Day 29 _模块二 -hashlib_configparse_logging
一、hashlib
Python的hashlib提供了常见的摘要算法,如MD5,SHA1等等。
什么是摘要算法呢?摘要算法又称哈希算法、散列算法。它通过一个函数,把任意长度的数据转换为一个长度固定的数据串(通常用16进制的字符串表示)。
摘要算法就是通过摘要函数f()对任意长度的数据data计算出固定长度的摘要digest,目的是为了发现原始数据是否被人篡改过。
摘要算法之所以能指出数据是否被篡改过,就是因为摘要函数是一个单向函数,计算f(data)很容易,但通过digest反推data却非常困难。而且,对原始数据做一个bit的修改,都会导致计算出的摘要完全不同。
我们以常见的摘要算法MD5为例,计算出一个字符串的MD5值:
import hashlib md5_obj =hashlib.md5() #md5算法的对象 res = md5_obj.hexdigest() #获取摘要之后的结果 print(res,type(res)) # 输出结果: # d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e <class 'str'>
user =input('user>>>') passwd = input('password>>>') md5_obj=hashlib.md5() md5_obj.update(passwd.encode('utf-8')) passwd =md5.obj.hexdigest() if user =='alex' and passwd =='aee949757a2e698417463d47acac93df': print('登录成功!')
md5_obj =hashlib.sha1()#实例化 #md5算法的对象 md5_obj.update(b'alex3714')#使用sha1 摘要算法对‘alex3714进行摘要’ res = md5_obj.hexdigest()#获取摘要后的结果 print(res,type(res)) # 输出结果为:8a003668a9c990f15148f9e4046e1410781533b6 <class 'str'> #相同的字符串使用相同的算法, 在任何时候 #等等的结果都是一致的.
一.1 加盐操作
#全世界的md5算法都是一样的. # 全世界的md5算法都是一样的 # 123456 111111 md5_obj = hashlib.md5() # md5算法的对象 md5_obj.update(b'123456') # 使用md5摘要算法对'alex3714'进行摘要 res = md5_obj.hexdigest() # 获取摘要之后的结果 print(res,type(res)) #aee949757a2e698417463d47acac93df 32位 # 123456 e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e # 撞库 #加盐 md5_obj = hashlib.md5('盐'.encode('utf-8')) #md5算法的对象 md5_obj.update(b'alex3714')#使用md5 摘要算法对‘alex3714’进行摘要 res = md5_obj.hexdigest() #获取摘要后的结果 print(res,type(res)) # 打印结果 :0e249b9c16ea1d840ce700587cada978 <class 'str'>
动态加盐
username ='alex' md5_obj = hashlib.md5(username.encode('utf-8')+'盐'.encode('utf-8')) md5_obj.update(b'alex3714') res =md5_obj.hexdigest() print(res) # 打印结果 :a106943dd5c1d5caf59bc80c05295ad6
校验文件一致性
#校验文件一致性 with open('userinfo','rb') as f : md5_obj =hashlib.md5() md5_obj.update(f.read()) res = md5_obj.hexdigest() print(res) #结果:84b2fe284833ac7903a7ac865e6c27a9 with open('userinfo','rb')as f: md5_obj =hashlib.md5() for line in f: md5_obj.update(line) #update 操作可以在hexdigest之前执行多次 #分次对一个长字符串进行摘要 res = md5_obj.hexdigest() #结果是对一个厂字符串摘要的摘要结果. print(res) # 输出结果 :84b2fe284833ac7903a7ac865e6c27a9
拼接校验
# md5_obj = hashlib.md5() # md5_obj.update(b'aaabbb') # res = md5_obj.hexdigest() # print(res) #6547436690a26a399603a7096e876a2d # # md5_obj = hashlib.md5() # md5_obj.update(b'aa') # md5_obj.update(b'abbb') # res = md5_obj.hexdigest() # print(res) #6547436690a26a399603a7096e876a2d
二、configparse
该模块适用于配置文件的格式与windows ini文件类似,可以包含一个或多个节(section),每个节可以有多个参数(键=值)。
# .py 里面的所有值 都不需要进行转换或者处理 直接当做变量使用 #通用性不高 # 文本格式 key = value # 都要进行文件处理 _ 通用 # ini # [北京校区] # section # 课程 = python,linux # option # python讲师 = egon,yuanhao,nezha,boss_gold # linux讲师 = 李导,何首乌 # [上海校区] # 课程 = go,linux # python讲师 = egon # linux讲师 = 李导,何首乌
import configparser config =configparser.ConfigParser() #confi 是一个操作配置文件的对象 config['DEFAULT'] ={'ServerAliveInterval': '45', 'Compression':'yes', 'CompressionLevel':'9', 'ForwardX11':'yes' } config['bitbucket.org'] = {'User':'hg'} config['topsecret.server.com'] ={'Host Port': '50022', 'ForwardX11':'no' } with open('example.ini','w')as configfile: config.write(configfile)
结果为
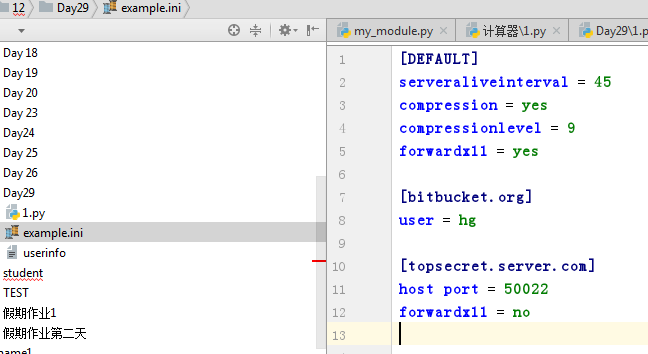
configparese的操作方法
import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read(('example.ini')) print(config.sections()) # 打印结果 ['bitbucket.org', 'topsecret.server.com'] print('bytebong.com' in config) #打印结果 False print('bitbucket.org' in config) #打印结果 True print( config[ 'DEFAULT']['Compression']) #获取 setion里 option的值 yes print(config['topsecret.server.com']['ForwardX11'])#获取 setion里option的值NO print(config['bitbucket.org'])#<Section: bitbucket.org> for key in config['bitbucket.org']: print(key) # 注意, 有default 会默认default的键 # user # serveraliveinterval # compression # compressionlevel # forwardx11 print(config.options('bitbucket.org')) #打印结果 ['user', 'serveraliveinterval', 'compression', 'compressionlevel', 'forwardx11'] #同for循环,找到‘bitbucket.org'下所有键. print(config.items('bitbucket.org')) #找到 ’bitbucket.org'下所有键值对 # [('serveraliveinterval', '45'), ('compression', 'yes'), ('compressionlevel', '9'), ('forwardx11', 'yes'), ('user', 'hg')] print(config.get('bitbucket.org','compression')) #结果 yes # get方法section下的key对应的value
增删改查
# 增删改操作 import configparser config = configparser.ConfigParser() config.read('example.ini') config.add_section('yuan') config.remove_option('topsecret.server.com','forwardx11') config.set('topsecret.server.com','k1','11111') config.set('yuan','k2','222222') config.write(open('new2.ini','w'))
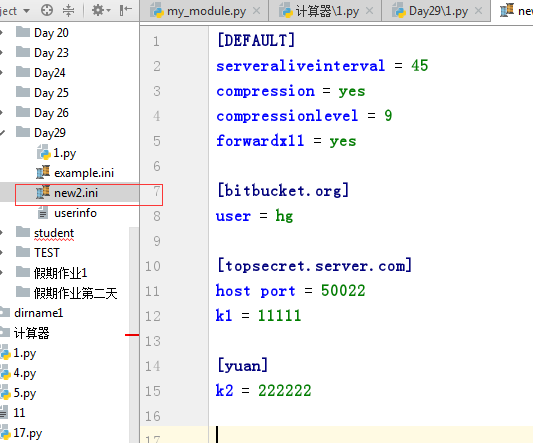
三 、logging
操作日志的模块
什么叫日志
#给用户看的
用户的重要行为
登录 涉及隐私
账单 资金
#给开发和运维和测试人员看的
自测 logging.debug(‘一些中间结果’)
测试 1+++++1
运维
#记录
打印在屏幕上
写入文件里
#logging 的优势
格式更加规范
等级更加鲜明
3.1 简单的配置方法
import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.ERROR, format='%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s', datefmt ='%a , %d %b %Y %H %M : %S', filename ='test.log', filemode ='a') logging.debug('debug message')#调试 logging.info('info message')#信息 logging.warning("warning message")#警告 logging.error('error message') #错误 logging.critical('critical message') #严重错误
结果
Wed, 14 Mar 2018 17:18:17 1.py[line:23] ERROR error message Wed, 14 Mar 2018 17:18:17 1.py[line:24] CRITICAL critical message Wed , 14 Mar 2018 17 20 : 22 1.py[line:10] ERROR error message Wed , 14 Mar 2018 17 20 : 22 1.py[line:11] CRITICAL critical message Wed , 14 Mar 2018 17 20 : 22 1.py[line:23] ERROR error message Wed , 14 Mar 2018 17 20 : 22 1.py[line:24] CRITICAL critical message
#使用logger对象的用法 import logging #首先创造一个logger对象 logger =logging.getLogger() #创建一个格式. fmt =logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s') #创建一个 文件句柄 控制向那个文件中输出什么格式. fh =logging.FileHandler('test3.log',encoding='utf-8') fh.setFormatter(fmt) #创建一个屏幕句柄 控制向屏幕输出 用什么格式 sh =logging.StreamHandler() sh.setFormatter(fmt) #将logger对象和文件句柄,屏幕句柄绑在一起. logger.addHandler(fh) logger.addHandler(sh) logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)#首先必须要整体对logger进行设置 sh.setLevel(logging.INFO) fh.setLevel(logging.WARNING) logger.debug('logger debug message') logger.info('logger info message') logger.warning('logger warning message') logger.error('logger error message') logger.critical('logger critical message')
输出结果
2018-03-14 18:47:13,752 - root - INFO - logger info message 2018-03-14 18:47:13,752 - root - WARNING - logger warning message 2018-03-14 18:47:13,752 - root - ERROR - logger error message 2018-03-14 18:47:13,752 - root - CRITICAL - logger critical message


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号