cat、head、sed 三盟友
在linux 中我们必不可少的会使用到这三个命令
他们有什么作用呢?
就是查看文档了,但他的功能远不止于此
来我们学习一下吧
cat
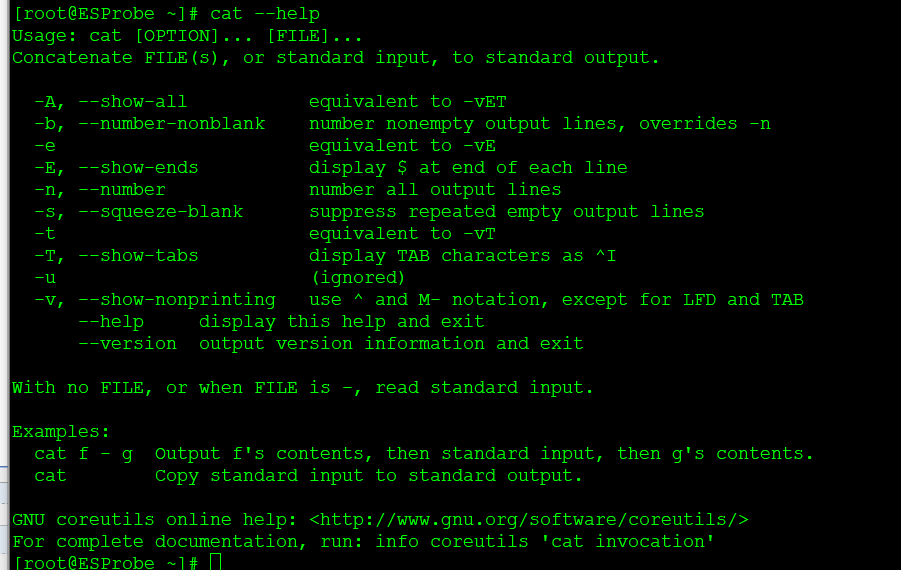
[root@ESProbe ~]# cat --help
Usage: cat [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Concatenate FILE(s), or standard input, to standard output.
-A, --show-all equivalent to -vET
-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides -n
-e equivalent to -vE
-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line
-n, --number number all output lines
-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines
-t equivalent to -vT
-T, --show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I
-u (ignored)
-v, --show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Examples:
cat f - g Output f's contents, then standard input, then g's contents.
cat Copy standard input to standard output.
GNU coreutils online help: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'cat invocation'
-b 显示行号
[root@ESProbe ~]# cat -b /etc/passwd
1 root❌0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
2 bin❌1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
3 daemon❌2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
4 adm❌3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin
5 lp❌4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
6 sync❌5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
7 shutdown❌6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
8 halt❌7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
9 mail❌8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
10 operator❌11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
11 games❌12💯games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
12 ftp❌14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin
13 nobody❌99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
14 systemd-network❌192:192:systemd Network Management:/:/sbin/nologin
15 dbus❌81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin
16 polkitd❌999:998:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin
17 sshd❌74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin
18 postfix❌89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin
19 es❌1000:1000::/home/es:/bin/bash
-A 显示所有字符
[root@ESProbe ~]# cat -A /etc/passwd
root❌0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash\(
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin\)
daemon❌2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin\(
adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin\)
lp❌4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin\(
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync\)
shutdown❌6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown\(
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt\)
mail❌8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin\(
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin\)
games❌12💯games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin\(
ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin\)
nobody❌99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin\(
systemd-network:x:192:192:systemd Network Management:/:/sbin/nologin\)
dbus❌81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin\(
polkitd:x:999:998:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin\)
sshd❌74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin\(
postfix:x:89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin\)
es❌1000:1000::/home/es:/bin/bash$
-E 显示结束符结尾多了一个\(符号
[root@ESProbe ~]# cat -E /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash\)
bin❌1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin\(
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin\)
adm❌3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin\(
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin\)
sync❌5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync\(
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown\)
halt❌7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt\(
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin\)
operator❌11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin\(
games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin\)
ftp❌14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin\(
nobody:x:99:99:Nobody:/:/sbin/nologin\)
systemd-network❌192:192:systemd Network Management:/:/sbin/nologin\(
dbus:x:81:81:System message bus:/:/sbin/nologin\)
polkitd❌999:998:User for polkitd:/:/sbin/nologin\(
sshd:x:74:74:Privilege-separated SSH:/var/empty/sshd:/sbin/nologin\)
postfix❌89:89::/var/spool/postfix:/sbin/nologin\(
es:x:1000:1000::/home/es:/bin/bash\)
head
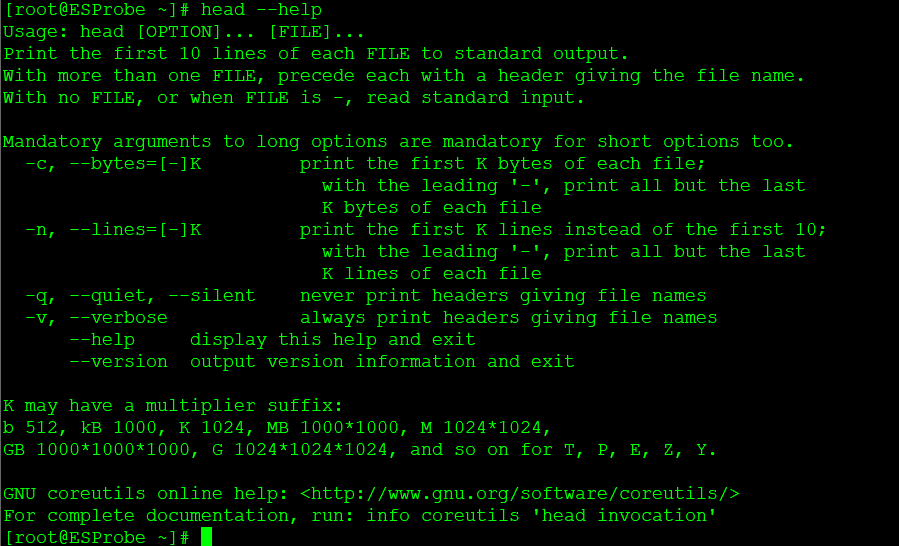
[root@ESProbe ~]# head --help
Usage: head [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Print the first 10 lines of each FILE to standard output.
With more than one FILE, precede each with a header giving the file name.
With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-c, --bytes=[-]K print the first K bytes of each file;
with the leading '-', print all but the last
K bytes of each file
-n, --lines=[-]K print the first K lines instead of the first 10;
with the leading '-', print all but the last
K lines of each file
-q, --quiet, --silent never print headers giving file names
-v, --verbose always print headers giving file names
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
K may have a multiplier suffix:
b 512, kB 1000, K 1024, MB 10001000, M 10241024,
GB 100010001000, G 102410241024, and so on for T, P, E, Z, Y.
GNU coreutils online help: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'head invocation'
eg:查看开头到第二行
[root@ESProbe ~]# head -n 2 /etc/passwd
root❌0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
bin❌1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
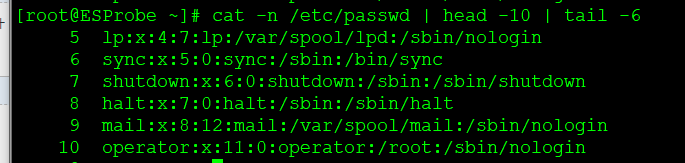
eg:查看前5-10 行内容
[root@ESProbe ~]# cat -n /etc/passwd | head -10 | tail -6
5 lp❌4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
6 sync❌5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
7 shutdown❌6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
8 halt❌7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
9 mail❌8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin
10 operator❌11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
sed
[root@ESProbe ~]# sed --help
Usage: sed [OPTION]... {script-only-if-no-other-script} [input-file]...
-n, --quiet, --silent
suppress automatic printing of pattern space
-e script, --expression=script
add the script to the commands to be executed
-f script-file, --file=script-file
add the contents of script-file to the commands to be executed
--follow-symlinks
follow symlinks when processing in place
-i[SUFFIX], --in-place[=SUFFIX]
edit files in place (makes backup if SUFFIX supplied)
-c, --copy
use copy instead of rename when shuffling files in -i mode
-b, --binary
does nothing; for compatibility with WIN32/CYGWIN/MSDOS/EMX (
open files in binary mode (CR+LFs are not treated specially))
-l N, --line-length=N
specify the desired line-wrap length for the `l' command
--posix
disable all GNU extensions.
-r, --regexp-extended
use extended regular expressions in the script.
-s, --separate
consider files as separate rather than as a single continuous
long stream.
-u, --unbuffered
load minimal amounts of data from the input files and flush
the output buffers more often
-z, --null-data
separate lines by NUL characters
--help
display this help and exit
--version
output version information and exit
If no -e, --expression, -f, or --file option is given, then the first
non-option argument is taken as the sed script to interpret. All
remaining arguments are names of input files; if no input files are
specified, then the standard input is read.
GNU sed home page: http://www.gnu.org/software/sed/.
General help using GNU software: http://www.gnu.org/gethelp/.
E-mail bug reports to: bug-sed@gnu.org.
Be sure to include the word sed'' somewhere in the Subject:'' field.
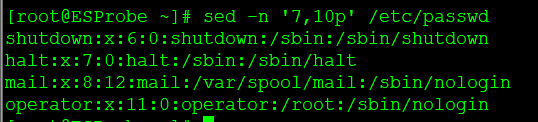
sed -n '70,75p' date.log 输出第70行到第75行的内容
sed -n '6p;260,400p; ' 文件名 输出第6行 和 260到400行
sed -n 5p 文件名 输出第5行