)。
-
书中已经给出相关代码,相关代码见【托管链接】