Django 中 app_name (应用命名空间) 和 namespace (实例命名空间) 的区别
转自:https://blog.51cto.com/jiajinh/2432449
补充理解:
先把官网上对应用命名空间(app_name)和实例命名空间(namespace)的解释贴上:
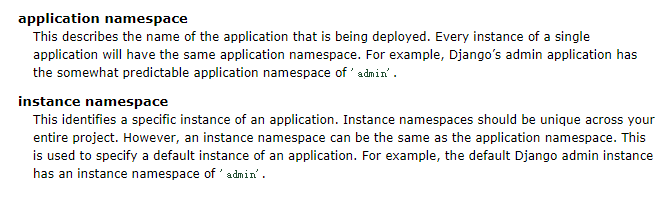
app_name(应用命名空间)通常在app.urls模块中指定,如:
app_name = "test" //应用命名空间 urlpatterns = [ path("article1/", views.test, name="url_a"), ]
namespace(实例命名空间)通常在ROOT_URLCONF模块(根url路由模块)中指定,如下面的:namespace="test1",namespace="test2",namespace="test3"
urlpatterns = [ //属于app_name = "test"应用命名空间的三个实例命名空间
re_path(r"^test_u1/", include("test_app.urls", namespace="test1")),
re_path(r"^test_u2/", include("test_app.urls", namespace="test2")),
re_path(r"^test_u3/", include("test_app.urls", namespace="test3")),
]
上面的urlpatterns列表中的三个url配置有不同的namespace(实例命名空间),但他们都路由到test_app.urls,且在test_app.urls中指定了app_name="test"(应用命名空间),此时,test就代表了指向了它的三个namespace之一,至于test具体代表哪个namespace,就要看当前应用(current application)是哪个,比如:
服务器收到来自 http://localhost:8000/test_u2/article1/的请求,该url匹配列表中的第二条,此时namespace="test2"的应用就称为当前应用(current application),这时候app_name="test"中的test就代表了这个当前应用对应的的实例命名空间,在模板标签{% url "test:url_a" %}中的test就代表了test2,等价于{% url "test2:url_a" %},从而反向解析出来的url为:/test_u2/article1/,如果有来自http://localhost:8000/test_u1/article1/的请求,那么namespace="test1"的应用就称为当前应用,test就代表了test1。总之,app_name可以代表许多实例命名空间,具体代表哪个,要看当前应用是哪个。
假设index.html中有模板标签{% url "test:url_a" %},而此时有来自http://localhost:8000/app01/index/ 的请求需要访问index.html,这个正在访问的url不属于上述三个namespace的任何一个,也就说是不存在当前应用,那么app_name就会默认指向urlpatterns中最后一个namespace即test3,那么index.html中的{% url "test:url_a" %}模板标签,就等价于{% url "test3:url_a" %}。如果namespace名和app_name一样,app_name就默认指向该namespace。




