实验三进程调度实验
1. 目的和要求
实验目的
用高级语言完成一个进程调度程序,以加深对进程的概念及进程调度算法的理解。
实验要求
设计一个有 N(N不小于5)个进程并发执行的进程调度模拟程序。
进程调度算法:“时间片轮转法”调度算法对N个进程进行调度。
2. 实验内容
完成两个算法(简单时间片轮转法、多级反馈队列调度算法)的设计、编码和调试工作,完成实验报告。
1) 每个进程有一个进程控制块(PCB)表示。进程控制块包含如下信息:进程名、优先级、到达时间、需要运行时间、已用CPU时间、进程状态等等。
2) 每个进程的状态可以是就绪 r(ready)、运行R(Running)、或完成F(Finished)三种状态之一。
3) 就绪进程获得 CPU后都只能运行一个时间片。用已占用CPU时间加1来表示。
4) 如果运行一个时间片后,进程的已占用 CPU时间已达到所需要的运行时间,则撤消该进程,如果运行一个时间片后进程的已占用CPU时间还未达所需要的运行时间,也就是进程还需要继续运行,应把它插入就绪队列等待下一次调度。
5) 每进行一次调度,程序都打印一次运行进程、就绪队列中各个进程的 PCB,以便进行检查
3、源程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<time.h>
#include <iostream.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
typedef struct PCB
{
int ID;
int Priority;
int CPUTime;
int ALLTime;
int Status;
}PCB;
typedef PCB Dt;
typedef struct Node
{
Dt data;
struct Node *next;
}Node;
Node *head=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node *head1=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node *head2=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
int n;
void create(int n)
{
int i=1;
srand((int)time(0));
head->next=NULL;
Node *q=head;
cout<<" 优先数 优先级 CPUTime AllTime Status "<<endl;
while(i<=n)
{
Node *p=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->data.ID=i;
p->data.CPUTime=0;
p->data.Status=0;
p->data.Priority=rand()%10+1;
p->data.ALLTime=rand()%8+1;
cout<<" "<<p->data.ID<<" "<<p->data.Priority<<" "<<
p->data.CPUTime<<" "<<p->data.ALLTime<<" "<<p->data.Status<<endl;
p->next=NULL;
q->next=p;
q=q->next;
i++;
}
Node *p0=head1;
head1->next=NULL;
for(q=head->next;q!=NULL;q=q->next)
{
Node *r=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
r->data.ID=q->data.ID;
r->data.CPUTime=q->data.CPUTime;
r->data.Status=q->data.Status;
r->data.Priority=q->data.Priority;
r->data.ALLTime=q->data.ALLTime;
p0->next=r;
r->next=NULL;
p0=p0->next;
}
Node *p1=head2;
head2->next=NULL;
for(q=head->next;q!=NULL;q=q->next)
{
Node *k=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
k->data.ID=q->data.ID;
k->data.CPUTime=q->data.CPUTime;
k->data.Status=q->data.Status;
k->data.Priority=q->data.Priority;
k->data.ALLTime=q->data.ALLTime;
p1->next=k;
k->next=NULL;
p1=p1->next;
}
}
void FCFS()
{
Node *p=head->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<"执行进程"<<endl<<p->data.ID;
p=p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"所有进程都执行完成"<<endl;
}
void SJF()
{
Node *p;
Node *pmin;
while(head2->next!=NULL)
{
pmin=head2->next;
for(p=head2->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
if(pmin->data.ALLTime>p->data.ALLTime)
pmin=p;
}
cout<<"执行剩余区间长度最短的进程"<<endl<<pmin->data.ID;
for(p=head2;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
if(p->next==pmin)
{
p->next=p->next->next;
free(pmin);
}
}
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"所有进程都执行完成"<<endl;
}
void action(Node *p)
{
Node *q=head->next;
while(q!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data.ID<<"执行一个时间片的进程"<<endl;
if(q!=p)
q->data.Priority=q->data.Priority+1;
else
{
q->data.Priority=q->data.Priority-3;
if(q->data.ALLTime>4)
q->data.ALLTime-=4;
else
q->data.ALLTime=0;
q->data.Status=1;
}
q=q->next;
}
}
void SearchMaxPRI(int m)
{
Node *p=head->next;
Node *q=head->next;
Node *q0=head;
while(q!=NULL)
{
if(q->data.ALLTime==0)
{
cout<<q->data.ID<<"进程已执行完成"<<endl;
n--;
q0->next=q0->next->next;
free(q);
q=q0->next;
}
else
{
if(q->data.Priority>p->data.Priority)
p=q;
q0=q0->next;
q=q->next;
}
}
if(n>0)
action(p);
}
void RR(int m)
{
Node *p;
while(head1->next!=NULL)
{
p=head1->next;
Node *prep=head1;
Node *q;
while(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data.ID<<"执行进程一个时间片"<<endl;
for(q=head1;q->next!=NULL;q=q->next)
{
if(q->next==p)
{
p->data.ALLTime-=4;
p->data.CPUTime+=4;
}
}
if(p->data.ALLTime<=0)
{
cout<<p->data.ID<<"进程已执行完成"<<endl;
prep->next=prep->next->next;
free(p);
p=prep->next;
}
else
{
prep=prep->next;
p=p->next;
}
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"进入下一次轮转"<<endl;
}
cout<<"所有进程都执行完成"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
cout<<"请输入系统进程数:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
int m=n;
if(n==0)
cout<<"此时没有就绪进程"<<endl;
else
{
create(n);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"先来先服务调度"<<endl;
FCFS();
cout<<endl;
cout<<"短进程优先调度"<<endl;
SJF();
cout<<endl;
cout<<"动态优先级调度"<<endl;
while(head->next!=NULL)
{
SearchMaxPRI(m);
}
cout<<"所有进程都执行完成"<<endl;
cout<<endl;
cout<<"时间片轮转调度"<<endl;
RR(m);
}
}
4、程序运行结果
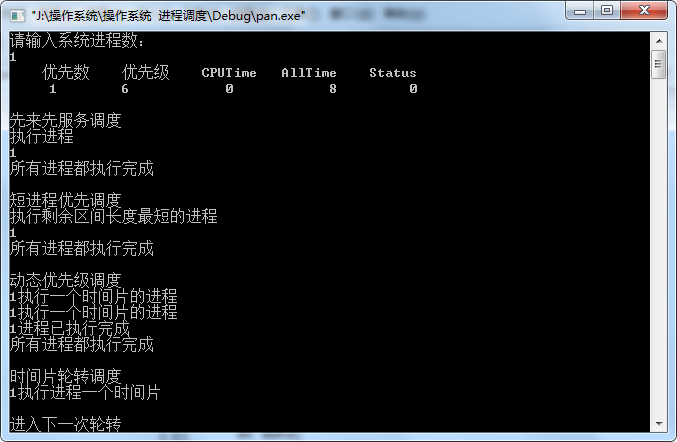
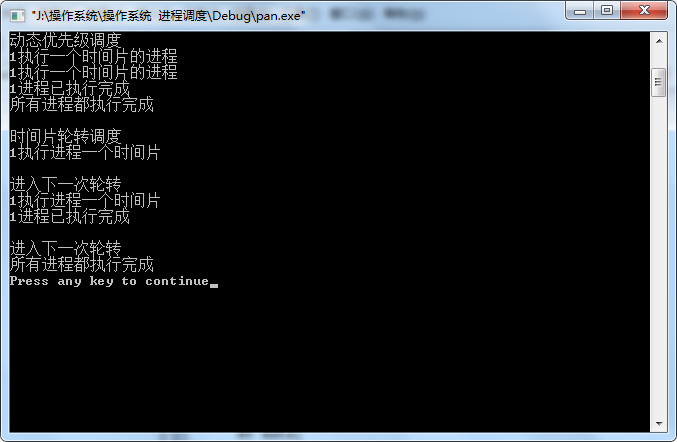


5、实验总结
对磁盘调度的四种算法——先来先服务算法,短进程优先调度算法,时间片轮转调度算法,动态优先级调度有了更深刻的理解和掌握,使我能够为进程调度选择适当的算法,提高CPU工作效率。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步