算法07 五大查找之:索引查找
上一篇总结了二分查找,这一篇要总结的是索引查找。
关于索引,我们很容易地联想到数据库中的索引,建立了索引,可以大大提高数据库的查询速度。
索引查找又称为分块查找,是一种介于顺序查找和二分查找之间的一种查找方法,索引查找的基本思想是:首先查找索引表,可用二分查找或顺序查找,然后在确定的块中进行顺序查找。
在实现索引查找算法前需要弄清楚以下三个术语。
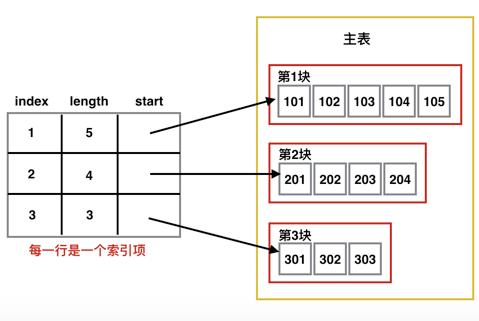
(1)主表。即要查找的序列。
(2)索引项。一般我们会将主表分成几个块,每个块建立一个索引,这个索引就叫索引项。
(3)索引表。即索引项的集合。
同时,索引项包括以下三点。
(1)index,即索引项在主表的关键字。
(2)start,即块内的第1个元素在主表中的位置。
(3)length,即块的长度。
索引查找的示意图
示意图如下:
索引查找的代码实现
代码:
IndexItem.java
public class IndexItem { public int index; public int start; public int length; public IndexItem(int index, int start, int length) { this.index = index; this.start = start; this.length = length; } public int getIndex() { return index; } public void setIndex(int index) { this.index = index; } public int getStart() { return start; } public void setStart(int start) { this.start = start; } public int getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(int length) { this.length = length; } }
IndexSearch.java
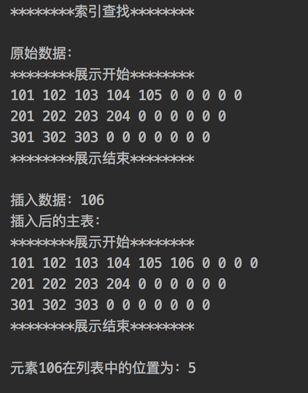
public class IndexSearch { // 主表 static int[] mainList = new int[]{ 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 201, 202, 203, 204, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 301, 302, 303, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // 索引表 static IndexItem[] indexItemList = new IndexItem[]{ new IndexItem(1, 0, 5), new IndexItem(2, 10, 4), new IndexItem(3, 20, 3) }; /** * 索引查找算法 * * @param key 给定值 * @return 返回给定值在表中的位置 */ public static int indexSearch(int key) { IndexItem item = null; // 建立索引规则 int index = key / 100; // ① 遍历索引表,找到对应的索引项 for (int i = 0; i < indexItemList.length; i++) { // 找到索引项 if (indexItemList[i].index == index) { item = indexItemList[i]; break; } } // 索引表中不存在该索引项 if (item == null) { return -1; } // ② 根据索引项,在主表中查找 for (int i = item.start; i < item.start + item.length; i++) { if (mainList[i] == key) { return i; } } return -1; } /** * 插入数据 * * @param key 要插入的值 * @return true表示插入成功,false表示插入失败 */ public static boolean insert(int key) { IndexItem item = null; // 建立索引规则 int index = key / 100; int i = 0; // 遍历索引表,找到对应的索引项 for (i = 0; i < indexItemList.length; i++) { if (indexItemList[i].index == index) { item = indexItemList[i]; break; } } // 索引表中不存在该索引项 if (item == null) { return false; } // 根据索引项将值插入到主表中 mainList[item.start + item.length] = key; // 更新索引表 indexItemList[i].length++; return true; } /** * 遍历打印 */ public static void display(int[] list) { System.out.println("********展示开始********"); if (list != null && list.length > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) { System.out.print(list[i] + " "); if ((i + 1) % 10 == 0) { System.out.println(""); } } } System.out.println("********展示结束********"); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("********索引查找********"); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("原始数据:"); display(mainList); System.out.println(""); int value = 106; System.out.println("插入数据:" + value); // 插入成功 if (insert(value)) { System.out.println("插入后的主表:"); display(mainList); System.out.println(""); System.out.println("元素" + value + "在列表中的位置为:" + indexSearch(value)); } } }
运行结果:
欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处
本文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/nnngu/p/8290367.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号