object detection[NMS]
非极大抑制,是在对象检测中用的较为频繁的方法,当在一个对象区域,框出了很多框,那么如下图:
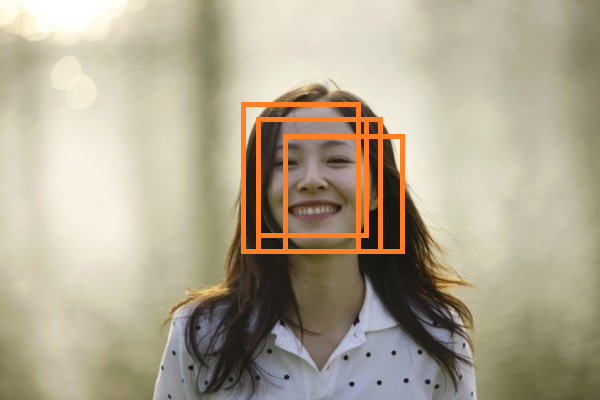
上图来自这里
目的就是为了在这些框中找到最适合的那个框.有以下几种方式:
- 1 nms
- 2 soft-nms
- 3 softer-nms
1. nms
主要就是通过迭代的形式,不断的以最大得分的框去与其他框做iou操作,并过滤那些iou较大(即交集较大)的框
IOU也是一种Tanimoto测量方法[见模式识别,希腊,书609页]
按照github上R-CNN的matlab代码,改成py的,具体如下:
def iou(xminNp,yminNp,xmaxNp,ymaxNp,areas,lastInd,beforeInd,threshold):
# 将lastInd指向的box,与之前的所有存活的box做比较,得到交集区域的坐标。
# np.maximum([3,1,4,2],3) 等于 array([3,3,4,3])
xminNpTmp = np.maximum(xminNp[lastInd], xminNp[beforeInd])
yminNpTmp = np.maximum(yminNp[lastInd], yminNp[beforeInd])
xmaxNpTmp = np.maximum(xmaxNp[lastInd], xmaxNp[beforeInd])
ymaxNpTmp = np.maximum(ymaxNp[lastInd], ymaxNp[beforeInd])
#计算lastInd指向的box,与存活box交集的,所有width,height
w = np.maximum(0.0,xmaxNpTmp-xminNpTmp)
h = np.maximum(0.0,ymaxNpTmp-yminNpTmp)
#计算存活box与last指向box的交集面积
# array([1,2,3,4]) * array([1,2,3,4]) 等于 array([1,4,9,16])
inter = w*h
iouValue = inter/(areas[beforeInd]+areas[lastInd]-inter)
indexOutput = [item[0] for item in zip(beforeInd,iouValue) if item[1] <= threshold ]
return indexOutput
def nms(boxes,threshold):
'''
boxes:n by 5的矩阵,n表示box个数,每一行分别为[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax,score]
'''
assert isinstance(boxes,numpy.ndarray),'boxes must numpy object'
assert boxes.shape[1] == 5,'the column Dimension should be 5'
xminNp = boxes[:,0]
yminNp = boxes[:,1]
xmaxNp = boxes[:,2]
ymaxNp = boxes[:,3]
scores = boxes[:,4]
#计算每个box的面积
areas = (xmaxNp-xminNp)*(ymaxNp-yminNp)
#对每个box的得分按升序排序
scoresSorted = sorted(list(enumerate(scores)),key = lambda item:item[1])
#提取排序后数据的原索引
index = [ item[0] for item in scoresSorted ]
pick = []
while index:
#将当前index中最后一个加入pick
lastInd = index[-1]
pick.append(lastInd)
#计算最后一个box与之前所有box的iou
index = iou(xminNp,yminNp,xmaxNp,ymaxNp,areas,lastInd,index[:-1],threshold)
return pick
if __name__ == '__main__':
nms(boxes,threshold)
2. soft-nms
import copy
def iou(xminNp,yminNp,xmaxNp,ymaxNp,scores,areas,remainInds,maxGlobalInd,Nt,sigma,threshold, method):
remainInds = np.array(remainInds)
# 将maxGlobalInd指向的box,与所有剩下的box做比较,得到交集区域的坐标。
# np.maximum([3,1,4,2],3) 等于 array([3,3,4,3])
xminNpTmp = np.maximum(xminNp[maxGlobalInd], xminNp[remainInds])
yminNpTmp = np.maximum(yminNp[maxGlobalInd], yminNp[remainInds])
xmaxNpTmp = np.maximum(xmaxNp[maxGlobalInd], xmaxNp[remainInds])
ymaxNpTmp = np.maximum(ymaxNp[maxGlobalInd], ymaxNp[remainInds])
# 计算box交集所有width,height
w = np.maximum(0.0,xmaxNpTmp-xminNpTmp)
h = np.maximum(0.0,ymaxNpTmp-yminNpTmp)
#计算IOU
# array([1,2,3,4]) * array([1,2,3,4]) 等于 array([1,4,9,16])
inter = w*h
iouValue = inter/(areas[remainInds]+areas[maxGlobalInd]-inter)
# 依据不同的方法进行权值更新
weight = np.ones_like(iouValue)
if method == 'linear': # linear
# 实现1 - iou
weight = weight - iouValue
weight[iouValue <= Nt] = 1
elif method == 'gaussian':
weight = np.exp(-(iouValue*iouValue)/sigma)
else: # original NMS
weight[iouValue > Nt] = 0
# 更新scores
scores[remainInds] = weight*scores[remainInds]
# 删除低于阈值的框
remainInds = remainInds[scores[remainInds] > threshold]
return remainInds.tolist(),scores
def soft_nms(boxes, threshold, sigma, Nt, method):
'''
boxes:n by 5的矩阵,n表示box个数,每一行分别为[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax,score]
# 1 - 先找到最大得分的box,放到结果集中;
# 2 - 然后将最大得分的box与剩下的做对比,去更新剩下的得分权值
# 3 - 删除低于最小值的框;
# 4 - 再找到剩下中最大的,循环
# 5 - 返回结果集
'''
assert isinstance(boxes,numpy.ndarray),'boxes must numpy object'
assert boxes.shape[1] == 5,'the column Dimension should be 5'
pick = []
copyBoxes = copy.deepcopy(boxes)
xminNp = boxes[:,0]
yminNp = boxes[:,1]
xmaxNp = boxes[:,2]
ymaxNp = boxes[:,3]
scores = copy.deepcopy(boxes[:,4]) # 会不断的更新其中的得分数值
remainInds = list(range(len(scores))) # 会不断的被分割成结果集,丢弃
#计算每个box的面积
areas = (xmaxNp-xminNp)*(ymaxNp-yminNp)
while remainInds:
# 1 - 先找到最大得分的box,放到结果集中;
maxLocalInd = np.argmax(scores[remainInds])
maxGlobalInd = remainInds[maxLocalInd]
pick.append(maxGlobalInd)
# 2 - 丢弃最大值在索引中的位置
remainInds.pop(maxLocalInd)
if not remainInds: break
# 3 - 更新scores,remainInds
remainInds,scores = iou(xminNp,yminNp,xmaxNp,ymaxNp,scores,areas,remainInds,maxGlobalInd,Nt,sigma,threshold, method)
return pick
if __name__ == '__main__':
soft_nms(boxes, 0.001, 0.5, 0.3, 'linear')
3. softer-nms
参考资料:
- 非极大抑制
- [首次提出nms] Rosenfeld A, Thurston M. Edge and curve detection for visual scene analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on computers, 1971 (5): 562-569.
- Theodoridis.S.,.Koutroumbas.K..Pattern.Recognition,.4ed,.AP,.2009
- [soft-nms] Bodla N, Singh B, Chellappa R, et al. Soft-nms—improving object detection with one line of code[C]//Computer Vision (ICCV), 2017 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2017: 5562-5570. 【code】
- [fitness nms] Tychsen-Smith L, Petersson L. Improving Object Localization with Fitness NMS and Bounded IoU Loss[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.00164, 2017.
- [learning NMS] J. H. Hosang, R. Benenson, and B. Schiele. Learning nonmaximum suppression. In CVPR, pages 6469–6477, 2017
- [softer-nms] He Y, Zhang X, Savvides M, et al. Softer-NMS: Rethinking Bounding Box Regression for Accurate Object Detection[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.08545, 2018.)



