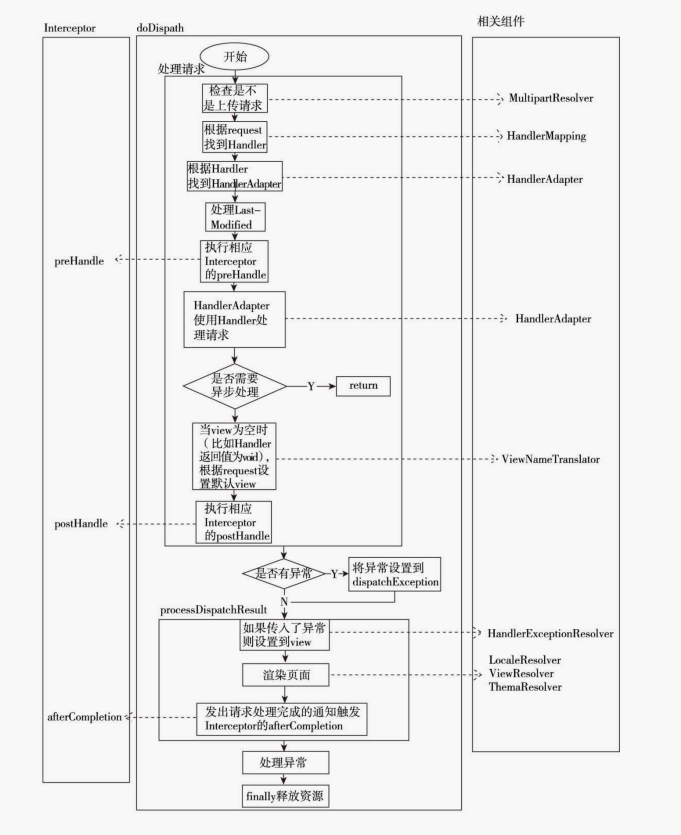
DispatcherServlet类的几点认识
- 1.主要方法:
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception
方法中主要代码有:
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
- 2.包含的几个类含义:
Handler:也就是处理器,它直接对应着MVC中的C也就是Controller层,它的具体表现形式有很多,可以是类,也可以是方法,如果你能想到别的表现形式也可以使用,它的类型是Object。我们前面例子中标注了@RequestMapping的所有方法都可以看成一个Handler。只要可以实际处理请求就可以是Handler。
HandlerMapping:是用来查找Handler的,在SpringMVC中会处理很多请求,每个请求都需要一个Handler来处理,具体接收到一个请求后使用哪个Handler来处理呢?这就是HandlerMapping要做的事情。HandlerAdapter:很多人对这个的理解都不准确,其实从名字上就可以看出它是一个Adapter,也就是适配器。因为SpringMVC中的Handler可以是任意的形式,只要能处理请求就OK,但是Servlet需要的处理方法的结构却是固定的,都是以request和response为参数的方法(如doService方法)。怎么让固定的Servlet处理方法调用灵活的Handler来进行处理呢?这就是HandlerAdapter要做的事情。
通俗点的解释就是Handler是用来干活的工具,HandlerMapping用于根据需要干的活找到相应的工具,HandlerAdapter是使用工具干活的人。比如,Handler就像车床、铣床、电火花之类的设备,HandlerMapping的作用是根据加工的需求选择用什么设备进行加工,而HandlerAdapter是具体操作设备的工人,不同的设备需要不同的工人去加工,车床需要车工,铣床需要铣工,如果让车工使用铣床干活就可能出问题,所以不同的Handler需要不同的HandlerAdapter去使用。我们都知道在干活的时候人是柔性最强、灵活度最高的,同时也是问题最多、困难最多的。SpringMVC中也一样,在九大组件中HandlerAdapter也是最复杂的,所以在后面学习HandlerAdapter的时候要多留心。另外View和ViewResolver的原理与Handler和HandlerMapping的原理类似。View是用来展示数据的,而ViewResolver用来查找View。通俗地讲就是干完活后需要写报告,写报告又需要模板(比如,是调查报告还是验收报告或者是下一步工作的请示等),View就是所需要的模板,模板就像公文里边的格式,内容就是Model里边的数据,ViewResolver就是用来选择使用哪个模板的。
具体代码如下:
1 protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; 3 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; 4 boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; 5 6 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); 7 8 try { 9 ModelAndView mv = null; 10 Exception dispatchException = null; 11 12 try { 13 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); 14 multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); 15 16 // Determine handler for the current request. 17 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); 18 if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { 19 noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); 20 return; 21 } 22 23 // Determine handler adapter for the current request. 24 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); 25 26 // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. 27 String method = request.getMethod(); 28 boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); 29 if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { 30 long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 31 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 32 logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); 33 } 34 if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { 35 return; 36 } 37 } 38 39 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { 40 return; 41 } 42 43 // Actually invoke the handler. 44 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 45 46 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 47 return; 48 } 49 50 applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); 51 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); 52 } 53 catch (Exception ex) { 54 dispatchException = ex; 55 } 56 catch (Throwable err) { 57 // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, 58 // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. 59 dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); 60 } 61 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); 62 } 63 catch (Exception ex) { 64 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); 65 } 66 catch (Throwable err) { 67 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, 68 new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); 69 } 70 finally { 71 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 72 // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion 73 if (mappedHandler != null) { 74 mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); 75 } 76 } 77 else { 78 // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. 79 if (multipartRequestParsed) { 80 cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); 81 } 82 } 83 } 84 }
方法执行过程如下图: