[PY3]——内置数据结构(1)——列表及其常用操作
列表及其常用操作_xmind图
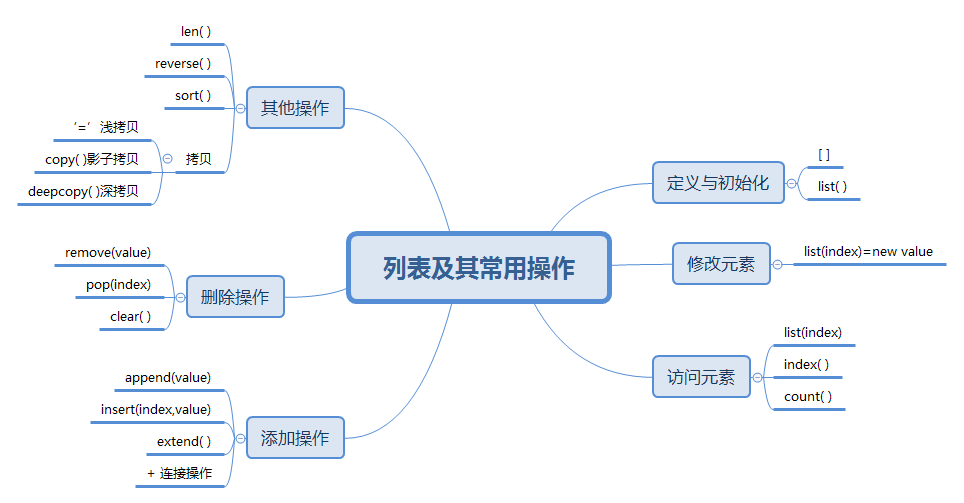
about列表
列表是一个序列,用于顺序存储数据
列表分为两种:ArrayList(用数组实现)、LinkedList(用链表实现)
定义与初始化
#list() 使用工厂函数list定义一个空列表 #[] 使用中括号定义一个空列表 #[1,2,3] 使用中括号定义有初始值的列表 #list(可迭代对象) 把可迭代对象转换为一个列表 In [1]: lst=list();print(lst) [] In [2]: lst=[];print(lst) [] In [3]: lst=[1,2,3];print(lst) [1, 2, 3] In [4]: lst=list(range(1,10));print(lst) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
修改列表元素
# 直接使用索引操作即可 list[index]=new value In [2]: lst=[1,2,3,2,4,3,5] In [3]: lst[4]=3 In [4]: print(lst) [1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5]
访问列表元素
1. list(index) 通过索引访问元素,索引规则为:
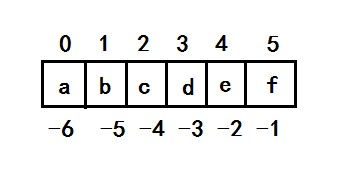
#索引从0开始 In [5]: print(lst[0]) 1 #负数索引从-1开始 In [6]: print(lst[-1]) 9 In [7]: print(lst[-2]) 8 #当索引(正负都是)超出范围,会报错IndexError In [6]: print(lst[10]) IndexError: list index out of range
2. index()
# index()主要用于查找列表中某个值的索引 In [3]:help(lst.index) index(...) method of builtins.list instance L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. Raises ValueError if the value is not present. In [3]: lst=[1,2,3,2,1] # 返回要查找的value的第一个索引 In [4]: lst.index(2) Out[4]: 1 # start参数指定从哪个索引开始查找 In [5]: lst.index(2,2) Out[5]: 3 # stop参数指定从到哪个索引结束,且[start,stop]的范围中不包含stop # 当value不能在[start,stop]的范围查找到,则报错ValueError In [6]: lst.index(2,2,3) ValueError: 2 is not in list # 若想缺省start值,可将其设为0(start的默认值为0,stop的默认值为-1) In [7]: lst.index(2,0,3) Out[7]: 1 # start和stop可以是负索引,但总是从左往右查找 In [8]: lst.index(2,-4,-1) Out[8]: 1
# 并且要注意:如果stop<start,就相当于在空列表中查找一个元素,则抛出ValueError In [9]: lst.index(2,-1,-4) ValueError: 2 is not in list
3. count()
# count()返回某个value值在列表中出现的次数 In [14]: help(lst.count) Help on built-in function count: count(...) method of builtins.list instance L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value In [15]: lst.count(2) Out[15]: 2 In [16]: lst.count(10) Out[16]: 0
添加列表元素
1. append() 用于在list末尾添加一个元素
# 原地修改list,返回结果为none In [5]: help(lst.append) Help on built-in function append: append(...) method of builtins.list instance L.append(object) -> None -- append object to end In [1]: lst=[1,2,3,2,3,3,5] In [2]: lst.append(9) In [3]: print(lst) [1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, 9]
2. insert() 用于在指定索引位置添加元素
# 原地修改list,返回结果为none In [12]: help(lst.insert) insert(...) method of builtins.list instance L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index In [13]: lst=[1,2,3,2,3,3,5,9] # 正数索引:实际是使得index位置上的元素为我们所添加的,后面的元素依次往后挪 In [14]: lst.insert(1,11);print(lst) [1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, 9] In [15]: lst.insert(0,'a');print(lst) ['a', 1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, 9] # 负数索引:实际是在index的前一个位置添加元素 In [16]: lst.insert(-1,'-a');print(lst) ['a', 1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, '-a', 9] # 当index超出索引范围,正数索引会在最后一个位置添加元素 In [17]: lst.insert(100,'100');print(lst) ['a', 1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, '-a', 9, '100'] # 当index超出索引范围,负数索引会在第0个位置添加元素 In [18]: lst.insert(-100,'-100');print(lst) ['-100', 'a', 1, 11, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 5, '-a', 9, '100'] # 比较append和insert: append的时间复杂度是O(1):常数时间,效率和数据规模无关 insert的时间复杂度是O(n):线性时间,效率和数据规模有关
3. extend()
# extend的参数是一个可迭代对象,在list末尾添加此可迭代对象 #原地修改list,返回结果为none In [1]: help(lst.extend) extend(...) method of builtins.list instance L.extend(iterable) -> None -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable In [1]: lst=[1,2,3] In [2]: lst.extend([4,5,6]);print(lst) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] In [3]: lst.extend(range(0,4));print(lst) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 1, 2, 3]
4. + list的连接操作
# 连接操作不修改list本身,返回一个新的list In [9]: lst=[1,2,3] In [10]: lst+[4,5,6] Out[10]: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] In [11]: print(lst) [1, 2, 3] In [12]: lst2=[4,5,6] In [13]: lst+lst2 Out[13]: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
删除列表元素
1. remove() 根据指定的value元素值删除元素,返回none
# 原地删除,返回为none In [1]: help(lst.remove) remove(...) method of builtins.list instance L.remove(value) -> None -- remove first occurrence of value. Raises ValueError if the value is not present. In [2]: lst=[0,1,2,3,2,4,5,6] # 删除list中值为4的元素 In [6]: lst.remove(4);print(lst) [0, 1, 2, 3, 2, 5, 6] # list中有两个相同的value时,删除第一个出现的 In [7]: lst.remove(2);print(lst) [0, 1, 3, 2, 5, 6] # 当value不存在,则抛出ValueError In [8]: lst.remove(10);print(lst) ValueError: list.remove(x): x not in list
2. pop() 根据index索引删除元素,返回被删除的元素
In [10]: help(lst.pop) pop(...) method of builtins.list instance L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last). Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range. # pop()不指定索引时,随机删除列表的一个元素,直到list为空 In [36]: lst=[1,0,9,8,2,6,9] In [37]: lst.pop() Out[37]: 9 In [38]: lst.pop() Out[38]: 6 In [39]: lst.pop() Out[39]: 2 In [40]: lst.pop() Out[40]: 8 In [41]: lst.pop() Out[41]: 9 In [42]: lst.pop() Out[42]: 0 In [43]: lst.pop() Out[43]: 1 In [44]: lst.pop() IndexError: pop from empty list # pop(index)指定index时,删除该索引对应的值 In [45]: lst=[1,0,9,8,2,6,9] In [46]: lst.pop(0) Out[46]: 1 In [47]: lst.pop(-1) Out[47]: 9 # pop()和pop(index)比较:pop()传递index参数时,时间复杂度是O(n) 不传递index参数时,时间复杂度是O(1)
3. clear() 清空一个列表
In [16]: help(lst.clear) clear(...) method of builtins.list instance L.clear() -> None -- remove all items from L In [17]: print(lst) [1, 2] In [18]: lst.clear() In [19]: print(lst) []
其他常用操作
1. len( )
# 求list长度 In [20]: lst=list(range(0,6)) In [21]: len(lst) Out[21]: 6
2. reverse ( )
# 反转列表 In [23]: help(lst.reverse) reverse(...) method of builtins.list instance L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* In [24]: print(lst) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] In [25]: lst.reverse() In [26]: print(lst) [5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
3. sort( )
# 对列表排序 In [27]: help(lst.sort) sort(...) method of builtins.list instance L.sort(key=None, reverse=False) -> None -- stable sort *IN PLACE* In [28]: lst=[1,2,3,2,7,8] In [29]: lst.sort() In [30]: print(lst) #默认为正序 [1, 2, 2, 3, 7, 8] In [31]: lst.sort(reverse=True);print(lst) #设置reverse=True为逆序 [8, 7, 3, 2, 2, 1]
# key=None 实际是可以自定义的一个函数参数(python的函数可以作为函数参数使用)
keys=[('x',3),('z',6),('y',1)]
keys.sort(key=lambda x:x[0])
print(keys)
[('x', 3), ('y', 1), ('z', 6)]
4. 拷贝
# 赋值操作‘=’是引用传递 也叫浅拷贝 In [32]: lst1=[0,1,2] In [33]: lst2=lst1 In [34]: print(lst2) [0, 1, 2] In [35]: lst2[2]=3 In [36]: print(lst1,lst2) #浅拷贝是lst1跟着变了 [0, 1, 3] [0, 1, 3] # copy()是影子拷贝 In [37]: help(lst.copy) copy(...) method of builtins.list instance L.copy() -> list -- a shallow copy of L def copy(lst): # copy()的实现 tmp = [] for i in lst: tmp.append(i) return tmp In [38]: lst1=[0,1,2] In [39]: lst2=lst1.copy() In [40]: print(lst2) [0, 1, 2] In [41]: lst2[2]=3 In [42]: print(lst1,lst2) [0, 1, 2] [0, 1, 3] In [43]: lst1=[0,[1,2,3],9] In [44]: lst2=lst1.copy() In [47]: print(lst2) [0, [1, 2, 3], 9] In [49]: lst2[1][1]=5 In [50]: print(lst2) [0, [1, 5, 3], 9] In [51]: print(lst1) [0, [1, 5, 3], 9] # deepcopy()深拷贝 In [52]: lst1=[0,[1,2,3],9] In [53]: import copy In [54]: lst2=copy.deepcopy(lst1) In [55]: print(lst2) [0, [1, 2, 3], 9] In [56]: lst2[1][1]=5 In [57]: print(lst2) [0, [1, 5, 3], 9] In [58]: print(lst1) [0, [1, 2, 3], 9]
5. 复制一个列表
lst=[1,2,3] copy_lst=lst[:]
print(copy_lst) [1, 2, 3]


