HDU 2017 Multi-University Training Contest - Team 4 1009 1011
Questionnaire
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 524288/524288 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 422 Accepted Submission(s): 320
Special Judge
Problem Description
In
order to get better results in official ACM/ICPC contests, the team
leader comes up with a questionnaire. He asked everyone in the team
whether to have more training.

Picture from Wikimedia Commons
Obviously many people don't want more training, so the clever leader didn't write down their words such as ''Yes'' or ''No''. Instead, he let everyone choose a positive integer ai to represent his opinion. When finished, the leader will choose a pair of positive interges m(m>1) and k(0≤k<m), and regard those people whose number is exactly k modulo m as ''Yes'', while others as ''No''. If the number of ''Yes'' is not less than ''No'', the leader can have chance to offer more training.
Please help the team leader to find such pair of m and k.

Picture from Wikimedia Commons
Obviously many people don't want more training, so the clever leader didn't write down their words such as ''Yes'' or ''No''. Instead, he let everyone choose a positive integer ai to represent his opinion. When finished, the leader will choose a pair of positive interges m(m>1) and k(0≤k<m), and regard those people whose number is exactly k modulo m as ''Yes'', while others as ''No''. If the number of ''Yes'' is not less than ''No'', the leader can have chance to offer more training.
Please help the team leader to find such pair of m and k.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer T, denoting the number of test cases.
In each test case, there is an integer n(3≤n≤100000) in the first line, denoting the number of people in the ACM/ICPC team.
In the next line, there are n distinct integers a1,a2,...,an(1≤ai≤109), denoting the number that each person chosen.
In each test case, there is an integer n(3≤n≤100000) in the first line, denoting the number of people in the ACM/ICPC team.
In the next line, there are n distinct integers a1,a2,...,an(1≤ai≤109), denoting the number that each person chosen.
Output
For each test case, print a single line containing two integers m and k, if there are multiple solutions, print any of them.
Sample Input
1
6
23 3 18 8 13 9
Sample Output
5 3
除以二,统计余数相同的个数
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.141592653589793238462 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(false) #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; int x,t,n; int main() { scanf("%d",&t); while(t--) { scanf("%d",&n); int pos=0,ans=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%d",&x); if(x&1) ans++; else pos++; } puts(ans>pos?"2 1":"2 0"); } }
Time To Get Up
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 524288/524288 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 458 Accepted Submission(s): 362
Problem Description
Little
Q's clock is alarming! It's time to get up now! However, after reading
the time on the clock, Little Q lies down and starts sleeping again.
Well, he has 5 alarms, and it's just the first one, he can continue sleeping for a while.
Little Q's clock uses a standard 7-segment LCD display for all digits, plus two small segments for the '':'', and shows all times in a 24-hour format. The '':'' segments are on at all times.
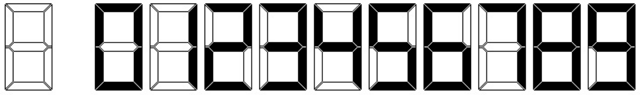
Your job is to help Little Q read the time shown on his clock.
Little Q's clock uses a standard 7-segment LCD display for all digits, plus two small segments for the '':'', and shows all times in a 24-hour format. The '':'' segments are on at all times.

Your job is to help Little Q read the time shown on his clock.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer T, denoting the number of test cases.
In each test case, there is an 7×21 ASCII image of the clock screen.
All digit segments are represented by two characters, and each colon segment is represented by one character. The character ''X'' indicates a segment that is on while ''.'' indicates anything else. See the sample input for details.
In each test case, there is an 7×21 ASCII image of the clock screen.
All digit segments are represented by two characters, and each colon segment is represented by one character. The character ''X'' indicates a segment that is on while ''.'' indicates anything else. See the sample input for details.
Output
For each test case, print a single line containing a string t in the format of H, where t(00:00≤t≤23:59), denoting the time shown on the clock.
Sample Input
1
.XX...XX.....XX...XX.
X..X....X......X.X..X
X..X....X.X....X.X..X
......XX.....XX...XX.
X..X.X....X....X.X..X
X..X.X.........X.X..X
.XX...XX.....XX...XX.
Sample Output
02:38
模拟。代码估计十分冗长
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <cstdlib> #include <iomanip> #include <cmath> #include <ctime> #include <map> #include <set> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) #define max(x,y) (x>y?x:y) #define min(x,y) (x<y?x:y) #define MAX 100000000000000000 #define MOD 1000000007 #define pi acos(-1.0) #define ei exp(1) #define PI 3.141592653589793238462 #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(false) #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f #define mem(a) (memset(a,0,sizeof(a))) typedef long long ll; char s[10][25]; int a[4][8],n; int solve(int *a) { if(a[1]==1 && a[2]==1 && a[3]==1 && a[4]==0 && a[5]==1 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==1) return 0; if(a[1]==0 && a[2]==0 && a[3]==1 && a[4]==0 && a[5]==0 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==7) return 1; if(a[1]==1 && a[2]==0 && a[3]==1 && a[4]==1 && a[5]==1 && a[6]==0 && a[7]==1) return 2; if(a[1]==1 && a[2]==0 && a[3]==1 && a[4]==1 && a[5]==0 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==1) return 3; if(a[1]==0 && a[2]==1 && a[3]==1 && a[4]==1 && a[5]==0 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==0) return 4; if(a[1]==1 && a[2]==1 && a[3]==0 && a[4]==1 && a[5]==0 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==1) return 5; if(a[1]==1 && a[2]==1 && a[3]==0 && a[4]==1 && a[5]==1 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==1) return 6; if(a[1]==1 && a[2]==0 && a[3]==1 && a[4]==0 && a[5]==0 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==0) return 7; if(a[1]==1 && a[2]==1 && a[3]==1 && a[4]==1 && a[5]==1 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==1) return 8; if(a[1]==1 && a[2]==1 && a[3]==1 && a[4]==1 && a[5]==0 && a[6]==1 && a[7]==1) return 9; } int main() { scanf("%d",&n); while(n--) { memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); for(int i=1;i<=7;i++) { scanf("%s",s[i]+1); } if(s[1][2]=='X') a[0][1]=1; if(s[1][7]=='X') a[1][1]=1; if(s[1][14]=='X') a[2][1]=1; if(s[1][19]=='X') a[3][1]=1; if(s[2][1]=='X') a[0][2]=1; if(s[2][6]=='X') a[1][2]=1; if(s[2][13]=='X') a[2][2]=1; if(s[2][18]=='X') a[3][2]=1; if(s[2][4]=='X') a[0][3]=1; if(s[2][9]=='X') a[1][3]=1; if(s[2][16]=='X') a[2][3]=1; if(s[2][21]=='X') a[3][3]=1; if(s[4][2]=='X') a[0][4]=1; if(s[4][7]=='X') a[1][4]=1; if(s[4][14]=='X') a[2][4]=1; if(s[4][19]=='X') a[3][4]=1; if(s[5][1]=='X') a[0][5]=1; if(s[5][6]=='X') a[1][5]=1; if(s[5][13]=='X') a[2][5]=1; if(s[5][18]=='X') a[3][5]=1; if(s[5][4]=='X') a[0][6]=1; if(s[5][9]=='X') a[1][6]=1; if(s[5][16]=='X') a[2][6]=1; if(s[5][21]=='X') a[3][6]=1; if(s[7][2]=='X') a[0][7]=1; if(s[7][7]=='X') a[1][7]=1; if(s[7][14]=='X') a[2][7]=1; if(s[7][19]=='X') a[3][7]=1; printf("%d%d:%d%d\n",solve(a[0]),solve(a[1]),solve(a[2]),solve(a[3])); } return 0; }

