Unity 之 Redux 模式(第一篇)—— 人物移动
2016-12-06 12:33 软件猫 阅读(1339) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 举报作者:软件猫
日期:2016年12月6日
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/softcat/p/6135195.html
在朋友的怂恿下,终于开始学 Unity 了,于是有了这篇文章。
本文用一个控制小人移动的示例,讲述如何在 Unity 中实现 Redux 架构。
关于 Flux、单向数据流是什么,请参考 阮一峰 大大的文章 http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/01/flux.html
Redux 是什么鬼
Reflux是根据 Facebook 提出的 Flux 创建的 node.js 单向数据流类库。它实现了一个简化版的 Flux 单向数据流。
如下图所示:
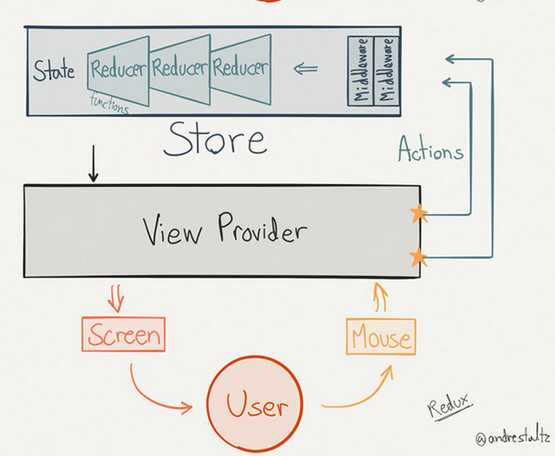
小明(User)在家打游戏,边看着屏幕,边用键盘鼠标控制游戏中的人物。
屏幕后面有个 ViewProvider(当然,小明才不管这个)。
ViewProvider 负责两个事情:
1、每一帧渲染前,根据数据(State)更新 GameObject 中的参数。
2、获取键盘鼠标的输入,然后向 Store 发 Action,告诉 Store,小明按了键盘⬆️键
别的事情它就不管了。它不能亲自去修改 State 数据。
Store 也负责两件事情:
1、保存游戏的数据,这里我们叫 State。
2、建了一个处理管道,里面丢了一堆 Reducer。Action 来了以后,会丢进这个管道里。管道中的 Reducer 会判断这个 Action 自己是否关心,如果关心,则处理 Action 中承载的数据,并更新 State。
它们两各司其职,并形成了一个单项数据流。
每个游戏通常只有一个 Store,集中管理游戏数据,方便 Load & Save。
Store 中的 State 是一个很大的数据树,保存了游戏中所有的数据。
通常建议这个树是扁平化的,一般只有两三层。这样在序列化和反序列化的时候可以得到更好的性能。
Unity 中的 GameObject 通常会对应一到多个 ViewProvider。
每个 ViewProvider 通常都会发出 Action。
每个 Action 都有对应的一到多个 Reducer 来处理数据。
实践1: 用常规的方式实现一个可以控制走动的小人
1、创建一个 Unity 2D 项目。
2、将下面的小人作为 Sprite 资源拖入 Project。
3、将小人从 Project 中拖入 Scene,并重命名为 Player。
4、设置 Position 为 0,0,0。
5、设置 Rotation 为 0,0,90,让小人面向上方。
6、选中 Player,点击菜单 Component -> Physics 2D -> Rigidbody 2D,为小人添加刚体组件。
7、创建如下脚本,并拖放到 Player 上。这段脚本用于处理 Player
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; public class PlayerMovement : MonoBehaviour { [SerializeField] float speed = 3f; Rigidbody2D rigid; float ax, ay; void Start () { rigid = GetComponent<Rigidbody2D> (); } void FixedUpdate () { getInput (); rotate (); move (); } // 获取摇杆输入 void getInput () { ax = Input.GetAxis ("Horizontal"); ay = Input.GetAxis ("Vertical"); } // 处理旋转 void rotate () { if (ax == 0 && ay == 0) return; float r = Mathf.Atan2 (ay, ax) * Mathf.Rad2Deg; rigid.MoveRotation (r); } // 处理移动 void move () { Vector2 m = new Vector2 (ax, ay); m = Vector2.ClampMagnitude (m, 1); Vector2 dest = (Vector2)transform.position + m; Vector2 p = Vector2.MoveTowards (transform.position, dest, speed * Time.fixedDeltaTime); rigid.MovePosition (p); } }
我们设置了一个 speed 参数,用于设置小人行走的速度。
我们创建了 FixedUpdate 方法,接受摇杆输入数据,然后分别处理小人的转向和移动。
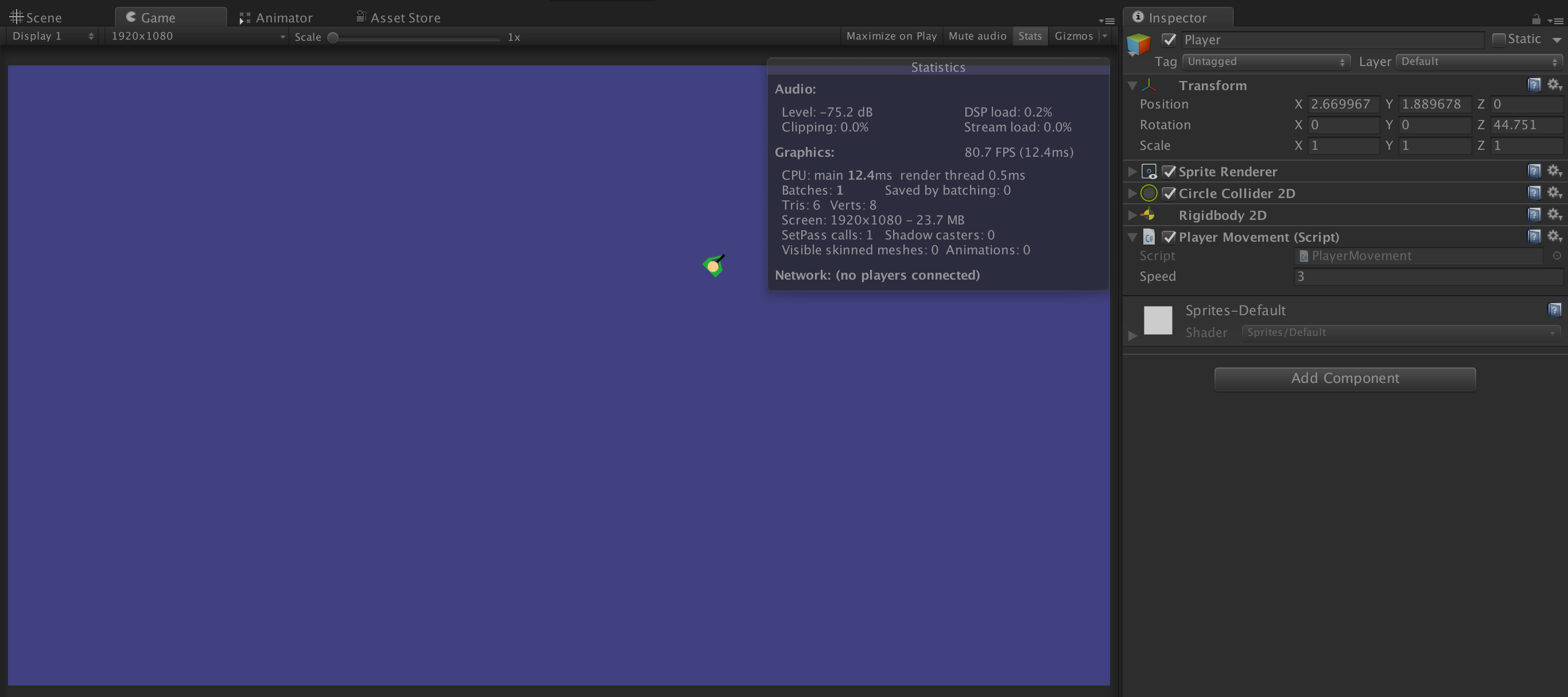
完成后点击 Play ,小人可以在 Game 视图中通过方向键控制移动。
实践2: 实现Redux模式
现在,我们来实现 Redux。
首先创建如下脚本文件:
| 文件名 | 描述 |
| IAction.cs | Action 接口 |
| IReducer.cs | Reducer 接口 |
| Store.cs | 存放 State,构建 Reducer 管道 |
| State.cs | State 数据的根 |
| ViewProvider.cs | PlayerViewProvider 的基类 |
| PlayerActions.cs | 存放多个 Player 相关的 Action |
| PlayerReducers.cs | 存放多个 Player 相关的 Reducer |
| PlayerState.cs | 保存和 Player 相关的 State |
| PlayerViewProvider.cs | 继承 ViewProvider,实现 Action 和 Render |
文件建好后,我们直接上代码:
1、IAction.cs
public interface IAction { }
这个比较简单,一个空接口。用于识别 Action 而已。
2、IReducer.cs
public interface IReducer { State Reduce (State state, IAction action); }
创建了一个接口,声明了 Reduce 方法。在 Store 管道中,循环调用所有的 Reducer,并执行这个方法。
方法传入当前的 State 和要处理的 Action。Reducer 判断如果是自己的 Action,则处理数据,并修改 State,然后将 State 返回。
注意:在 Redux 模式中,通常建议 State 是一个不变量,Reducer 并不直接修改它,而是创建一个修改过的 State 的副本,然后将其返回。
使用不变量有很多好处,比如我们可以轻松实现一个 Do - Undo 的功能。不过游戏里这个功能大多时候不太有用(特例:纸牌)
但是在游戏开发中,由于考虑到性能问题,这里还是舍弃了这个特性。
3、Store.cs
using UnityEngine; using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Reflection; public class Store : MonoBehaviour { // 保存 State 数据 public static State State { get; private set; } // Reducer 列表 static List<IReducer> reducerList; // 静态构造函数 static Store () { State = new State (); // 反射获取项目中所有继承 IReducer 的类,生成实例,并加入 reducerList 列表 reducerList = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies () .SelectMany (a => a.GetTypes ().Where (t => t.GetInterfaces ().Contains (typeof(IReducer)))) .Select (t => Activator.CreateInstance (t) as IReducer) .ToList (); } // ViewProvider 调用 Dispatch 方法,传入 Action // 循环调用所有的 Reducer,传入当前的 State 与 Action // 将 Reducer 返回的 State 保存 public static void Dispatch (IAction action) { foreach (IReducer reducer in reducerList) { State = reducer.Reduce (State, action); } } // 状态改变事件 public static Action<State> StateChanged; public static Action<State> FixedStateChanged; // FixedUpdate 时执行,监测 State 是否变更,并抛出 FixedStateChanged 事件 void FixedUpdate () { StartCoroutine (AfterFixedUpdate ()); } IEnumerator AfterFixedUpdate () { yield return new WaitForFixedUpdate (); if (!State.IsFixedStateChanged) yield break; State.IsFixedStateChanged = false; if (FixedStateChanged != null) FixedStateChanged (State); } // LateUpdate 时执行,监测 State 是否变更,并抛出 StateChanged 事件 void LateUpdate () { if (!State.IsStateChanged) return; State.IsStateChanged = false; if (StateChanged != null) StateChanged (State); } }
Store 负责下面的事情:
a、保存 State
b、创建 Reducer 管道,用于处理 Action
c、在每一个固定帧,所有的 GameObject 执行完 FixedUpdate 后,执行 AfterFixedUpdate,抛出 FixedStateChanged 事件。
详见 Unity 之 AfterFixedUpdate,在所有 GameObject FixedUpdate 后执行
d、在 LateUpdate 时,抛出 StateChanged 事件。
由于物理引擎需要使用固定帧率的 FixedUpdate,这里把 FixedStateChanged 和 StateChanged 分开,分别抛出事件。
4、State.cs
// State 根。用于存放其他模块定义的 State。 public class State { // 变更标记。Reducer 如果更改了 State 中的数据,需要将此值设置为 True。 public bool IsStateChanged { get; set; } // 物理引擎的数据变更单独记录 public bool IsFixedStateChanged { get; set; } // Player 模块定义的 State public Player.PlayerState Player { get; private set; } public State () { Player = new Player.PlayerState (); } }
IsStateChanged 会被 Reducer 修改为 True。Store 会通过 IsChanged 触发 OnStateChanged 事件,并通知 ViewProvider。
同样,IsFixedStateChanged = true 会触发 OnFixedStateChanged 事件。
5、ViewProvider.cs
using UnityEngine; // 继承了 MonoBehaviour,可用于附加到 GameObject 上 public class ViewProvider : MonoBehaviour { // 注册 StateChanged 和 FixedStateChanged 事件 protected virtual void Awake () { Store.StateChanged += OnStateChanged; Store.FixedStateChanged += OnFixedStateChanged; } // 注销 StateChanged 和 FixedStateChanged 事件 protected virtual void OnDestroy () { Store.StateChanged -= OnStateChanged; Store.FixedStateChanged -= OnFixedStateChanged; } // 处理状态变更 protected virtual void OnStateChanged (State state) { } // 处理物理引擎相关状态变更 protected virtual void OnFixedStateChanged (State state) { } }
ViewProvider 基类。注册/注销 OnStateChanged 和 OnFixedStateChanged 事件。子类可以 override 这两个方法,实现相应的游戏数据变更。
1-5 我们把框架搭好了,下面开始实现 PlayerMovement 。
6、PlayerActions.cs
using UnityEngine; namespace Player { // Player 初始化,设置坐标、旋转角度与移动速度 public class InitAction : IAction { public Vector2 position { get; set; } public float rotation { get; set; } public float speed { get; set; } } // 移动轴 public class AxisAction : IAction { public float x { get; set; } public float y { get; set; } } }
两个 Action
7、PlayerReducers.cs
using UnityEngine; namespace Player { // 处理初始化过程 public class InitReducer : IReducer { public State Reduce (State state, IAction action) { // 检测 action 类型是不是自己想要的,如果不是,则说明自己不需要做什么,直接返回 state 即可。 if (!(action is InitAction)) return state; InitAction a = action as InitAction; // 初始化 PlayerState state.Player.Position = a.position; state.Player.Rotation = a.rotation; state.Player.Speed = a.speed; return state; } } // 处理摇杆数据 public class AxisReducer : IReducer { public State Reduce (State state, IAction action) { // 检测 action 类型是不是自己想要的,如果不是,则说明自己不需要做什么,直接返回 state 即可。 if (!(action is AxisAction)) return state; AxisAction a = action as AxisAction; // 如果摇杆在 0 点,则不需要处理数据,直接返回 state。 if (a.x == 0 && a.y == 0) return state; // 根据 action 传入的摇杆数据修改 state float speed = state.Player.Speed; Vector2 position = state.Player.Position; // 旋转 state.Player.Rotation = Mathf.Atan2 (a.y, a.x) * Mathf.Rad2Deg; // 位移 Vector2 m = new Vector2 (a.x, a.y); m = Vector2.ClampMagnitude (m, 1); Vector2 dest = position + m; state.Player.Position = Vector2.MoveTowards (position, dest, speed * Time.fixedDeltaTime); // 每次修改 state 之后,需要告诉 state 已经被修改过了 state.IsFixedStateChanged = true; return state; } } }
InitReducer:读取了游戏的初始化数据,并传给State。它并不知道初始化数据是从哪里来的(也许是某个xml,或者来自网络),只管自己执行初始化动作。
AxisReducer:我们把 PlayerMovement 中的代码搬了过来。
8、PlayerState.cs
using UnityEngine; namespace Player { public class PlayerState { // 玩家坐标 public Vector2 Position { get; set; } // 玩家面向的方向 public float Rotation { get; set; } // 移动速度 public float Speed { get; set; } } }
这个文件写好后,在 State 中加入 PlayerState 类型的属性,并在 State 构造函数中初始化。
9、PlayerViewProvider.cs
using UnityEngine; namespace Player { public class PlayerViewProvider: ViewProvider { [SerializeField] float speed = 3f; Rigidbody2D rigid = null; void Start () { rigid = GetComponent<Rigidbody2D> (); // 执行初始化 Store.Dispatch (new InitAction () { position = transform.position, rotation = transform.rotation.eulerAngles.z, speed = this.speed, }); } void FixedUpdate () { // 获取轴数据,并传递 Action float ax = Input.GetAxis ("Horizontal"); float ay = Input.GetAxis ("Vertical"); if (ax != 0 || ay != 0) { Store.Dispatch (new AxisAction () { x = ax, y = ay }); } } protected override void OnFixedStateChanged (State state) { if (rigid != null) { // 刚体旋转和移动 rigid.MoveRotation (state.Player.Rotation); rigid.MovePosition (state.Player.Position); } } } }
最终,我们通过 PlayerViewProvider 将上面所有的代码连起来。
在 Start 时初始化数据,这里我们是直接取的 Unity 编辑器中的数据。真实游戏数据会来自网络或游戏存档。
在 FixedUpdate 时获取移动轴数据,然后执行 Action。
在 OnFixedStateChanged 中改变刚体数据。
脚本写好后,我们创建一个空 GameObject,重命名为 Store,拖入 Store 脚本。
然后把 PlayerViewProvider 拖到 Player 这个 GameObject 上,并关掉实践1中的 PlayerMovement。
执行游戏!大功告成!
重要!这一篇旨在说明 Redux 模式。实际开发中,Rigidbody2D.MovePosition 会根据碰撞物来决定最终的 Position 和 Rotation。在下一篇,我们会针对这个问题进行改造。


