OpenCV3.4两种立体匹配算法效果对比
以OpenCV自带的Aloe图像对为例:


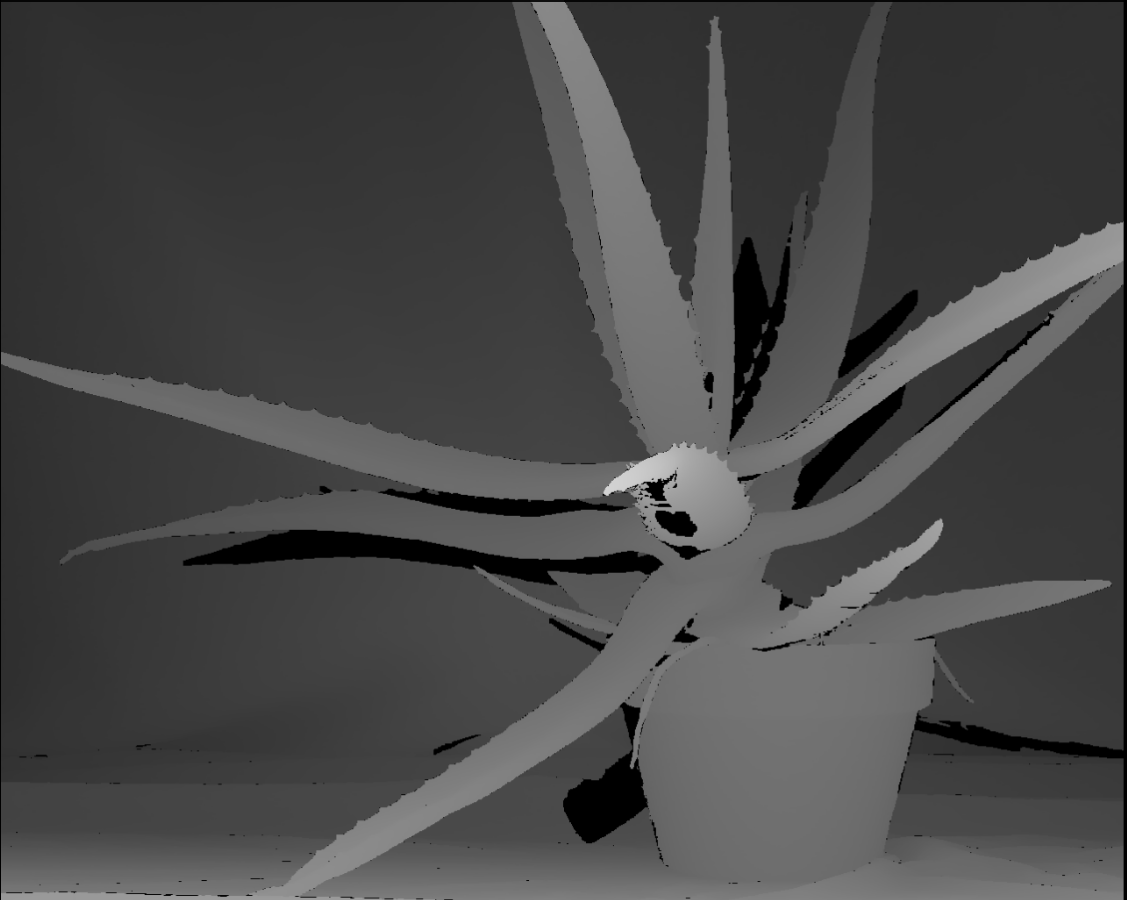
1.BM算法(Block Matching)
参数设置如下:
int numberOfDisparities = ((imgSize.width / 8) + 15) & -16; cv::Ptr<cv::StereoBM> bm = cv::StereoBM::create(16, 9); cv::Rect roi1, roi2; bm->setROI1(roi1); bm->setROI2(roi2); bm->setPreFilterCap(31); bm->setBlockSize(9); bm->setMinDisparity(0); bm->setNumDisparities(numberOfDisparities); bm->setTextureThreshold(10); bm->setUniquenessRatio(15); bm->setSpeckleWindowSize(100); bm->setSpeckleRange(32); bm->setDisp12MaxDiff(1); bm->compute(imgL, imgR, disp);
效果如下:
BM算法得到的视差图(左),空洞填充后得到的视差图(右)

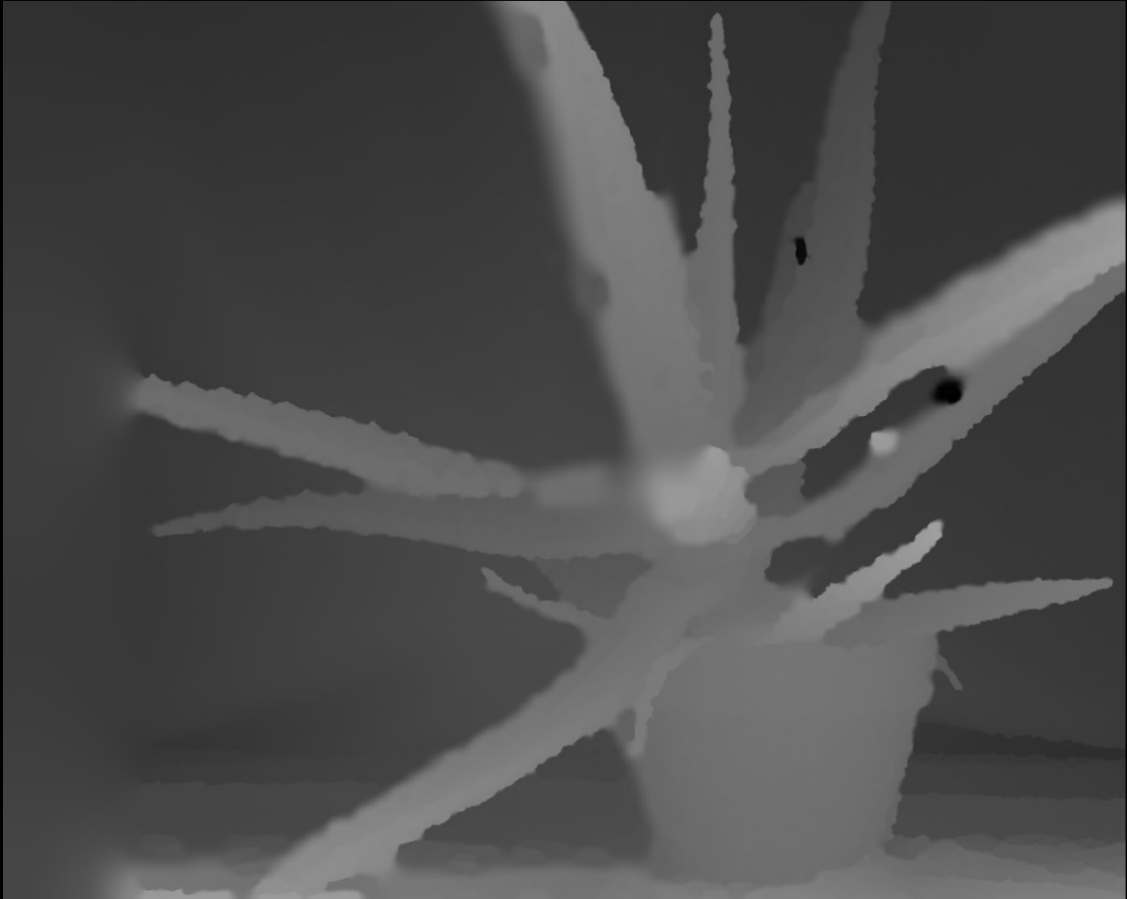
2.SGBM(Semi-Global Block matching)算法:
参数设置如下:
enum { STEREO_BM = 0, STEREO_SGBM = 1, STEREO_HH = 2, STEREO_VAR = 3, STEREO_3WAY = 4 }; int numberOfDisparities = ((imgSize.width / 8) + 15) & -16; cv::Ptr<cv::StereoSGBM> sgbm = cv::StereoSGBM::create(0, 16, 3); sgbm->setPreFilterCap(63); int SADWindowSize = 9; int sgbmWinSize = SADWindowSize > 0 ? SADWindowSize : 3; sgbm->setBlockSize(sgbmWinSize); int cn = imgL.channels(); sgbm->setP1(8 * cn*sgbmWinSize*sgbmWinSize); sgbm->setP2(32 * cn*sgbmWinSize*sgbmWinSize); sgbm->setMinDisparity(0); sgbm->setNumDisparities(numberOfDisparities); sgbm->setUniquenessRatio(10); sgbm->setSpeckleWindowSize(100); sgbm->setSpeckleRange(32); sgbm->setDisp12MaxDiff(1); int alg = STEREO_SGBM; if (alg == STEREO_HH) sgbm->setMode(cv::StereoSGBM::MODE_HH); else if (alg == STEREO_SGBM) sgbm->setMode(cv::StereoSGBM::MODE_SGBM); else if (alg == STEREO_3WAY) sgbm->setMode(cv::StereoSGBM::MODE_SGBM_3WAY); sgbm->compute(imgL, imgR, disp);
效果如图:
SGBM算法得到的视差图(左),空洞填充后得到的视差图(右)


可见SGBM算法得到的视差图相比于BM算法来说,减少了很多不准确的匹配点,尤其是在深度不连续区域,速度上SGBM要慢于BM算法。OpenCV3.0以后没有实现GC算法,可能是出于速度考虑,以后找时间补上对比图,以及各个算法的详细原理分析。
后面我填充空洞的效果不是很好,如果有更好的方法,望不吝赐教。
preFilterCap()匹配图像预处理
- 两种立体匹配算法都要先对输入图像做预处理,OpenCV源码中中调用函数 static void prefilterXSobel(const cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst, int preFilterCap),参数设置中preFilterCap在此函数中用到。函数步骤如下,作用主要有两点:对于无纹理区域,能够排除噪声干扰;对于边界区域,能够提高边界的区分性,利于后续的匹配代价计算:
- 先利用水平Sobel算子求输入图像x方向的微分值Value;
- 如果Value<-preFilterCap, 则Value=0;
如果Value>preFilterCap,则Value=2*preFilterCap;
如果Value>=-preFilterCap &&Value<=preFilterCap,则Value=Value+preFilterCap; - 输出处理后的图像作为下一步计算匹配代价的输入图像。

static void prefilterXSobel(const cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst, int ftzero) { int x, y; const int OFS = 256 * 4, TABSZ = OFS * 2 + 256; uchar tab[TABSZ]; cv::Size size = src.size(); for (x = 0; x < TABSZ; x++) tab[x] = (uchar)(x - OFS < -ftzero ? 0 : x - OFS > ftzero ? ftzero * 2 : x - OFS + ftzero); uchar val0 = tab[0 + OFS]; for (y = 0; y < size.height - 1; y += 2) { const uchar* srow1 = src.ptr<uchar>(y); const uchar* srow0 = y > 0 ? srow1 - src.step : size.height > 1 ? srow1 + src.step : srow1; const uchar* srow2 = y < size.height - 1 ? srow1 + src.step : size.height > 1 ? srow1 - src.step : srow1; const uchar* srow3 = y < size.height - 2 ? srow1 + src.step * 2 : srow1; uchar* dptr0 = dst.ptr<uchar>(y); uchar* dptr1 = dptr0 + dst.step; dptr0[0] = dptr0[size.width - 1] = dptr1[0] = dptr1[size.width - 1] = val0; x = 1; for (; x < size.width - 1; x++) { int d0 = srow0[x + 1] - srow0[x - 1], d1 = srow1[x + 1] - srow1[x - 1], d2 = srow2[x + 1] - srow2[x - 1], d3 = srow3[x + 1] - srow3[x - 1]; int v0 = tab[d0 + d1 * 2 + d2 + OFS]; int v1 = tab[d1 + d2 * 2 + d3 + OFS]; dptr0[x] = (uchar)v0; dptr1[x] = (uchar)v1; } } for (; y < size.height; y++) { uchar* dptr = dst.ptr<uchar>(y); x = 0; for (; x < size.width; x++) dptr[x] = val0; } }
自己实现的函数如下:

void mySobelX(cv::Mat srcImg, cv::Mat dstImg, int preFilterCap) { assert(srcImg.channels() == 1); int radius = 1; int width = srcImg.cols; int height = srcImg.rows; uchar *pSrcData = srcImg.data; uchar *pDstData = dstImg.data; for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) { int idx = i*width + j; if (i >= radius && i < height - radius && j >= radius && j < width - radius) { int diff0 = pSrcData[(i - 1)*width + j + 1] - pSrcData[(i - 1)*width + j - 1]; int diff1 = pSrcData[i*width + j + 1] - pSrcData[i*width + j - 1]; int diff2 = pSrcData[(i + 1)*width + j + 1] - pSrcData[(i + 1)*width + j - 1]; int value = diff0 + 2 * diff1 + diff2; if (value < -preFilterCap) { pDstData[idx] = 0; } else if (value >= -preFilterCap && value <= preFilterCap) { pDstData[idx] = uchar(value + preFilterCap); } else { pDstData[idx] = uchar(2 * preFilterCap); } } else { pDstData[idx] = 0; } } } }
函数输入,输出结果如图:
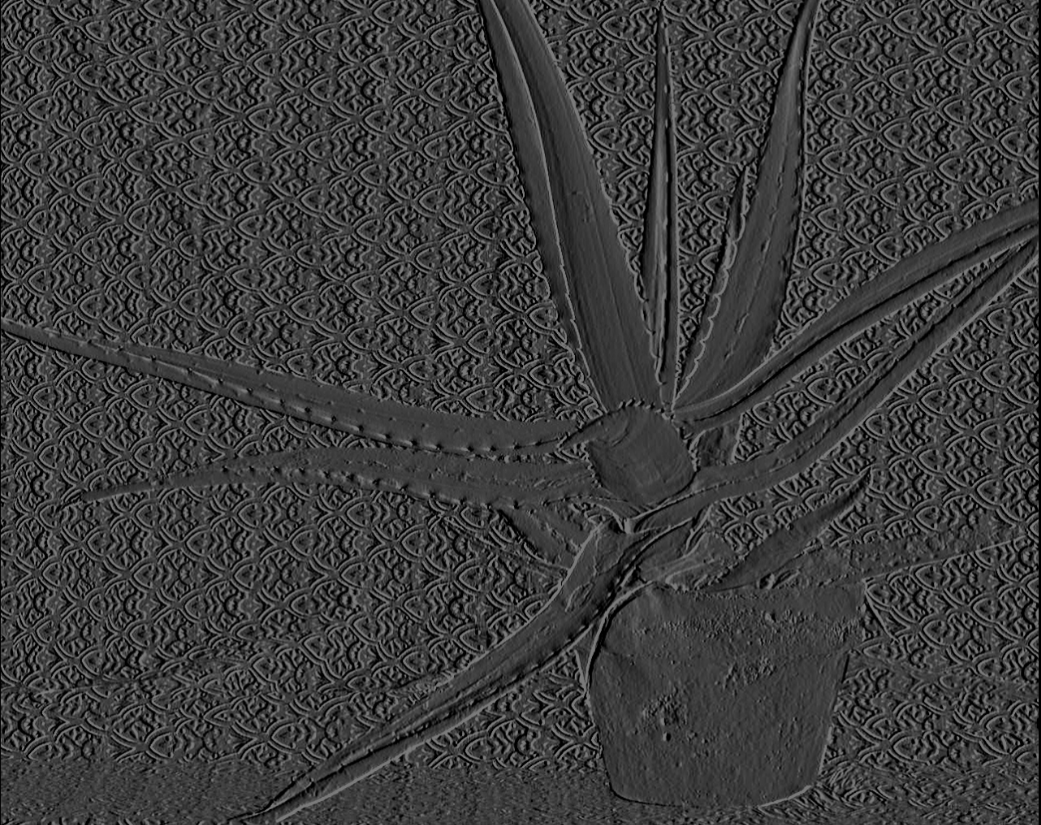


filterSpeckles()视差图后处理
- 两种立体匹配算法在算出初始视差图后会进行视差图后处理,包括中值滤波,连通域检测等。其中中值滤波能够有效去除视差图中孤立的噪点,而连通域检测能够检测出视差图中因噪声引起小团块(blob)。在BM和SGBM中都有speckleWindowSize和speckleRange这两个参数,speckleWindowSize是指设置检测出的连通域中像素点个数,也就是连通域的大小。speckleRange是指设置判断两个点是否属于同一个连通域的阈值条件。大概流程如下:
- 判断当前像素点四邻域的邻域点与当前像素点的差值diff,如果diff<speckRange,则表示该邻域点与当前像素点是一个连通域,设置一个标记。然后再以该邻域点为中心判断其四邻域点,步骤同上。直至某一像素点四邻域的点均不满足条件,则停止。
- 步骤1完成后,判断被标记的像素点个数count,如果像素点个数count<=speckleWindowSize,则说明该连通域是一个小团块(blob),则将当前像素点值设置为newValue(表示错误的视差值,newValue一般设置为负数或者0值)。否则,表示该连通域是个大团块,不做处理。同时建立标记值与是否为小团块的关系表rtype[label],rtype[label]为0,表示label值对应的像素点属于小团块,为1则不属于小团块。
- 处理下一个像素点时,先判断其是否已经被标记:
如果已经被标记,则根据关系表rtype[label]判断是否为小团块(blob),如果是,则直接将该像素值设置为newValue;如果不是,则不做处理。继续处理下一个像素。
如果没有被标记,则按照步骤1处理。 - 所有像素点处理后,满足条件的区域会被设置为newValue值,后续可以用空洞填充等方法重新估计其视差值。
OpenCV中有对应的API函数,void filterSpeckles(InputOutputArray img, double newVal, int maxSpeckleSize, double maxDiff, InputOutputArray buf=noArray() )
函数源码如下,使用时根据视差图或者深度图数据类型设置模板中的数据类型:

typedef cv::Point_<short> Point2s; template <typename T> void filterSpecklesImpl(cv::Mat& img, int newVal, int maxSpeckleSize, int maxDiff, cv::Mat& _buf) { using namespace cv; int width = img.cols, height = img.rows, npixels = width*height; size_t bufSize = npixels*(int)(sizeof(Point2s) + sizeof(int) + sizeof(uchar)); if (!_buf.isContinuous() || _buf.empty() || _buf.cols*_buf.rows*_buf.elemSize() < bufSize) _buf.create(1, (int)bufSize, CV_8U); uchar* buf = _buf.ptr(); int i, j, dstep = (int)(img.step / sizeof(T)); int* labels = (int*)buf; buf += npixels * sizeof(labels[0]); Point2s* wbuf = (Point2s*)buf; buf += npixels * sizeof(wbuf[0]); uchar* rtype = (uchar*)buf; int curlabel = 0; // clear out label assignments memset(labels, 0, npixels * sizeof(labels[0])); for (i = 0; i < height; i++) { T* ds = img.ptr<T>(i); int* ls = labels + width*i; for (j = 0; j < width; j++) { if (ds[j] != newVal) // not a bad disparity { if (ls[j]) // has a label, check for bad label { if (rtype[ls[j]]) // small region, zero out disparity ds[j] = (T)newVal; } // no label, assign and propagate else { Point2s* ws = wbuf; // initialize wavefront Point2s p((short)j, (short)i); // current pixel curlabel++; // next label int count = 0; // current region size ls[j] = curlabel; // wavefront propagation while (ws >= wbuf) // wavefront not empty { count++; // put neighbors onto wavefront T* dpp = &img.at<T>(p.y, p.x); //current pixel value T dp = *dpp; int* lpp = labels + width*p.y + p.x; //current label value //bot if (p.y < height - 1 && !lpp[+width] && dpp[+dstep] != newVal && std::abs(dp - dpp[+dstep]) <= maxDiff) { lpp[+width] = curlabel; *ws++ = Point2s(p.x, p.y + 1); } //top if (p.y > 0 && !lpp[-width] && dpp[-dstep] != newVal && std::abs(dp - dpp[-dstep]) <= maxDiff) { lpp[-width] = curlabel; *ws++ = Point2s(p.x, p.y - 1); } //right if (p.x < width - 1 && !lpp[+1] && dpp[+1] != newVal && std::abs(dp - dpp[+1]) <= maxDiff) { lpp[+1] = curlabel; *ws++ = Point2s(p.x + 1, p.y); } //left if (p.x > 0 && !lpp[-1] && dpp[-1] != newVal && std::abs(dp - dpp[-1]) <= maxDiff) { lpp[-1] = curlabel; *ws++ = Point2s(p.x - 1, p.y); } // pop most recent and propagate // NB: could try least recent, maybe better convergence p = *--ws; } // assign label type if (count <= maxSpeckleSize) // speckle region { rtype[ls[j]] = 1; // small region label ds[j] = (T)newVal; } else rtype[ls[j]] = 0; // large region label } } } } }
或者下面博主自己整理一遍的代码:

typedef cv::Point_<short> Point2s; template <typename T> void myFilterSpeckles(cv::Mat &img, int newVal, int maxSpeckleSize, int maxDiff) { int width = img.cols; int height = img.rows; int imgSize = width*height; int *pLabelBuf = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*imgSize);//标记值buffer Point2s *pPointBuf = (Point2s*)malloc(sizeof(short)*imgSize);//点坐标buffer uchar *pTypeBuf = (uchar*)malloc(sizeof(uchar)*imgSize);//blob判断标记buffer //初始化Labelbuffer int currentLabel = 0; memset(pLabelBuf, 0, sizeof(int)*imgSize); for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) { T *pData = img.ptr<T>(i); int *pLabel = pLabelBuf + width*i; for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) { if (pData[j] != newVal) { if (pLabel[j]) { if (pTypeBuf[pLabel[j]]) { pData[j] = (T)newVal; } } else { Point2s *pWave = pPointBuf; Point2s curPoint((T)j, (T)i); currentLabel++; int count = 0; pLabel[j] = currentLabel; while (pWave >= pPointBuf) { count++; T *pCurPos = &img.at<T>(curPoint.y, curPoint.x); T curValue = *pCurPos; int *pCurLabel = pLabelBuf + width*curPoint.y + curPoint.x; //bot if (curPoint.y < height - 1 && !pCurLabel[+width] && pCurPos[+width] != newVal && abs(curValue - pCurPos[+width]) <= maxDiff) { pCurLabel[+width] = currentLabel; *pWave++ = Point2s(curPoint.x, curPoint.y + 1); } //top if (curPoint.y > 0 && !pCurLabel[-width] && pCurPos[-width] != newVal && abs(curValue - pCurPos[-width]) <= maxDiff) { pCurLabel[-width] = currentLabel; *pWave++ = Point2s(curPoint.x, curPoint.y - 1); } //right if (curPoint.x < width-1 && !pCurLabel[+1] && pCurPos[+1] != newVal && abs(curValue - pCurPos[+1]) <= maxDiff) { pCurLabel[+1] = currentLabel; *pWave++ = Point2s(curPoint.x + 1, curPoint.y); } //left if (curPoint.x > 0 && !pCurLabel[-1] && pCurPos[-1] != newVal && abs(curValue - pCurPos[-1]) <= maxDiff) { pCurLabel[-1] = currentLabel; *pWave++ = Point2s(curPoint.x - 1, curPoint.y); } --pWave; curPoint = *pWave; } if (count <= maxSpeckleSize) { pTypeBuf[pLabel[j]] = 1; pData[j] = (T)newVal; } else { pTypeBuf[pLabel[j]] = 0; } } } } } free(pLabelBuf); free(pPointBuf); free(pTypeBuf); }
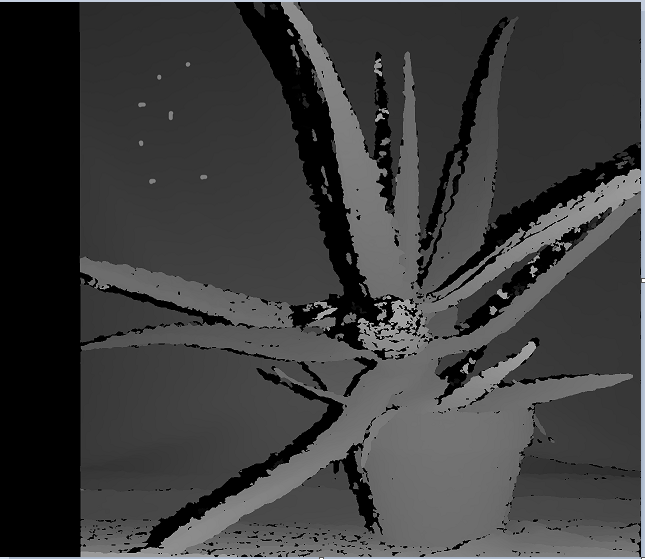
如下视差图中左上角部分有7个小团块,设置speckleWindowSize和speckleRange分别为50和32,连通域检测后结果为如下图右,小团块能够全部检测出来,方便后续用周围视差填充。当然还有一个缺点就是,图像中其他地方尤其是边界区域也会被检测为小团块,后续填充可能会对边界造成平滑。


---------------------------------
业精于勤而荒于嬉 行成于思而毁于随
---------------------------------




