C++复合类型(结构体)
其实c++的结构体可以理解为类似于python的字典,我个人理解, 但有区别
先看结构
#include <iostream> 关键字 标记成为新类型的名称 struct inflatable { std::string mystr; 结构成员 char name[20]; float volume; double price; };
c++ 在声明结构变量的时候可以省略关键字struct
同时还要注意外部声明, 和局部声明

#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> struct inflatable { std::string mystr; char name[20]; float volume; double price; }; int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { using namespace std; inflatable guest = { "hello", "Glorious Gloria", 1.88, 29.99 }; inflatable pal = { "world", "Audacious Arthur", 3.12, 32.99 }; int a=12.40; std::cout << guest.mystr << '\n'; std::cout << a << '\n'; std::cout << "Expand your guest list with <<" << guest.name << ">>" << "and" << "<<" << pal.name << ">>" << '\n'; std::cout << "you can have both for $" << guest.price + pal.price <<'\n'; return 0; }
其他结构属性
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> struct inflatable { std::string mystr; char name[20]; float volume; double price; }; int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { using namespace std; inflatable guest = { "hello", "Glorious Gloria", 1.88, 29.99 }; inflatable choice = guest; 这种方法叫成员赋值
或者
inflatable choice;
choice = guest;
std::cout << "Expand your guest list with <<" << guest.name << ">>" << '\n'; std::cout << "choice choice.mystr ---->" << choice.mystr << '\n'; return 0; }
还可以
struct inflatable { std::string mystr; char name[20]; float volume; double price; } mr_glitz = {"hello", "Glorious", 1.11, 11};
当然,也可以不赋值
结构数组
也可以创建元素为结构的数组, 方法和创建基本类型数组完全相同。例如:
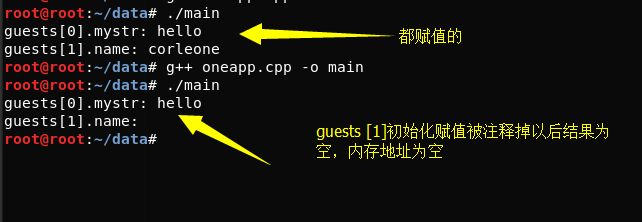
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstring> struct inflatable { std::string mystr; char name[20]; float volume; double price; } mr_glitz = {"hello", "Glorious", 1.11, 11}; int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { using namespace std; inflatable guests[2] = { {"hello", "doman", 2.1, 2.22}, // {"world", "corleone", 2.2, 3333} }; std::cout << "guests[0].mystr: " << guests[0].mystr << '\n'; std::cout << "guests[1].name: " << guests[1].name << '\n'; return 0; }
结构中的位字段
struct torgle_register { unsigned int SN : 4; unsigned int :4; bool goodIN : 1; bool goodTorgle : 1; } torgle_register tr = {14, true, false};
作者:沐禹辰
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/renfanzi/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/renfanzi/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接。



