新版Azure Automation Account 浅析(二) --- 更新Powershell模块和创建Runbook
前篇我们讲了怎样创建一个自动化账户以及创建时候“Run As Account”选项背后的奥秘。这一篇针对在Azure自动化账户中使用Powershell Runbook的用户讲一下怎样更新powershell 模块。
更新Powershell模块
首先,我们需要先了解一下Azure Automation的系统架构。我们已经知道用户可以通过运行Runbook来实现自动化运维,Runbook运行则是在Azure Automation的沙盒里执行的,沙盒是一组由Azure管理的虚机资源, 我们可以把其当做是Azure的一个PaaS服务。Pass服务自然是需要提供可伸缩高可用多租客隔离的运行环境。显然,我们需要能够为Runbook的运行环境指定所需要的Powershell模块和版本。同时,我们还需要能够升级更新相关的powershell模块。
打开我们前面创建的azpoctest自动化账户,在左边菜单选择“共享的资源”-》“模块”。
非常好,用户可以添加自定义的模块“添加模块”,也可以升级已有模块版本“更新Azure模块”。用户还可以浏览powershell模块库来导入新模块。
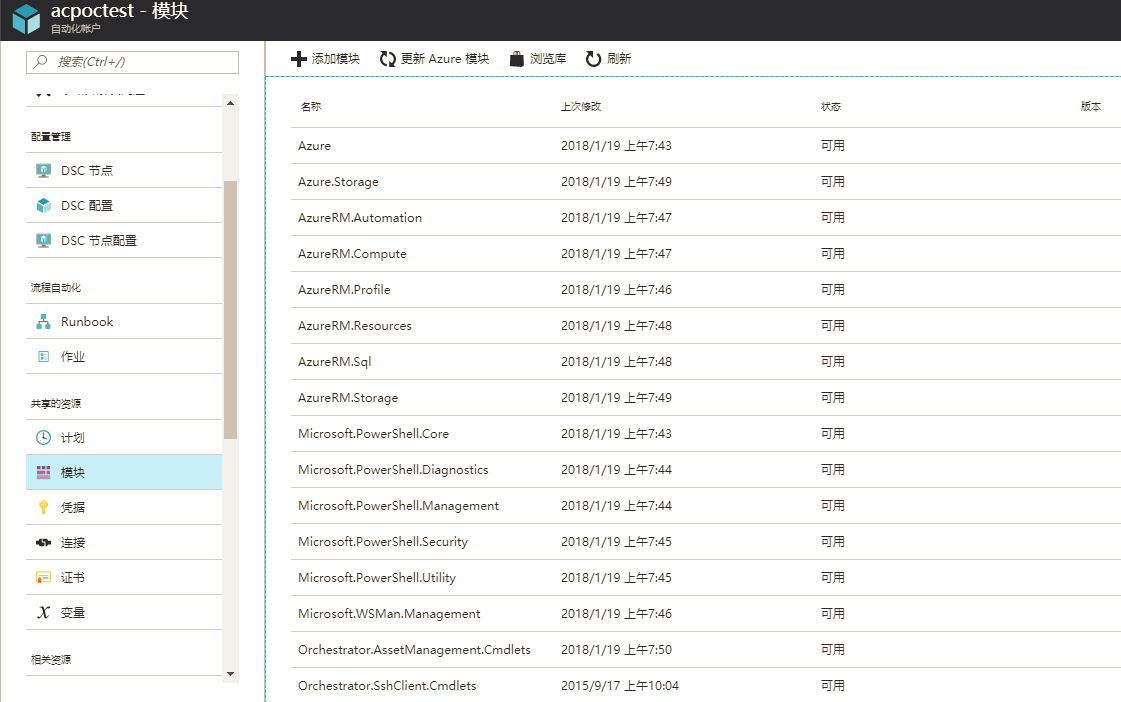
仔细研究一下这个页面,目测创建自动化账户时候自带的模块远少于目前Azure已经release的Powershell模块。如果需要运行Runbook来自动化运维Azure资源的话,目前这些模块是远远不够的。
记得光是ARM相关的powershell模块就有几十个,一个个导入的话工作量实在太大,那我们能不能像在powershell 命令行那样,用Install-Module和Import-Module两条命令就可以完成所有AzureRM
相关的模块安装呢?
点击“浏览库”,选择“AzureRM”,点击“导入”。“确定”按钮是灰色的,显然在Azure Portal中不支持有依赖关系的模块集中导入。

记得16年在Global做Automation Account的时候,毫无怨言地填坑,手动一个个把这些模块导入。今天我们换个填坑的法子
接下来我们会写一个Runbook,用脚本来导入AzureRM的Powershell模块
创建Runbook
在自动化账户左边菜单选取“流程自动化”-》“Runbook”-》“添加Runbook“ ,创建一个新的Runbook

创建成功后,浏览器会自动跳转到Runbook编辑器,我们可以开始写Powershell脚本了
首先,因为Runbook是运行在一个多租户的沙盒中,我们需要登录这个自动化账户所在的Azure订阅才能为这个自动化账户导入模块。
登录的代码可以reuse我们在上一篇提到的Runbook模板
$connectionName = "AzureRunAsConnection"
try
{
# Get the connection "AzureRunAsConnection "
$servicePrincipalConnection=Get-AutomationConnection -Name $connectionName
"Logging in to Azure..."
Add-AzureRmAccount `
-ServicePrincipal `
-TenantId $servicePrincipalConnection.TenantId `
-ApplicationId $servicePrincipalConnection.ApplicationId `
-CertificateThumbprint $servicePrincipalConnection.CertificateThumbprint `
-EnvironmentName AzureChinaCloud
}
catch {
if (!$servicePrincipalConnection)
{
$ErrorMessage = "Connection $connectionName not found."
throw $ErrorMessage
} else{
Write-Error -Message $_.Exception
throw $_.Exception
}
}
接下来,我们需要在Powershell Gallery里查找导入模块及其版本,如果存在,我们会先去找一个模块实际存储的Blob Storage地址,用New-AzureRmAutomationModule这条命令来导入
如果有Dependency的模块,脚本会首先去导入Dependency模块。下文脚本包含了资源组,自动化账户,模块(AzureRM)和模块版本(最新),考虑到模块和模块版本在不同时期可能有变化,这2部分其实可以做参数化,由Automation的variable来存储。那样脚本就不需要经常修改。
param( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [String] $ResourceGroupName, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [String] $AutomationAccountName, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [String] $ModuleName, [Parameter(Mandatory=$false)] [String] $ModuleVersion ) $ModulesImported = @() function _doImport { param( [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [String] $ResourceGroupName, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [String] $AutomationAccountName, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [String] $ModuleName, # if not specified latest version will be imported [Parameter(Mandatory=$false)] [String] $ModuleVersion ) $Url = "https://www.powershellgallery.com/api/v2/Search()?`$filter=IsLatestVersion&searchTerm=%27$ModuleName%27&targetFramework=%27%27&includePrerelease=false&`$skip=0&`$top=40" $SearchResult = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Get -Uri $Url -UseBasicParsing if($SearchResult.Length -and $SearchResult.Length -gt 1) { $SearchResult = $SearchResult | Where-Object -FilterScript { return $_.properties.title -eq $ModuleName } } if(!$SearchResult) { Write-Error "Could not find module '$ModuleName' on PowerShell Gallery." } else { $ModuleName = $SearchResult.properties.title # get correct casing for the module name $PackageDetails = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Get -UseBasicParsing -Uri $SearchResult.id if(!$ModuleVersion) { # get latest version $ModuleVersion = $PackageDetails.entry.properties.version } $ModuleContentUrl = "https://www.powershellgallery.com/api/v2/package/$ModuleName/$ModuleVersion" # Make sure module dependencies are imported $Dependencies = $PackageDetails.entry.properties.dependencies if($Dependencies -and $Dependencies.Length -gt 0) { $Dependencies = $Dependencies.Split("|") # parse depencencies, which are in the format: module1name:module1version:|module2name:module2version: $Dependencies | ForEach-Object { if($_ -and $_.Length -gt 0) { $Parts = $_.Split(":") $DependencyName = $Parts[0] $DependencyVersion = $Parts[1] # check if we already imported this dependency module during execution of this script if(!$ModulesImported.Contains($DependencyName)) { $AutomationModule = Get-AzureRmAutomationModule ` -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName ` -AutomationAccountName $AutomationAccountName ` -Name $DependencyName ` -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue # check if Automation account already contains this dependency module of the right version if((!$AutomationModule) -or $AutomationModule.Version -ne $DependencyVersion) { $DependencyVersion = $DependencyVersion.Split("[")[0].Split("]")[0] Write-Output "Importing dependency module $DependencyName of version $DependencyVersion first." # this dependency module has not been imported, import it first _doImport ` -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName ` -AutomationAccountName $AutomationAccountName ` -ModuleName $DependencyName ` -ModuleVersion $DependencyVersion $ModulesImported += $DependencyName } } } } } # Find the actual blob storage location of the module do { $ActualUrl = $ModuleContentUrl $ModuleContentUrl = (Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $ModuleContentUrl -MaximumRedirection 0 -UseBasicParsing -ErrorAction Ignore).Headers.Location } while(!$ModuleContentUrl.Contains(".nupkg")) $ActualUrl = $ModuleContentUrl Write-Output "Importing $ModuleName module of version $ModuleVersion from $ActualUrl to Automation" $AutomationModule = New-AzureRmAutomationModule ` -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName ` -AutomationAccountName $AutomationAccountName ` -Name $ModuleName ` -ContentLink $ActualUrl while( $AutomationModule.ProvisioningState -ne "Created" -and $AutomationModule.ProvisioningState -ne "Succeeded" -and $AutomationModule.ProvisioningState -ne "Failed" ) { Write-Verbose -Message "Polling for module import completion" Start-Sleep -Seconds 10 $AutomationModule = $AutomationModule | Get-AzureRmAutomationModule } if($AutomationModule.ProvisioningState -eq "Failed") { Write-Error "Importing $ModuleName module to Automation failed." } else { Write-Output "Importing $ModuleName module to Automation succeeded." } } } _doImport ` -ResourceGroupName "chdaiAC" ` -AutomationAccountName "acpoctest" ` -ModuleName "AzureRM" ` -ModuleVersion $ModuleVersion
编辑完成,点击保存。随后继续点击“测试窗格”。这个功能将测试我们刚完成的Runbook。
在输出窗口会看到后台沙盒运行脚本把AzureRM的dependency模块一个个被导入到自动化账户

最后导入AzureRM的时候运行会报错,这个没有关系。AzureRM模块本身不包含任何功能。所以ARM管理的Powershell命令都在AzureRM的Dependency 模块里。
现在回到模块列表,可以看到AzureRM相关模块已经全部导入了

现在万事具备,下一篇我们可以开始在日常工作中运用Azure自动化账户

