【译】TetroGL: An OpenGL Game Tutorial in C++ for Win32 Platforms - Part 1
这个系列专注于使用C++和OpenGL在windows平台上开发2D游戏,项目目标是在系列结束后能开发出一个类似俄罗斯方块的游戏。本系列分为3篇文章:
第一部分:涉及win32消息循环,窗口创建和OpenGL的搭建,并且你将会学习如何绘制一些简单的图形。
第二部分:涉及资源处理和简单动画的显示
第三部分:将前面的内容包含进来,并且讨论游戏逻辑。
项目设置
作者做了两项设置:
1) LinkeràInput中,在” Addition Dependencies”中加入”opengl32.lib”,
2) 禁掉UNICODE,“c/c++”à” Preprocessor”,在Preprocessor Definitions中将"Inherit from parent or project defaults"不选中。
消息循环
Windows系统为每个应用程序创建一个消息队列,当指定应用程序的窗口上发生一个事件时,系统会把消息推入到这个队列中。你的应用程序应当检索并处理这些消息。这就是所谓的“消息循环“,是win32应用程序的核心。
一个典型的消息循环如下:
 MSG Message;
MSG Message; Message.message = (~WM_QUIT);
Message.message = (~WM_QUIT); // Loop until a WM_QUIT message is received
// Loop until a WM_QUIT message is received while (Message.message != WM_QUIT)
while (Message.message != WM_QUIT) {
{ if (PeekMessage(&Message, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE))
if (PeekMessage(&Message, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE)) {
{ // If a message was waiting in the message queue, process it
// If a message was waiting in the message queue, process it TranslateMessage(&Message);
TranslateMessage(&Message); DispatchMessage(&Message);
DispatchMessage(&Message); }
} else
else {//空闲时
{//空闲时 // Do processing stuff here
// Do processing stuff here
 }
} }
}
TranslateMessage函数的目的是为了将虚键消息(WM_KEYDOWN和WM_KEYUP)为字符消息(WM_CHAR).最后DispatchMessage会将消息定向到正确的窗口处理程序。
 // The application class, which simply wraps the message queue and process
// The application class, which simply wraps the message queue and process // the command line.
// the command line. class CApplication
class CApplication {
{ public:
public: CApplication(){}
CApplication(){} CApplication(HINSTANCE hInstance);
CApplication(HINSTANCE hInstance); ~CApplication();
~CApplication();
 // Parses the command line to see if the application
// Parses the command line to see if the application // should be in fullscreen mode.
// should be in fullscreen mode. void ParseCmdLine(LPSTR lpCmdLine);
void ParseCmdLine(LPSTR lpCmdLine); // Creates the main window and start the message loop.
// Creates the main window and start the message loop. void Run();
void Run(); void SetHInst(HINSTANCE hInstance);
void SetHInst(HINSTANCE hInstance);
 private:
private: HINSTANCE m_hInstance;
HINSTANCE m_hInstance; // Specifies if the application has to be started in fullscreen
// Specifies if the application has to be started in fullscreen // mode. This option is supplied through the command line
// mode. This option is supplied through the command line // ("-fullscreen" option).
// ("-fullscreen" option). bool m_bFullScreen;
bool m_bFullScreen; };
};
ParseCmdLine函数功能非常直观:仅仅简单地检查命令行中是否有参数"-fullscreen",如果有,则设置m_bFullScreen为true,表示窗口模式为全屏模式。
 void CApplication::Run()
void CApplication::Run() {
{ // Create the main window first
// Create the main window first CMainWindow mainWindow(800,600,m_bFullScreen);
CMainWindow mainWindow(800,600,m_bFullScreen);
 MSG Message;
MSG Message; Message.message = ~WM_QUIT;
Message.message = ~WM_QUIT; DWORD dwNextDeadLine = GetTickCount() + 30;
DWORD dwNextDeadLine = GetTickCount() + 30; DWORD dwSleep = 30;
DWORD dwSleep = 30; bool bUpdate = false;
bool bUpdate = false; // Loop until a WM_QUIT message is received
// Loop until a WM_QUIT message is received while (Message.message != WM_QUIT)
while (Message.message != WM_QUIT) {
{ // Wait until a message comes in or until the timeout expires. The
// Wait until a message comes in or until the timeout expires. The // timeout is recalculated so that this function will return at
// timeout is recalculated so that this function will return at // least every 30 msec.
// least every 30 msec. DWORD dwResult = MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx(0,NULL,dwSleep,QS_ALLEVENTS,0);
DWORD dwResult = MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx(0,NULL,dwSleep,QS_ALLEVENTS,0); if (dwResult != WAIT_TIMEOUT)
if (dwResult != WAIT_TIMEOUT) {
{ // If the function returned with no timeout, it means that a
// If the function returned with no timeout, it means that a  // message has been received, so process it.
// message has been received, so process it. if (PeekMessage(&Message, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE))
if (PeekMessage(&Message, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE)) {
{ // If a message was waiting in the message queue, process it
// If a message was waiting in the message queue, process it TranslateMessage(&Message);
TranslateMessage(&Message); DispatchMessage(&Message);
DispatchMessage(&Message); }
}
 // If the current time is close (or past) to the
// If the current time is close (or past) to the  // deadline, the application should be processed.
// deadline, the application should be processed. if (GetTickCount() >= dwNextDeadLine-1)
if (GetTickCount() >= dwNextDeadLine-1) bUpdate = true;
bUpdate = true; }
} else
else // On a timeout, the application should be processed.
// On a timeout, the application should be processed. bUpdate = true;
bUpdate = true;
 // Check if the application should be processed
// Check if the application should be processed if (bUpdate)
if (bUpdate) {
{ DWORD dwCurrentTime = GetTickCount();
DWORD dwCurrentTime = GetTickCount(); // Update the main window
// Update the main window mainWindow.Update(dwCurrentTime);
mainWindow.Update(dwCurrentTime); // Draw the main window
// Draw the main window mainWindow.Draw();
mainWindow.Draw();
 dwNextDeadLine = dwNextDeadLine + 30;
dwNextDeadLine = dwNextDeadLine + 30; dwSleep = 30;
dwSleep = 30; }
} else
else dwSleep = dwNextDeadLine - GetCurrentTime();
dwSleep = dwNextDeadLine - GetCurrentTime(); }
} }
}
函数第一行创建主窗口。和常见的消息循环不同,由于在2D游戏中并不需要很快地刷新屏幕,以固定地速率(这里是30毫秒)刷新,对于绘制动画和其他处理已经足够了。
作者在这里使用的技巧就是出于这个目的,他使用了MsgWaitForMultipleObjectsEx函数来等待任何事件的发生,再判断是30毫秒的时限已到,还是有事件要处理,若是后者,则先处理事件,在处理完后,若此时也已经接近30毫秒的时限的话,就重绘界面,若是超时发生了,则说明30毫秒时限已到,需要去刷新界面了。若这两种情况都没有的话,这个函数不会消耗 CPU周期,线程只是被挂起,不参与调度。
主窗口
创建窗口
 CMainWindow::CMainWindow(int iWidth, int iHeight, bool bFullScreen)
CMainWindow::CMainWindow(int iWidth, int iHeight, bool bFullScreen)  : m_hWindow(NULL), m_hDeviceContext(NULL), m_hGLContext(NULL),
: m_hWindow(NULL), m_hDeviceContext(NULL), m_hGLContext(NULL),  m_bFullScreen(bFullScreen)
m_bFullScreen(bFullScreen) {
{ RegisterWindowClass();
RegisterWindowClass();
 RECT WindowRect;
RECT WindowRect; WindowRect.top = WindowRect.left = 0;
WindowRect.top = WindowRect.left = 0; WindowRect.right = iWidth;
WindowRect.right = iWidth; WindowRect.bottom = iHeight;
WindowRect.bottom = iHeight;
 // Window Extended Style
// Window Extended Style DWORD dwExStyle = 0;
DWORD dwExStyle = 0;  // Windows Style
// Windows Style DWORD dwStyle = 0;
DWORD dwStyle = 0; 
 if (m_bFullScreen)
if (m_bFullScreen) {
{ DEVMODE dmScreenSettings;
DEVMODE dmScreenSettings; memset(&dmScreenSettings,0,sizeof(dmScreenSettings));
memset(&dmScreenSettings,0,sizeof(dmScreenSettings));  dmScreenSettings.dmSize = sizeof(dmScreenSettings);
dmScreenSettings.dmSize = sizeof(dmScreenSettings);  dmScreenSettings.dmPelsWidth = iWidth;
dmScreenSettings.dmPelsWidth = iWidth;  dmScreenSettings.dmPelsHeight = iHeight;
dmScreenSettings.dmPelsHeight = iHeight;  dmScreenSettings.dmBitsPerPel = 32;
dmScreenSettings.dmBitsPerPel = 32;  dmScreenSettings.dmFields = DM_PELSWIDTH | DM_PELSHEIGHT | DM_BITSPERPEL;
dmScreenSettings.dmFields = DM_PELSWIDTH | DM_PELSHEIGHT | DM_BITSPERPEL;
 // Change the display settings to fullscreen. On error, throw
// Change the display settings to fullscreen. On error, throw  // an exception.
// an exception. if (ChangeDisplaySettings(&dmScreenSettings,CDS_FULLSCREEN)
if (ChangeDisplaySettings(&dmScreenSettings,CDS_FULLSCREEN) != DISP_CHANGE_SUCCESSFUL)
!= DISP_CHANGE_SUCCESSFUL) {
{ throw CException("Unable to swith to fullscreen mode");
throw CException("Unable to swith to fullscreen mode"); }
}
 dwExStyle = WS_EX_APPWINDOW;
dwExStyle = WS_EX_APPWINDOW;  dwStyle = WS_POPUP;
dwStyle = WS_POPUP;  // In fullscreen mode, we hide the cursor.
// In fullscreen mode, we hide the cursor. ShowCursor(FALSE);
ShowCursor(FALSE); }
} else
else {
{ dwExStyle = WS_EX_APPWINDOW | WS_EX_WINDOWEDGE;
dwExStyle = WS_EX_APPWINDOW | WS_EX_WINDOWEDGE; dwStyle = WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW;
dwStyle = WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW;  }
}
 // Adjust the window to the true requested size
// Adjust the window to the true requested size AdjustWindowRectEx(&WindowRect, dwStyle, FALSE, dwExStyle);
AdjustWindowRectEx(&WindowRect, dwStyle, FALSE, dwExStyle);  // Now create the main window
// Now create the main window m_hWindow = CreateWindowEx(dwExStyle,TEXT(WINDOW_CLASSNAME),
m_hWindow = CreateWindowEx(dwExStyle,TEXT(WINDOW_CLASSNAME),  TEXT("Tutorial1"),
TEXT("Tutorial1"),  WS_CLIPSIBLINGS | WS_CLIPCHILDREN | dwStyle,
WS_CLIPSIBLINGS | WS_CLIPCHILDREN | dwStyle, 0, 0, WindowRect.right-WindowRect.left,
0, 0, WindowRect.right-WindowRect.left,  WindowRect.bottom-WindowRect.top,
WindowRect.bottom-WindowRect.top,  NULL, NULL,
NULL, NULL,  GetModuleHandle(NULL),
GetModuleHandle(NULL),  this);
this); if (m_hWindow==NULL)
if (m_hWindow==NULL) throw CException("Cannot create the main window");
throw CException("Cannot create the main window");
 CreateContext();
CreateContext(); InitGL();
InitGL(); ShowWindow(m_hWindow,SW_SHOW);
ShowWindow(m_hWindow,SW_SHOW); // Call OnSize manually because in fullscreen mode it will be
// Call OnSize manually because in fullscreen mode it will be  // called only when the window is created (which is too early
// called only when the window is created (which is too early // because OpenGL is not initialized yet).
// because OpenGL is not initialized yet). OnSize(iWidth,iHeight);
OnSize(iWidth,iHeight); }
}
在构造函数中,检查完是否需要进入全屏模式后,通过调用ChangeDisplaySettings来切换到全屏模式,然后调用AdjustWindowRectEx来调整矩形的大小,但这个函数在全屏模式下没什么作用,最后CreateContext和InitGL对OpenGL进行初始化。
 LRESULT CMainWindow::OnEvent(HWND Handle, UINT Message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
LRESULT CMainWindow::OnEvent(HWND Handle, UINT Message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) {
{ if (Message == WM_CREATE)
if (Message == WM_CREATE) {
{ // Get the creation parameters.
// Get the creation parameters. CREATESTRUCT* pCreateStruct = reinterpret_cast<CREATESTRUCT*>(lParam);
CREATESTRUCT* pCreateStruct = reinterpret_cast<CREATESTRUCT*>(lParam);
 // Set as the "user data" parameter of the window
// Set as the "user data" parameter of the window SetWindowLongPtr(Handle, GWLP_USERDATA,
SetWindowLongPtr(Handle, GWLP_USERDATA,  reinterpret_cast<long>(pCreateStruct->lpCreateParams));
reinterpret_cast<long>(pCreateStruct->lpCreateParams)); }
}
 // Get the CMainWindow instance corresponding to the window handle
// Get the CMainWindow instance corresponding to the window handle CMainWindow* pWindow = reinterpret_cast<CMainWindow*>
CMainWindow* pWindow = reinterpret_cast<CMainWindow*> (GetWindowLongPtr(Handle, GWLP_USERDATA));
(GetWindowLongPtr(Handle, GWLP_USERDATA)); if (pWindow)
if (pWindow) pWindow->ProcessEvent(Message,wParam,lParam);
pWindow->ProcessEvent(Message,wParam,lParam);
 return DefWindowProc(Handle, Message, wParam, lParam);
return DefWindowProc(Handle, Message, wParam, lParam); }
}
由于OnEvent函数是静态的,因此就没法访问非静态成员,为了解决这个问题,在调用CreateWindowEx创建窗口时最后一个参数传的是this指针。传给窗口处理过程的第一个消息是WM_CREATE,当接收到这个消息时,wParam参数中包含一个CREATESTRUCT指针,它里面包含了额外的数据,在这里是指向CMainWindow的指针。但遗憾的是,不是每个消息都有这个结构,所以要保存起来供后面使用。因此调用SetWindowLongPtr,它的目的是为一个特定的窗口保存一些用户数据(GWLP_USERDATA)。在这里,作者保存了到类实例的指针。当接收到其他消息时,我们只是简单地通过GetWindowLongPtr来取回这个指针,然后访问非静态函数ProcessEvent,而这个函数负责具体的消息处理。
 void CMainWindow::ProcessEvent(UINT Message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
void CMainWindow::ProcessEvent(UINT Message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) {
{ switch (Message)
switch (Message) {
{ // Quit when we close the main window
// Quit when we close the main window case WM_CLOSE :
case WM_CLOSE : PostQuitMessage(0);
PostQuitMessage(0); break;
break; case WM_SIZE:
case WM_SIZE: OnSize(LOWORD(lParam),HIWORD(lParam));
OnSize(LOWORD(lParam),HIWORD(lParam)); break;
break; case WM_KEYDOWN :
case WM_KEYDOWN : break;
break; case WM_KEYUP :
case WM_KEYUP : break;
break; }
} }
}
异常处理
 class CException : public std::exception
class CException : public std::exception {
{ public:
public: const char* what() const { return m_strMessage.c_str(); }
const char* what() const { return m_strMessage.c_str(); }
 CException(const std::string& strMessage="") : m_strMessage(strMessage) { }
CException(const std::string& strMessage="") : m_strMessage(strMessage) { } virtual ~CException() { }
virtual ~CException() { }
 std::string m_strMessage;
std::string m_strMessage; };
};
使用的实例:
 CApplication theApp;
CApplication theApp;
 int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE Instance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPSTR lpCmdLine, INT)
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE Instance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPSTR lpCmdLine, INT) {
{ try
try {
{ // Create the application class,
// Create the application class,  // parse the command line and
// parse the command line and // start the app.
// start the app. theApp.SetHInst(Instance);
theApp.SetHInst(Instance); theApp.ParseCmdLine(lpCmdLine);
theApp.ParseCmdLine(lpCmdLine); theApp.Run();
theApp.Run(); }
} catch(CException& e)
catch(CException& e) {
{ MessageBox(NULL,e.what(),"Error",MB_OK|MB_ICONEXCLAMATION);
MessageBox(NULL,e.what(),"Error",MB_OK|MB_ICONEXCLAMATION); }
}
 return 0;
return 0; }
}
初始化OpenGL
CreateContext用来初始化绘制上下文,使得OpenGL基本元素可以在窗口上绘制:
 void CMainWindow::CreateContext()
void CMainWindow::CreateContext() {
{ // Describes the pixel format of the drawing surface
// Describes the pixel format of the drawing surface PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR pfd;
PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR pfd; memset(&pfd, 0, sizeof(PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR));
memset(&pfd, 0, sizeof(PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR)); pfd.nSize = sizeof(PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR);
pfd.nSize = sizeof(PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR); pfd.nVersion = 1; // Version Number
pfd.nVersion = 1; // Version Number pfd.dwFlags = PFD_DRAW_TO_WINDOW | // Draws to a window
pfd.dwFlags = PFD_DRAW_TO_WINDOW | // Draws to a window PFD_SUPPORT_OPENGL | // The format must support OpenGL
PFD_SUPPORT_OPENGL | // The format must support OpenGL PFD_DOUBLEBUFFER; // Support for double buffering
PFD_DOUBLEBUFFER; // Support for double buffering pfd.iPixelType = PFD_TYPE_RGBA; // Uses an RGBA pixel format
pfd.iPixelType = PFD_TYPE_RGBA; // Uses an RGBA pixel format pfd.cColorBits = 32; // 32 bits colors
pfd.cColorBits = 32; // 32 bits colors
 if (!(m_hDeviceContext=GetDC(m_hWindow)))
if (!(m_hDeviceContext=GetDC(m_hWindow)))  throw CException("Unable to create rendering context");
throw CException("Unable to create rendering context");
 int PixelFormat;
int PixelFormat; // Do Windows find a matching pixel format ?
// Do Windows find a matching pixel format ? if (!(PixelFormat=ChoosePixelFormat(m_hDeviceContext,&pfd)))
if (!(PixelFormat=ChoosePixelFormat(m_hDeviceContext,&pfd)))  throw CException("Unable to create rendering context");
throw CException("Unable to create rendering context"); // Set the new pixel format
// Set the new pixel format if(!SetPixelFormat(m_hDeviceContext,PixelFormat,&pfd))
if(!SetPixelFormat(m_hDeviceContext,PixelFormat,&pfd))  throw CException("Unable to create rendering context");
throw CException("Unable to create rendering context"); // Create the OpenGL rendering context
// Create the OpenGL rendering context if (!(m_hGLContext=wglCreateContext(m_hDeviceContext)))
if (!(m_hGLContext=wglCreateContext(m_hDeviceContext)))  throw CException("Unable to create rendering context");
throw CException("Unable to create rendering context"); // Activate the rendering context
// Activate the rendering context if(!wglMakeCurrent(m_hDeviceContext,m_hGLContext))
if(!wglMakeCurrent(m_hDeviceContext,m_hGLContext)) throw CException("Unable to create rendering context");
throw CException("Unable to create rendering context");  }
}
函数的第一部分填充PIXELFORMATDESCRIPTOR结构体:缓冲区用来绘制到窗口上,支持OpenGL,使用双缓存(为了避免闪烁)。然后调用ChoosePixelFormat来检查像素格式是否支持,这个函数返回一个像素格式索引(若没有找到匹配的,则返回0)。一旦存在这样的像素格式索引,则通过SetPixelFormat来设置新像素格式。然后调用wglCreateContext创建OpenGL绘制上下文,最后,调用wglMakeCurrent,这指明线程接下来的OpenGL调用会绘制在这个设备上下文上。
InitGL函数很简单:
 void CMainWindow::InitGL()
void CMainWindow::InitGL() {
{ // Enable 2D texturing
// Enable 2D texturing glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D); // Choose a smooth shading model
// Choose a smooth shading model glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH);
glShadeModel(GL_SMOOTH); // Set the clear color to black
// Set the clear color to black glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glClearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); }
}
再看OnSize函数
 void CMainWindow::OnSize(GLsizei width, GLsizei height)
void CMainWindow::OnSize(GLsizei width, GLsizei height) {
{ // Sets the size of the OpenGL viewport
// Sets the size of the OpenGL viewport glViewport(0,0,width,height);
glViewport(0,0,width,height);
 // Select the projection stack and apply
// Select the projection stack and apply  // an orthographic projection
// an orthographic projection glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity();
glLoadIdentity(); glOrtho(0.0,width,height,0.0,-1.0,1.0);
glOrtho(0.0,width,height,0.0,-1.0,1.0); glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW); }
}
正交投影
透视投影

绘制简单图形
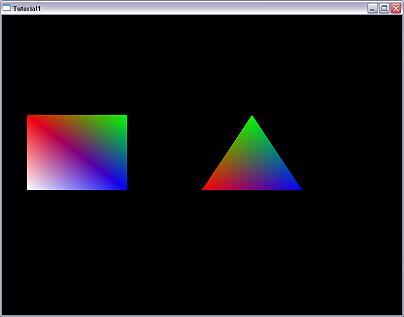
 void CMainWindow::Draw()
void CMainWindow::Draw() {
{ // Clear the buffer
// Clear the buffer glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
 // Here goes the drawing code
// Here goes the drawing code glBegin(GL_QUADS);
glBegin(GL_QUADS); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glVertex3i(50,200,0);
glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glVertex3i(50,200,0); glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); glVertex3i(250,200,0);
glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); glVertex3i(250,200,0); glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); glVertex3i(250,350,0);
glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); glVertex3i(250,350,0); glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0); glVertex3i(50,350,0);
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0); glVertex3i(50,350,0); glEnd();
glEnd();
 glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES);
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES); glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glVertex3i(400,350,0);
glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glVertex3i(400,350,0); glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); glVertex3i(500,200,0);
glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0); glVertex3i(500,200,0); glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); glVertex3i(600,350,0);
glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); glVertex3i(600,350,0); glEnd();
glEnd();
 SwapBuffers(m_hDeviceContext);
SwapBuffers(m_hDeviceContext); }
}
作者:洞庭散人
出处:http://phinecos.cnblogs.com/
posted on 2008-06-26 21:01 Phinecos(洞庭散人) 阅读(3861) 评论(9) 编辑 收藏 举报







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· [AI/GPT/综述] AI Agent的设计模式综述
2006-06-26 myeclipse开发struts应用程序小示例