数据结构07 二叉树
这篇文章开始总结 树和二叉树。
什么是树呢?
1、树的定义
(1)有且仅有一个特定的称为根(root) 的节点。
(2)当 n>1 时,其余节点可分为 m(m>0) 个互不相交的集合。其中每个集合本身又是一个棵树,并称为根的子树。
2、树的表示方法
最常见的是 树形表示法 和 广义表表示法,下面是树形表示法,如图所示。
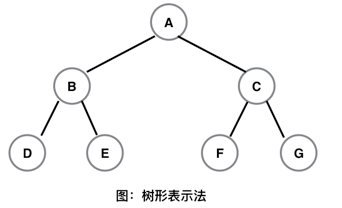
上图的 广义表表示法为:(A(B(D,E),C(F,G)))
3、常见的术语
(1)父节点,孩子节点,兄弟节点。以上图为例,A是B和C的父节点,B和C是A的孩子节点,B和C之间互为兄弟节点。
(2)节点的度和树的度。节点的度即节点有几个分支,比如节点A有两个分支B和C,那么节点A的度就是2,树的度即为一棵树中节点的最大度数,所以上图的树的度也是2。
(3)有序树和无序树。如果将树中节点的子树看成是从左至右依次有序且不能交换,则称该树为有序树,否则称为无序树。
(4)森林。在上图中,如果将根节点A拿掉,那么B子树和C子树合并就是森林了。
(5)二叉树。二叉树是一种特殊的树。它的每个节点最多只有两棵子树。
4、二叉树的常见性质
性质1:在二叉树的第 i 层上最多有 2i-1 个节点 (i>=1)
性质2:深度为 k 的二叉树最多有 2k-1 个节点 (k>=1)
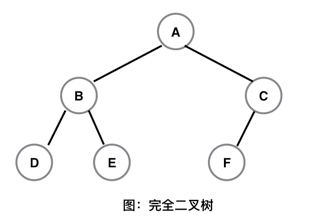
性质3:满二叉树:一棵深度为 k 且有 2k-1 个节点的二叉树称为 满二叉树。
完全二叉树:一棵深度为 k 的二叉树,其前 k-1 层是一棵满二叉树,而最下面一层(即第k层) 上的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置上。这样的二叉树称为 完全二叉树。
满二叉树一定是完全二叉树,但完全二叉树不一定是满二叉树。
下面是 满二叉树 和 完全二叉树 的图示:

5、二叉树的两种存储结构
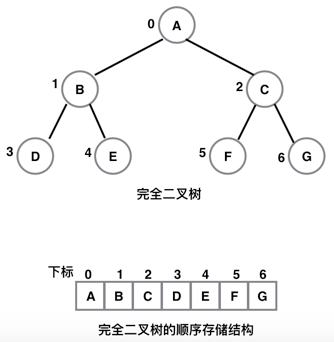
5-1:顺序存储
对于完全二叉树而言,可以使用顺序存储结构。但对于一般的二叉树而言,使用顺序存储结构会有两个缺点:一、如果不是完全二叉树,则必须将其转化为完全二叉树;二、增加了很多虚节点,浪费资源空间。
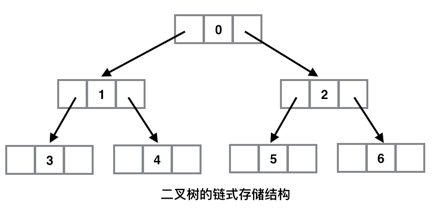
5-2:链式存储
链式存储是最常用的一种二叉树存储结构。每个节点设置三个域,分别是值域、左指针域和右指针域,用 data 表示值域,lchild 和 rchild 分别表示指向左子树、右子树的指针域。如下图:
6、二叉树的常见操作
6-1:插入节点
思路:首先找到要插入节点的父节点,然后确定插入到父节点的左边还是右边,最后将节点插入。
6-2:查找节点
思路:运用递归查找。
6-3:计算树的深度
思路:分别递归左子树和右子树,取长度较大的那一个作为整个树的深度。
6-4:遍历之 先序遍历
思路:先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,再遍历右子树
6-5:遍历之 中序遍历
思路:先遍历左子树,再访问根节点,最后遍历右子树
6-6:遍历之 后序遍历
思路:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后访问根节点
6-7:遍历之 按层遍历
思路:从上到下,从左到右遍历节点
7、二叉树的常见操作的代码实现
代码如下:
节点类Node.java
public class Node { public int data; // 数据域 public Node left; // 左孩子 public Node right; // 右孩子 }
BinTree.java
import java.util.Scanner; public class BinTree { // 按层遍历的存储空间长度 public static int length; /** * 生成根节点 */ public static Node createRoot() { Node root = new Node(); System.out.println("请输入根节点,以便生成树:"); root.data = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); System.out.println("根节点生成成功"); return root; } /** * 插入节点 * * @param root 二叉树的根节点 * @return 返回二叉树的根节点 * @throws Exception */ public static Node insert(Node root) throws Exception { while (true) { System.out.println("请输入待插入节点的数据:"); Node node = new Node(); node.data = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); // 获取父节点数据 System.out.println("请输入它(待插入节点) 的父节点:"); int parentNodeData = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); // 确定插入方向 System.out.println("请确定要插入到父节点的:1 左侧, 2 右侧"); int direction = new Scanner(System.in).nextInt(); // 插入节点 root = insertNode(root, node, parentNodeData, direction); if (root == null) { System.out.println("未找到父节点,请重新输入!"); continue; } System.out.println("插入成功,是否继续? 1继续,2退出"); if (new Scanner(System.in).nextInt() == 1) continue; else break; // 退出循环 } return root; } /** * 从insert()方法抽取出来的需要递归的部分 * * @param root 二叉树的根节点 * @param node 待插入节点 * @param parentNodeData 待插入节点的父节点 * @param direction 插入到左边还是右边 * @return 返回二叉树的根节点 * @throws Exception */ public static Node insertNode(Node root, Node node, int parentNodeData, int direction) throws Exception { if (root == null) return null; // 找到父节点 if (root.data == parentNodeData) { switch (direction) { case 1: if (root.left != null) throw new Exception("左节点已存在,不能插入!"); else root.left = node; break; case 2: if (root.right != null) throw new Exception("右节点已存在,不能插入!"); else root.right = node; break; } } // 向左子树查找父节点(递归) insertNode(root.left, node, parentNodeData, direction); // 向右子树查找父节点(递归) insertNode(root.right, node, parentNodeData, direction); return root; } /** * 查找节点 */ public static boolean getNode(Node root, int data) { if (root == null) return false; // 查找成功 if (root.data == data) return true; // 递归查找 boolean result1 = getNode(root.left, data); boolean result2 = getNode(root.right, data); return result1 || result2; } /** * 获取二叉树的深度 * 思路:分别递归左子树和右子树,取长度较大的那一个作为整个树的深度 * * @param root 二叉树的根节点 * @return */ public static int getLength(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; int leftLength, rightLength; // 递归左子树的深度 leftLength = getLength(root.left); // 递归右子树的深度 rightLength = getLength(root.right); if (leftLength > rightLength) return leftLength + 1; else return rightLength + 1; } /** * 先序遍历 * 思路:先访问根节点,然后遍历左子树,再遍历右子树 * * @param root 根节点 */ public static void DLR(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // 输出节点的值 System.out.print(root.data + " "); // 递归遍历左子树 DLR(root.left); // 递归遍历右子树 DLR(root.right); } /** * 中序遍历 * 思路:先遍历左子树,再访问根节点,最后遍历右子树 * * @param root 根节点 */ public static void LDR(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // 遍历左子树 LDR(root.left); // 输出节点的值 System.out.print(root.data + " "); // 遍历右子树 LDR(root.right); } /** * 后序遍历 * 思路:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后访问根节点 * * @param root 根节点 */ public static void LRD(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // 遍历左子树 LRD(root.left); // 遍历右子树 LRD(root.right); // 输出节点的值 System.out.print(root.data + " "); } /** * 按层遍历 * 思路:从上到下,从左到右遍历节点 * * @param root 根节点 */ public static void traversalLevel(Node root) { if (root == null) return; int head = 0; int tail = 0; // 申请保存空间 Node[] nodeList = new Node[length]; // 将当前二叉树保存到数组中 nodeList[tail] = root; // 计算tail的位置 tail = (tail + 1) % length; // 除留余数法 while (head != tail) { Node tempNode = nodeList[head]; // 计算head的位置 head = (head + 1) % length; // 输出节点的值 System.out.print(tempNode.data + " "); // 如果左子树不为空,则将左子树保存到数组的tail位置 if (tempNode.left != null) { nodeList[tail] = tempNode.left; // 重新计算tail的位置 tail = (tail + 1) % length; } // 如果右子树不为空,则将右子树保存到数组的tail位置 if (tempNode.right != null) { nodeList[tail] = tempNode.right; // 重新计算tail的位置 tail = (tail + 1) % length; } } } }
BinTreeTest.java
public class BinTreeTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { System.out.println("*******链式存储的二叉树*******"); // 创建根节点 Node root = BinTree.createRoot(); // 1、插入节点 System.out.println("********插入节点*******"); BinTree.insert(root); // 2、查找节点 System.out.print("查找data为2的节点是否存在:"); boolean result = BinTree.getNode(root, 2); System.out.println(result); // 3、获取二叉树的深度 System.out.println("当前二叉树的深度为:" + BinTree.getLength(root)); // 4、先序遍历 System.out.print("先序遍历:"); BinTree.DLR(root); System.out.println(""); // 5、中序遍历 System.out.print("中序遍历:"); BinTree.LDR(root); System.out.println(""); // 6、后序遍历 System.out.print("后序遍历:"); BinTree.LRD(root); System.out.println(""); // 7、按层遍历 System.out.print("按层遍历:"); BinTree.length = 100; BinTree.traversalLevel(root); System.out.println(""); } }
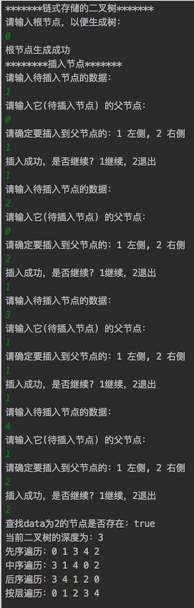
运行结果:
欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/nnngu/p/8308220.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号