1.学习总结(2分)
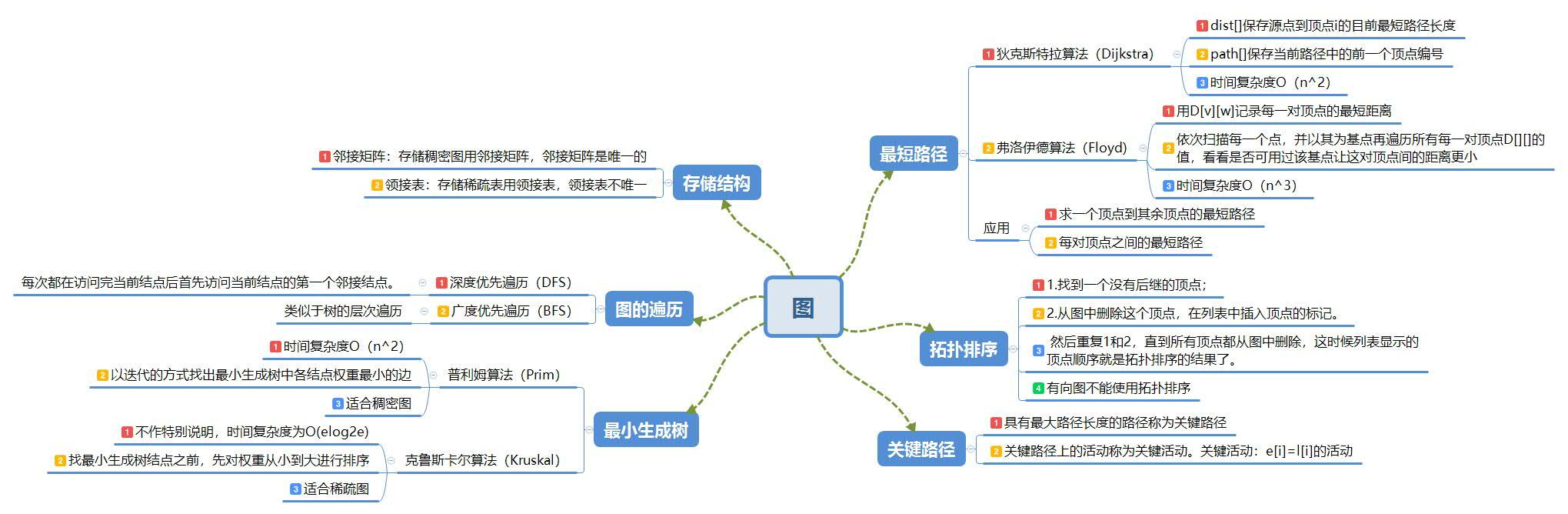
1.1图的思维导图
1.2 图结构学习体会
深度遍历
- 深度优先遍历的策略就是首先访问第一个邻接结点,然后再以这个被访问的邻接结点作为初始结点,访问它的第一个邻接结点。总结起来可以这样说:每次都在访问完当前结点后首先访问当前结点的第一个邻接结点。
广度遍历
- 访问图中的一个点之后,一次访问v的各个未曾访问过的邻接点,然后分别从这些邻接点出发,依次访问它们的邻接点,并且使“先被访问的顶点的邻接点”先于“后被访问的顶点的邻接点”被访问。所以广度遍历要用队列来完成。
Prim和Kruscal算法
- Prim算法首先以一个结点作为最小生成树的初始结点,然后以迭代的方式找出最小生成树中各结点权重最小的边,并加到最小生成树中。(加入之后如果产生回路了就要跳过这条边,选择下一个结点。)当所有的结点都加入到最小生成树中后,就找出了这个连通图的最小生成树
- Kruskal算法在找最小生成树结点之前,需要对权重从小到大进行排序。将排序好的权重边依次加入到最小生成树中,(如果加入时产生回路就跳过这条边,加入下一条边)。当所有的结点都加入到最小生成树中后,就找到了这个连通图的最小生成树。
Dijkstra算法
- 算法思想:设G=(V,E)是一个带权有向图,把图中顶点集合V分成两组,第一组为已求出最短路径的顶点集合(用S表示,初始时S中只有一个源点,以后每求得一条最短路径 , 就将加入到集合S中,直到全部顶点都加入到S中,算法就结束了),第二组为其余未确定最短路径的顶点集合(用U表示),按最短路径长度的递增次序依次把第二组的顶点加入S中。在加入的过程中,总保持从源点v到S中各顶点的最短路径长度不大于从源点v到U中任何顶点的最短路径长度。此外,每个顶点对应一个距离,S中的顶点的距离就是从v到此顶点的最短路径长度,U中的顶点的距离,是从v到此顶点只包括S中的顶点为中间顶点的当前最短路径长度。
拓扑排序算法
- 1.找到一个没有后继的顶点;2.从图中删除这个顶点,在列表中插入顶点的标记。 然后重复1和2,直到所有顶点都从图中删除,这时候列表显示的顶点顺序就是拓扑排序的结果了,有向图就不能使用拓扑排序。
2.PTA实验作业
2.1题目1:7-2 排座位
1.设计思路
建图,宾客的关系放到图中。
对visited[][]进行初始化为0
若friends[a][b]==1,则为朋友关系,直接输出“No problem”
定义一个变量flag=0;
将vitited中相应宾客的值置为1;
对宾客a,b进行VIS函数调用,类似于图的深度遍历
对a,b检查是否存在共同的朋友
存在,flag=1
不存在,则flag=0;
if(宾客是敌人关系){
存在共同朋友,输出"OK but..."
否则输出“No way”
}
else(不是朋友也不是敌人){
存在共同朋友,输出"No problem"
否则输出“OK”
}
2.代码截图

3.PTA提交列表说明

- 一开始不小心将函数中(iy)便返回写成了(ix),导致falg的返回值错误,既只对了(friends[a][b]==1)直接输出的部分,朋友的朋友的情况判断错误。
题目二:7-3 六度空间
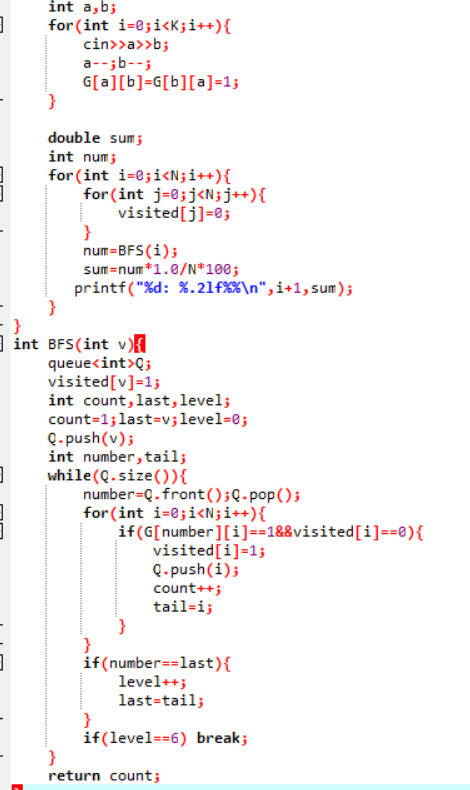
1.设计思路
先建图和对visited[]初始化为0
从顶点v=1开始对图进行广度遍历
将v进队列
while(队列不为空){
将number置为队列头元素,删除队列头元素;
遍历顶点i=0 to i<N{
若visited[i]==0且G[number][i]==1;
将i进队,visited[i]置为1,记录节点数,同时记录i的数值
}
}
若访问到该层的最后一个节点
层数加一,改变这一层访问的最后一个节点
层数达到6便结束,返回记录的节点数
2.代码截图
3.PTA提交列表说明
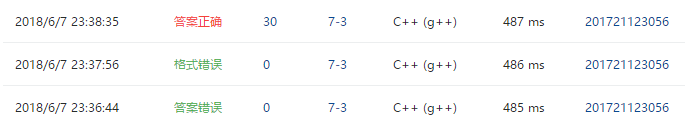
- 忘记将进队的i的visited[i]置为1,导致节点数错误。格式错误是没把分子乘1.0,没能保留小数点后两位。
2.1题目1:7-4 公路村村通
1.设计思路
给G[][]和lowcost[]数组赋初值;
找出N-1个顶点 i=1 to i=N{
在(V-U)中找出离U中最近的顶点
用k记录最近顶点的编号
累加顶点间最短路径的数值
给lowcost[k]赋值-1,标记k已经加入U
for j=1 to j=N
修改lowcost[]中的值
}
判断输入数据是否以保证畅通
不能则返回-1
否则返回最短路径的总和sum
2.代码截图
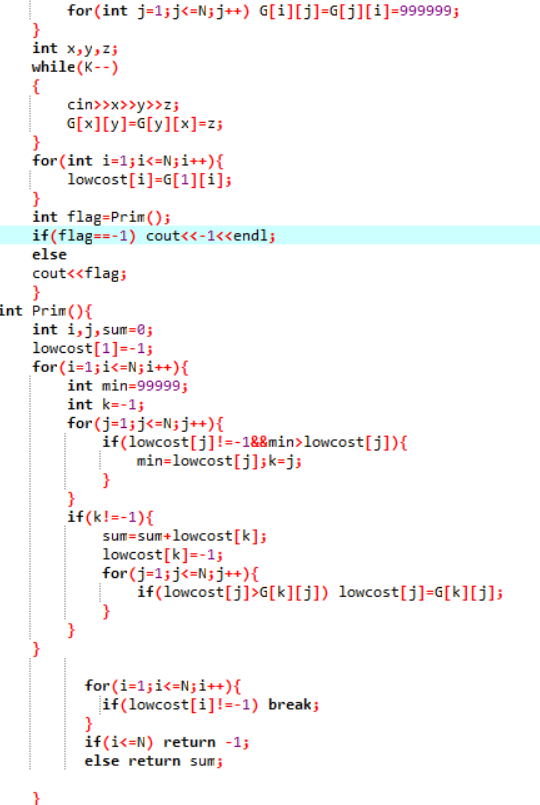
3.PTA提交列表说明

- 这道题是用最小生成树中Prim()算法计算的,书中有类似代码,但一直写一直是部分正确,怎么改都是,去网上查了下代码,思路基本也一样,然后提交网上的代码就全对了,而自己的还不知道哪错了,然后根据网上对的代码一直改自己代码中认为错误的地方,在PTA上反复提交,找了半小时才发现是因为我给G[][]的赋的初值太小了,网上是999999,虽然知道错在哪里了,但还是一脸懵逼,为什么G[][]=999999能全对。。。。。。
.3.截图本周题目集的PTA最后排名
3.1 PTA排名

3.2 我的总分:2.5
4. 阅读代码
#ifndef __GRAPH_H__
#define __GRAPH_H__
typedef struct graph *Graph;
Graph graph_create(int n);
void graph_destroy(Graph);
void graph_add_edge(Graph, int source, int sink);
int graph_vertex_count(Graph);
int graph_edge_count(Graph);
int graph_out_degree(Graph, int source);
int graph_has_edge(Graph, int source, int sink);
void graph_foreach(Graph g, int source,
void (*f)(Graph g, int source, int sink, void *data),
void *data);
#endif
/* basic directed graph type */
/* the implementation uses adjacency lists
* represented as variable-length arrays */
/* these arrays may or may not be sorted: if one gets long enough
/* and you call graph_has_edge on its source, it will be */
struct graph {
int n; /* number of vertices */
int m; /* number of edges */
struct successors {
int d; /* number of successors */
int len; /* number of slots in array */
char is_sorted; /* true if list is already sorted */
int list[1];
/* actual list of successors */
} *alist[1];
};
/* create a new graph with n vertices labeled 0..n-1 and no edges */
Graph
graph_create(int n)
{
Graph g;
int i;
g = malloc(sizeof(struct graph) + sizeof(struct successors *) * (n-1));
assert(g);
g->n = n;
g->m = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
g->alist[i] = malloc(sizeof(struct successors));
assert(g->alist[i]);
g->alist[i]->d = 0;
g->alist[i]->len = 1;
g->alist[i]->is_sorted= 1;
}
return g;
}
/* free all space used by graph */
void
graph_destroy(Graph g)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < g->n; i++) free(g->alist[i]);
free(g);
}
/* add an edge to an existing graph */
void
graph_add_edge(Graph g, int u, int v)
{
assert(u >= 0);
assert(u < g->n);
assert(v >= 0);
assert(v < g->n);
/* do we need to grow the list? */
while(g->alist[u]->d >= g->alist[u]->len) {
g->alist[u]->len *= 2;
g->alist[u] =
realloc(g->alist[u],
sizeof(struct successors) + sizeof(int) * (g->alist[u]->len - 1));
}
/* now add the new sink */
g->alist[u]->list[g->alist[u]->d++] = v;
g->alist[u]->is_sorted = 0;
/* bump edge count */
g->m++;
}
/* return the number of vertices in the graph */
int
graph_vertex_count(Graph g)
{
return g->n;
}
/* return the number of vertices in the graph */
int
graph_edge_count(Graph g)
{
return g->m;
}
/* return the out-degree of a vertex */
int
graph_out_degree(Graph g, int source)
{
assert(source >= 0);
assert(source < g->n);
return g->alist[source]->d;
}
/* when we are willing to call bsearch */
#define BSEARCH_THRESHOLD (10)
static int
intcmp(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return *((const int *) a) - *((const int *) b);
}
/* return 1 if edge (source, sink) exists), 0 otherwise */
int
graph_has_edge(Graph g, int source, int sink)
{
int i;
assert(source >= 0);
assert(source < g->n);
assert(sink >= 0);
assert(sink < g->n);
if(graph_out_degree(g, source) >= BSEARCH_THRESHOLD) {
/* make sure it is sorted */
if(! g->alist[source]->is_sorted) {
qsort(g->alist[source]->list,
g->alist[source]->d,
sizeof(int),
intcmp);
}
/* call bsearch to do binary search for us */
return
bsearch(&sink,
g->alist[source]->list,
g->alist[source]->d,
sizeof(int),
intcmp)
!= 0;
} else {
/* just do a simple linear search */
/* we could call lfind for this, but why bother? */
for(i = 0; i < g->alist[source]->d; i++) {
if(g->alist[source]->list[i] == sink) return 1;
}
/* else */
return 0;
}
}
/* invoke f on all edges (u,v) with source u */
/* supplying data as final parameter to f */
void
graph_foreach(Graph g, int source,
void (*f)(Graph g, int source, int sink, void *data),
void *data)
{
int i;
assert(source >= 0);
assert(source < g->n);
for(i = 0; i < g->alist[source]->d; i++) {
f(g, source, g->alist[source]->list[i], data);
}
}
- 这段代码有动态分配的数组来存放邻接节点,这是一份PineWiki网站里面提供的一份图的表示的代码,实现的很优美吧?动态分配数组,长度可以扩展,既不浪费空间,又不会带来性能损失,它告诉我们鱼和熊掌也是可以兼得的。
5. 代码Git提交记录截图















