Spring源码情操陶冶-tx:advice解析器
承接Spring源码情操陶冶-自定义节点的解析。本节关于事务进行简单的解析
spring配置文件样例
简单的事务配置,对save/delete开头的方法加事务,get/find开头的设置为不加事务只读模式
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser解析器
tx:advice节点对应的解析器为TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser,下面针对该解析器作下详细的解读
实例化对象
直接看复写的getBeanClass()方法
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return TransactionInterceptor.class;
}
即TxAdviceBeanDefinitionParser解析器最终解析tx:advice节点为TransactionInterceptor对象
通用的属性集合
private static final String METHOD_ELEMENT = "method";
private static final String METHOD_NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name";
private static final String ATTRIBUTES_ELEMENT = "attributes";
private static final String TIMEOUT_ATTRIBUTE = "timeout";
private static final String READ_ONLY_ATTRIBUTE = "read-only";
private static final String PROPAGATION_ATTRIBUTE = "propagation";
private static final String ISOLATION_ATTRIBUTE = "isolation";
private static final String ROLLBACK_FOR_ATTRIBUTE = "rollback-for";
private static final String NO_ROLLBACK_FOR_ATTRIBUTE = "no-rollback-for";
针对上述的属性,我们可以看下其中的具体解析
doParse()-解析tx:advice节点
源码端上
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
// 解析transaction-manager属性对应的bean ref名,默认名为transactionManager
builder.addPropertyReference("transactionManager", TxNamespaceHandler.getTransactionManagerName(element));
// 解析子节点tx:attributes
List<Element> txAttributes = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(element, ATTRIBUTES_ELEMENT);
if (txAttributes.size() > 1) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error(
"Element <attributes> is allowed at most once inside element <advice>", element);
}
else if (txAttributes.size() == 1) {
// Using attributes source.
Element attributeSourceElement = txAttributes.get(0);
// 解析tx:attribute集合
RootBeanDefinition attributeSourceDefinition = parseAttributeSource(attributeSourceElement, parserContext);
builder.addPropertyValue("transactionAttributeSource", attributeSourceDefinition);
}
else {
// 注册解析器用于解析注解@Transactional
builder.addPropertyValue("transactionAttributeSource",
new RootBeanDefinition("org.springframework.transaction.annotation.AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource"));
}
}
对于@Transactional方式的解析我们不在此处展开,我们先看下通用的parseAttributeSource()方法解析tx:attribute集合,其会被包装为NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource.class对象。源码如下
private RootBeanDefinition parseAttributeSource(Element attrEle, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 解析tx:method节点
List<Element> methods = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(attrEle, METHOD_ELEMENT);
ManagedMap<TypedStringValue, RuleBasedTransactionAttribute> transactionAttributeMap =
new ManagedMap<TypedStringValue, RuleBasedTransactionAttribute>(methods.size());
transactionAttributeMap.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(attrEle));
//
for (Element methodEle : methods) {
// 解析name属性,其可符合ant-style模式.包装成TypedStringValue对象
String name = methodEle.getAttribute(METHOD_NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
TypedStringValue nameHolder = new TypedStringValue(name);
nameHolder.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(methodEle));
// 解析propagation、isolation、timeout、read-only属性
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute attribute = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
String propagation = methodEle.getAttribute(PROPAGATION_ATTRIBUTE);
String isolation = methodEle.getAttribute(ISOLATION_ATTRIBUTE);
String timeout = methodEle.getAttribute(TIMEOUT_ATTRIBUTE);
String readOnly = methodEle.getAttribute(READ_ONLY_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(propagation)) {
attribute.setPropagationBehaviorName(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.PREFIX_PROPAGATION + propagation);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(isolation)) {
attribute.setIsolationLevelName(RuleBasedTransactionAttribute.PREFIX_ISOLATION + isolation);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(timeout)) {
try {
attribute.setTimeout(Integer.parseInt(timeout));
}
catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().error("Timeout must be an integer value: [" + timeout + "]", methodEle);
}
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(readOnly)) {
attribute.setReadOnly(Boolean.valueOf(methodEle.getAttribute(READ_ONLY_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
// 解析rollback-for、no-rollback-for属性
List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules = new LinkedList<RollbackRuleAttribute>();
if (methodEle.hasAttribute(ROLLBACK_FOR_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String rollbackForValue = methodEle.getAttribute(ROLLBACK_FOR_ATTRIBUTE);
addRollbackRuleAttributesTo(rollbackRules,rollbackForValue);
}
if (methodEle.hasAttribute(NO_ROLLBACK_FOR_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String noRollbackForValue = methodEle.getAttribute(NO_ROLLBACK_FOR_ATTRIBUTE);
addNoRollbackRuleAttributesTo(rollbackRules,noRollbackForValue);
}
attribute.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
transactionAttributeMap.put(nameHolder, attribute);
}
// 最后包装成NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource对象,存放上述的配置
RootBeanDefinition attributeSourceDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource.class);
attributeSourceDefinition.setSource(parserContext.extractSource(attrEle));
attributeSourceDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("nameMap", transactionAttributeMap);
return attributeSourceDefinition;
}
代码很简单,都是解析属性的,不过还是对上述的一些配置作下白话的总结
-
name 支持ant-style语法,即匹配对应的方法,比如
save*,匹配saveUser()/save()等方法 -
propagation 事务传播方式,对应spring的TransactionDefinition接口类常量
- required 对应
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,对当前的方法判断如果不存在事务,则创建事务。默认配置 - required_new 对应
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED_NEW,对当前方法判断如果存在事务,则创建新事务,待方法执行完毕后恢复事务;反之创建新事务,让方法运行在新事务环境下。即当前方法将运行在独立的新事务下 - supports 对应
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS,对当前方法判断如果存在事务,则加入该事务;反之则让方法处于非事务状态执行 - not_spported 对应
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED,对当前方法判断如果存在事务,则挂起该事务,等方法执行完毕后,再恢复事务。即当前方法不需要事务支持 - mandatory 对应
PROPAGATION_MANDATORY,对当前方法判断如果存在事务,则加入该事务;反之不能新建事务,且抛出异常。即必须处于事务下运行 - never 对应
PROPAGATION_NEVER,对当前方法判断如果存在事务,则抛异常;反之正常运行。即必须在非事务下运行 - nested 对应
PROPAGATION_NESTED,可嵌入式的事务。
- required 对应
-
isolation 事务隔离级别,对应spring的TransactionDefinition接口类常量
- default 对应
ISOLATION_DEFAULT,不作隔离要求,可能会导致dirty read/unrepeatable read/phantom read - read_uncommitted 对应JDBC Connection的
TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED,可能会导致dirty read/unrepeatable read/phantom read - read_committed 对应JDBC Connection的
TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED,可能会导致unrepeatable read/phantom read - reaptable_read 对应JDBC Connection的
TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ,可能会导致phantom read - serializable 对应JDBC Connection的
TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE,最安全但最耗性能
其中关于脏读、不可重复读、幻读的概念见引文。另附言博主对不可重复读、幻读的理解两者均是在同一事务中会出现的情况,执行的条件均一样。但不可重复读关心返回的数据是否一致,而幻读关心返回的数据条数是否一致
- default 对应
-
timeout 超时参数,单位为s。其只应用于事务传播方式为
Required/Required_new,默认为-1 -
read-only 是否配置事务只读,默认为false
-
rollback-for 异常回滚策略配置,即出现何种异常进行回滚,可配置多个异常,支持
,分隔。注意此处的配置的异常名也符合ant-style模式 -
no-rollback-for 异常不回滚策略配置,即出现何种异常不进行回滚,可配置多个异常,支持
,分隔。注意此处的配置的异常名也符合ant-style模式
事务拦截逻辑-TransactionInterceptor
UML一览
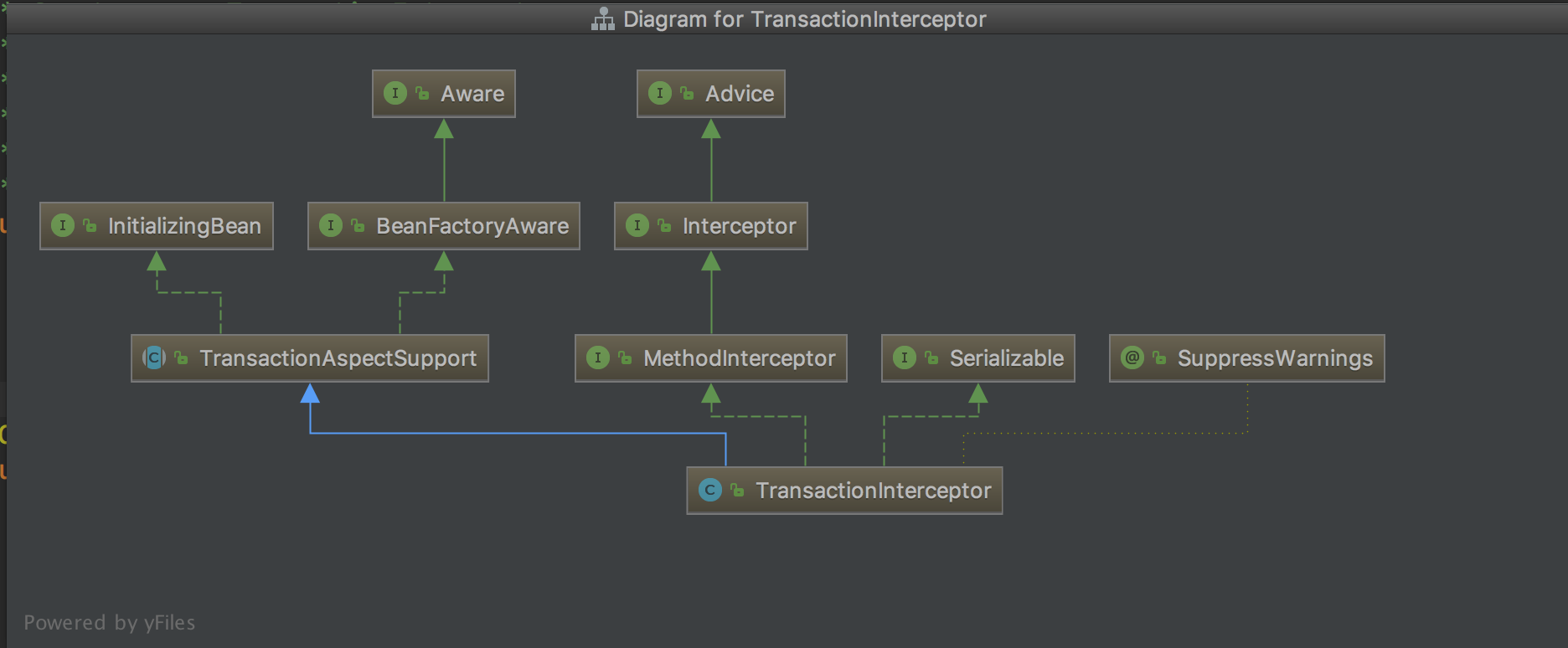
通过上图我们发现其也是Advice接口的实现类,说明此类可应用于aop:advisor配置
invoke()-MethodInterceptor公共调用方法
所有的Advisor封装类都会含有MethodInterceptor的实现类的引用,我们可以看下事务处理的切面处理方式
@Override
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new InvocationCallback() {
@Override
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
});
}
其会调用invokeWithinTransation()方法来解决此类问题,通过表面文字我们可以猜出其会判断对相应的方法是否添加事务来执行,由于代码过长,博主就截取重要的片段来分析
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
从以上的代码可知,我们可以得到以下结论
- 根据method对应的事务配置,创建
TransactionInfo对象。即判断是否对相应的方法加上事务- 再执行相应的方法的业务
- 如果执行业务过程中,出现异常则根据异常匹配规则进行相应的回滚策略
- 无第三点的条件则会保存当前的事务状态
- 最后提交事务,使增删改查操作生效,保持一致性、原子性
小结
tx:advice配置多与spring aop结合使用,通过切面的解耦使其可以在方法每次执行的时候根据配置是否添加事务,是个很好的代码设计。




