Android中数据的保存
1. 概述
在Android中有以下几种保存数据方式:
1). 使用sharedPreference去保存:只有应用程序自己可以访问
2). 保存在应用程序私有的文件夹下:只有应用程序自己可以访问
3). 使用File形式保存在file/cache目录下
4). 保存到公共的sd卡上:其他的应用程序也可以访问
5). 使用数据库去保存(MySQL)
其中1.2.3的共性都是保存在当前应用的目录下的私有数据
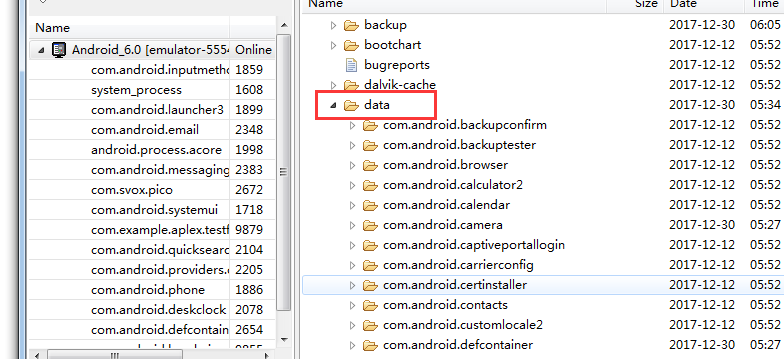
2. 方法一:File方式保存
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); try{ File f = new File("/data/data/com.example.aplex.testforgit/test.txt"); BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f)) ; writer.write("hahahehe"); writer.close(); }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } }
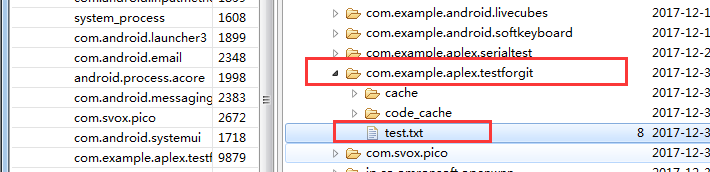
3. 方法二:File方式保存(data/cache目录下)
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
try{
//1. 保存在应用的cache中
{
File f = new File(getCacheDir(),"cache.txt");
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f)) ;
writer.write("hahahehe");
writer.close();
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//2. 保存在应用的file中
try {
File f = new File(getFilesDir(),"file.txt");
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f)) ;
writer.write("hahahehe");
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
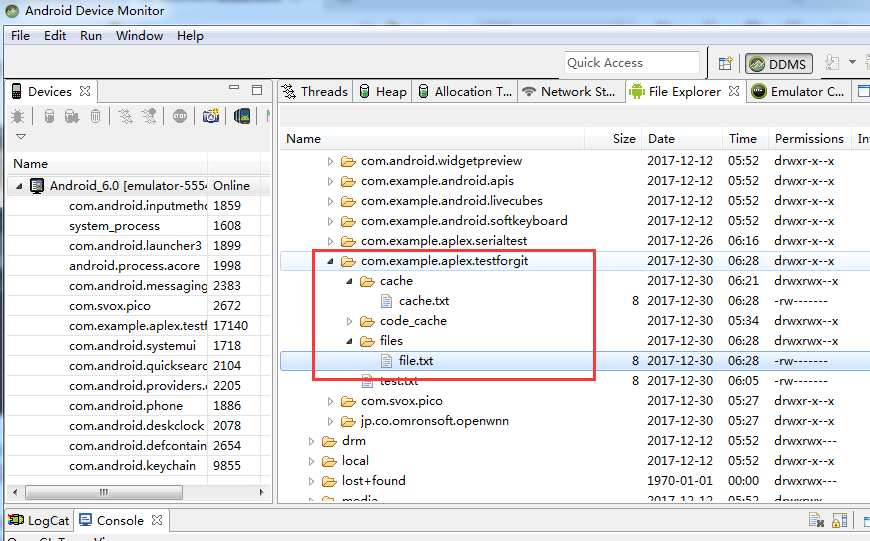
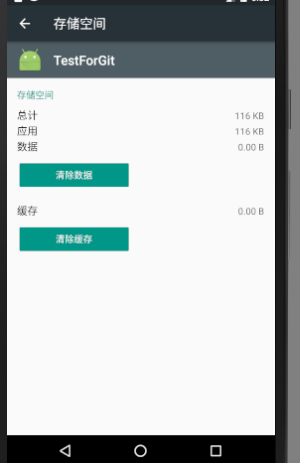
注意:清除数据会把data目录下改应用的所有数据都清除掉,而清除缓存则只会清除cache目录下的数据
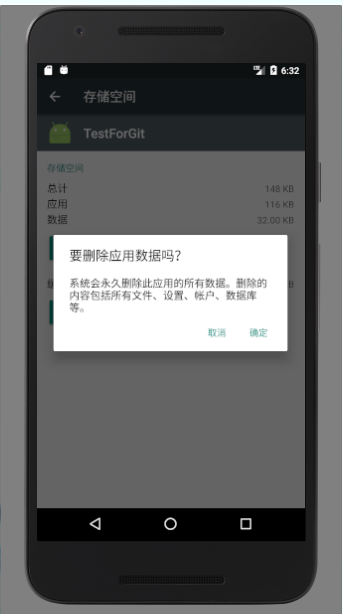
4. 方法三:使用sharedPreference去保存
Xml 文件可以用来保存数据
注意: 使用sharedPreferences保存数据时, 生成的xml 文件是
在 /data/data/包名/shared_prefs 目录下.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.example.aplex_new1.myapplication.MainActivity"> <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="请输入账号" android:inputType="number" android:id="@+id/ed"/> <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="清输入密码:" android:inputType="numberPassword" android:id="@+id/ed2"/> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="确认" android:id="@+id/bt" /> </LinearLayout>
package com.example.aplex_new1.myapplication; import android.content.SharedPreferences; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { Button bt1; EditText accountView; EditText pwdView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); bt1 = findViewById(R.id.bt); accountView = findViewById(R.id.ed); pwdView = findViewById(R.id.ed2); //获取到mydata.xml对象,没有则会创建一个 SharedPreferences sp = getSharedPreferences("mydata", 0); //拿到编辑器 SharedPreferences.Editor ed = sp.edit(); //获取出mydata.xml中键值为account的数据 String account = sp.getString("account", ""); //获取出mydata.xml中键值为pwd的数据 String pwd = sp.getString("pwd",""); //显示出来 accountView.setText(account); pwdView.setText(pwd); bt1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View view) { SharedPreferences sp = getSharedPreferences("mydata", 0); SharedPreferences.Editor ed = sp.edit(); String account = accountView.getText().toString(); String pwd = pwdView.getText().toString(); //放入数据中 ed.putString("account", account); ed.putString("pwd", pwd); //提交 ed.apply(); } }); } }
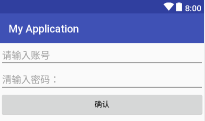
现象:第一次点击应用
账号密码都为空
在输入完账号密码后,退出,再次点击,则会回显出来
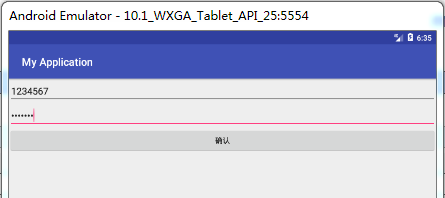
因为数据已经保存进了XML文件中去了
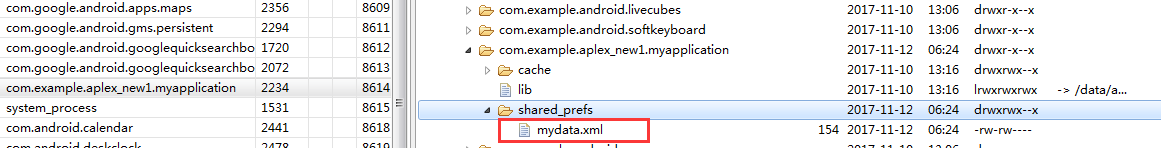
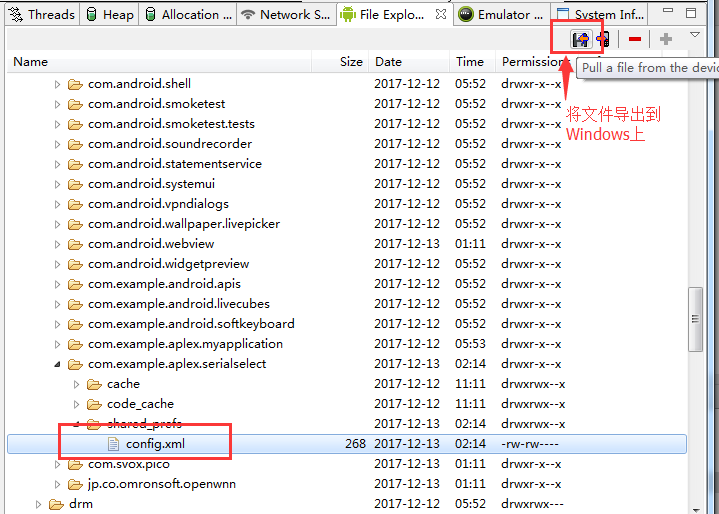
打开mydata.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8' standalone='yes' ?> <map> <string name="account">1234567</string> <string name="pwd">1234567</string> </map>
4. 方法四:保存到公共的sd卡上:
1. 概念和代码
AndroidManifest.xml
<!-- 在SDCard中创建与删除文件权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS" />
<!-- 往SDCard写入数据权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name=".MainActivity"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application>
SDFileHelper.java
public class SDFileHelper { String TAG = "SDFileHelper"; private Context context; public SDFileHelper() { } public SDFileHelper(Context context) { super(); this.context = context; } //往SD卡写入文件的方法 public void savaFileToSD(String filename, String filecontent) throws Exception { //如果手机已插入sd卡,且app具有读写sd卡的权限 if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) { filename = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + "/" + filename; Log.d(TAG,"文件名:"+filename); //这里就不要用openFileOutput了,那个是往手机内存中写数据的 FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(filename); output.write(filecontent.getBytes()); //将String字符串以字节流的形式写入到输出流中 output.close(); //关闭输出流 } else Toast.makeText(context, "SD卡不存在或者不可读写", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } //读取SD卡中文件的方法 //定义读取文件的方法: public String readFromSD(String filename) throws IOException { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(""); if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) { filename = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + "/" + filename; //打开文件输入流 FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(filename); byte[] temp = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; //读取文件内容: while ((len = input.read(temp)) > 0) { sb.append(new String(temp, 0, len)); } //关闭输入流 input.close(); } return sb.toString(); } }
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{ private EditText editname; private EditText editdetail; private Button btnsave; private Button btnclean; private Button btnread; private Context mContext; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); mContext = getApplicationContext(); bindViews(); } private void bindViews() { editname = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edittitle); editdetail = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editdetail); btnsave = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnsave); btnclean = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnclean); btnread = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnread); btnsave.setOnClickListener(this); btnclean.setOnClickListener(this); btnread.setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View v) { switch (v.getId()){ case R.id.btnclean: editdetail.setText(""); editname.setText(""); break; case R.id.btnsave: String filename = editname.getText().toString(); String filedetail = editdetail.getText().toString(); SDFileHelper sdHelper = new SDFileHelper(mContext); try { sdHelper.savaFileToSD(filename, filedetail); Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "数据写入成功", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "数据写入失败", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } break; case R.id.btnread: String detail = ""; SDFileHelper sdHelper2 = new SDFileHelper(mContext); try { String filename2 = editname.getText().toString(); detail = sdHelper2.readFromSD(filename2); } catch(IOException e){e.printStackTrace();} Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), detail, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; } } }
2. 6.0上SD卡的权限和动态申请权限的问题(重点!!)
Android6.0之后系统对权限的管理更加严格了,不但要在AndroidManifest中添加,还要在应用运行的时候动态申请。下面是动态申请SD卡读写的权限
1. 在AndroidManifest中添加SD卡读写的权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
2. 申请权限
申请权限有两种方式:
1). 手动打开权限:
Settings-->Apps-->找到所需要的应用-->Permissions-->打开权限
2). 在程序中动态申请权限(重点):
private static final int REQUEST_EXTERNAL_STORAGE = 1; private static String[] PERMISSIONS_STORAGE = { "android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE", "android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" }; public static void verifyStoragePermissions(Activity activity) { try { //检测是否有写的权限 int permission = ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(activity, "android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"); if (permission != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { // 没有写的权限,去申请写的权限,会弹出对话框 ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(activity, PERMISSIONS_STORAGE,REQUEST_EXTERNAL_STORAGE); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
5. 方法五:使用数据库(MySQL)去保存



