机器学习实战之logistic回归分类
利用logistic回归进行分类的主要思想:根据现有数据对分类边界建立回归公式,并以此进行分类。
logistic优缺点:
优点:计算代价不高,易于理解和实现。
缺点:容易欠拟合,分类精度可能不高。 .
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型数据。
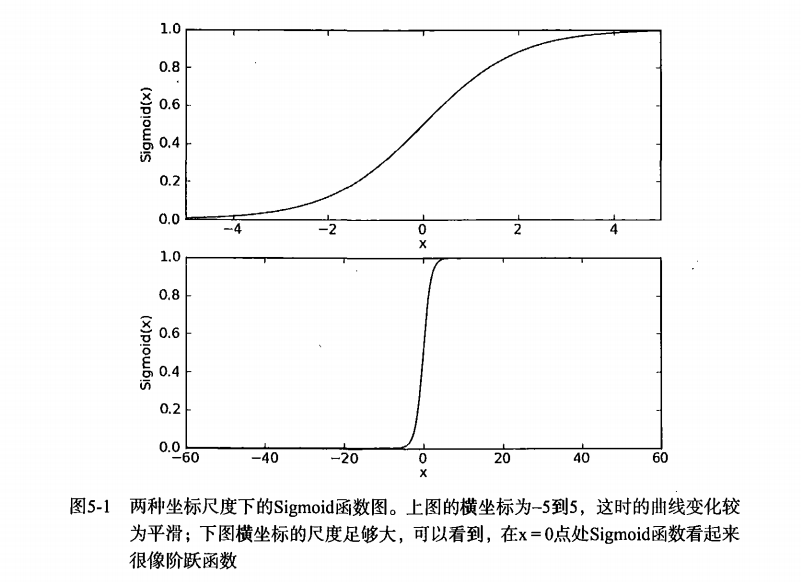
sigmoid函数: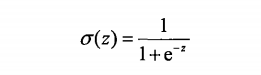
梯度上升法:
梯度:
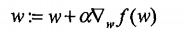
该公式将一直被迭代执行,直至达到某个停止条件为止,比如迭代次数达到某个指定值或算
法达到某个可以允许的误差范围。
随机梯度上升法:
梯度上升算法在每次更新回归系数时都需要遍历整个数据集, 该方法在处理100个左右的数
据集时尚可,但如果有数十亿样本和成千上万的特征,那么该方法的计算复杂度就太高了。一种
改进方法是一次仅用一个样本点来更新回归系数,该方法称为随机梯度上升算法。由于可以在新
样本到来时对分类器进行增量式更新,因而随机梯度上升算法是一个在线学习算法。与 “ 在线学
习”相对应,一次处理所有数据被称作是“批处理” 。
梯度下降法:
你最经常听到的应该是梯度下降算法,它与这里的梯度上升算法是一样的,只是公式中的
加法需要变成减法。因此,对应的公式可以写成: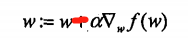
梯度上升算法用来求函数的最大值,而梯度下降算法用来求函数的最小值。
logistic预测疝气病预测病马的死亡率代码:
%matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import random # 加载数据集 def loadDataSet(): dataMat = [] labelMat = [] fr = open('./testSet.txt') for line in fr.readlines(): lineData = line.strip().split() dataMat.append([1.0, float(lineData[0]), float(lineData[1])]) labelMat.append(int(lineData[2])) return dataMat, labelMat # sigmoid 函数 def sigmoid(inX): return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-inX)) # 梯度上升 def gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels, maxCycles): dataMatrix = np.mat(dataMatIn) labelsMatrix = np.mat(classLabels).transpose() # 转置,将行向量转置为列向量 m, n = np.shape(dataMatrix) alpha = 0.001 W = np.ones((n, 1)) for i in range(maxCycles): h = sigmoid(dataMatrix * W) # (100, 1) error = labelsMatrix - h # (100, 1) W = W + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose() * error # (3, 100) * (100, 1) return W #改进版随机梯度上升 def stocGradAscent1(dataMatrixIn, classLabels, numIter=150): dataMatrix = np.array(dataMatrixIn) m,n = np.shape(dataMatrix) weights = np.ones(n) #initialize to all ones for j in range(numIter): dataIndex = list(range(m)) for i in range(m): alpha = 4.0/(1.0+j+i)+0.01 #apha decreases with iteration, does not randIndex = int(random.uniform(0,len(dataIndex)))#go to 0 because of the constant h = sigmoid(sum(dataMatrix[randIndex]*weights)) error = classLabels[randIndex] - h weights = weights + alpha * error * dataMatrix[randIndex] del(dataIndex[randIndex]) return np.mat(weights.reshape(n, 1)) def plotBestFit(weights, dataMat, labelMat): dataArr = np.array(dataMat) n = np.shape(dataArr)[0] xcord1 = []; ycord1 = [] xcord2 = []; ycord2 = [] for i in range(n): if labelMat[i] == 1: xcord1.append(dataArr[i, 1]); ycord1.append(dataArr[i, 2]) else: xcord2.append(dataArr[i, 1]); ycord2.append(dataArr[i, 2]) fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111) ax.scatter(xcord1, ycord1, s = 30, c = 'red', marker = 's') ax.scatter(xcord2, ycord2, s = 30, c = 'green') x = np.arange(-4.0, 4.0, 0.1) y = ((np.array((-weights[0] - weights[1] * x) / weights[2]))[0]).transpose() ax.plot(x, y) plt.xlabel('X1') plt.ylabel('X2') plt.show() # 预测 def classifyVector(inX, weights): prob = sigmoid(sum(inX * weights)) if prob > 0.5: return 1.0 else: return 0.0 # 对训练集进行训练,并且对测试集进行测试 def colicTest(): trainFile = open('horseColicTraining.txt') testFile = open('horseColicTest.txt') trainingSet = []; trainingLabels = [] for line in trainFile.readlines(): currLine = line.strip().split('\t') lineArr = [] for i in range(21): lineArr.append(float(currLine[i])) trainingSet.append(lineArr) trainingLabels.append(float(currLine[21])) # 开始训练 weights = stocGradAscent1(trainingSet, trainingLabels, 400) errorCount = 0.0 numTestVec = 0.0 for line in testFile.readlines(): numTestVec += 1.0 currLine = line.strip().split('\t') lineArr = [] for i in range(21): lineArr.append(float(currLine[i])) if int(classifyVector(np.array(lineArr), weights)) != int(currLine[21]): errorCount += 1.0 errorRate = errorCount / float(numTestVec) print("the error rate is:%f" % errorRate) return errorRate # 多次测试求平均值 def multiTest(): testTimes = 10 errorRateSum = 0.0 for i in range(testTimes): errorRateSum += colicTest() print("the average error rate is:%f" % (errorRateSum / float(testTimes))) multiTest()



