LINQ体验(17)——LINQ to SQL语句之动态查询
2008-03-25 22:47 李永京 阅读(42016) 评论(46) 编辑 收藏 举报高级特性
本文介绍LINQ的高级特性,其包括大家都关心的动态查询的用法,另外简单提下ID标识这个知识。
动态查询
有这样一个场景:应用程序可能会提供一个用户界面,用户可以使用该用户界面指定一个或多个谓词来筛选数据。这种情况在编译时不知道查询的细节,动态查询将十分有用。
在LINQ中,Lambda表达式是许多标准查询运算符的基础,编译器创建lambda表达式以捕获基础查询方法(例如 Where、Select、Order By、Take While 以及其他方法)中定义的计算。表达式目录树用于针对数据源的结构化查询,这些数据源实现IQueryable<T>。例如,LINQ to SQL 提供程序实现 IQueryable<T>接口,用于查询关系数据存储。C#和Visual Basic编译器会针对此类数据源的查询编译为代码,该代码在运行时将生成一个表达式目录树。然后,查询提供程序可以遍历表达式目录树数据结构,并将其转换为适合于数据源的查询语言。
表达式目录树在LINQ中用于表示分配给类型为Expression<TDelegate>的变量的Lambda表达式。还可用于创建动态LINQ查询。
System.Linq.Expressions命名空间提供用于手动生成表达式目录树的API。Expression类包含创建特定类型的表达式目录树节点的静态工厂方法,例如,ParameterExpression(表示一个已命名的参数表达式)或 MethodCallExpression(表示一个方法调用)。编译器生成的表达式目录树的根始终在类型Expression<TDelegate>的节点中,其中TDelegate是包含至多五个输入参数的任何TDelegate委托;也就是说,其根节点是表示一个lambda表达式。
下面几个例子描述如何使用表达式目录树来创建动态LINQ查询。
1.Select
下面例子说明如何使用表达式树依据 IQueryable 数据源构造一个动态查询,查询出每个顾客的ContactName,并用GetCommand方法获取其生成SQL语句。
//依据IQueryable数据源构造一个查询 IQueryable<Customer> custs = db.Customers; //组建一个表达式树来创建一个参数 ParameterExpression param = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Customer), "c"); //组建表达式树:c.ContactName Expression selector = Expression.Property(param, typeof(Customer).GetProperty("ContactName")); Expression pred = Expression.Lambda(selector, param); //组建表达式树:Select(c=>c.ContactName) Expression expr = Expression.Call(typeof(Queryable), "Select", new Type[] { typeof(Customer), typeof(string) }, Expression.Constant(custs), pred); //使用表达式树来生成动态查询 IQueryable<string> query = db.Customers.AsQueryable() .Provider.CreateQuery<string>(expr); //使用GetCommand方法获取SQL语句 System.Data.Common.DbCommand cmd = db.GetCommand(query); Console.WriteLine(cmd.CommandText);
生成的SQL语句为:
SELECT [t0].[ContactName] FROM [dbo].[Customers] AS [t0]
2.Where
下面一个例子是“搭建”Where用法来动态查询城市在伦敦的顾客。
IQueryable<Customer> custs = db.Customers; //创建一个参数c ParameterExpression param = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Customer), "c"); //c.City=="London" Expression left = Expression.Property(param, typeof(Customer).GetProperty("City")); Expression right = Expression.Constant("London"); Expression filter = Expression.Equal(left, right); Expression pred = Expression.Lambda(filter, param); //Where(c=>c.City=="London") Expression expr = Expression.Call(typeof(Queryable), "Where", new Type[] { typeof(Customer) }, Expression.Constant(custs), pred); //生成动态查询 IQueryable<Customer> query = db.Customers.AsQueryable() .Provider.CreateQuery<Customer>(expr);
生成的SQL语句为:
SELECT [t0].[CustomerID], [t0].[CompanyName], [t0].[ContactName], [t0].[ContactTitle], [t0].[Address], [t0].[City], [t0].[Region], [t0].[PostalCode], [t0].[Country], [t0].[Phone], [t0].[Fax] FROM [dbo].[Customers] AS [t0] WHERE [t0].[City] = @p0 -- @p0: Input NVarChar (Size = 6; Prec = 0; Scale = 0) [London]
3.OrderBy
本例既实现排序功能又实现了过滤功能。
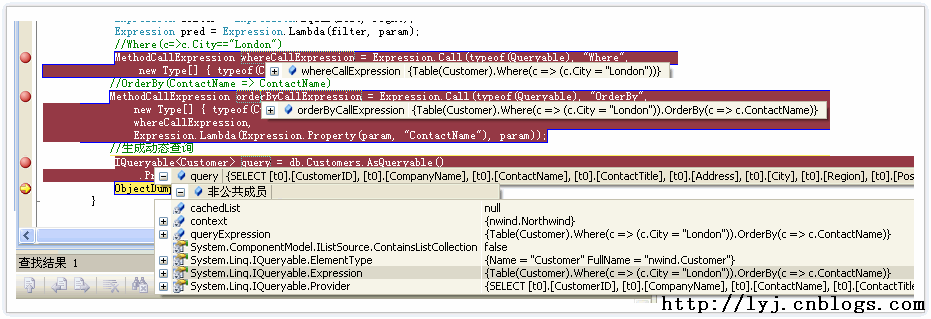
IQueryable<Customer> custs = db.Customers; //创建一个参数c ParameterExpression param = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Customer), "c"); //c.City=="London" Expression left = Expression.Property(param, typeof(Customer).GetProperty("City")); Expression right = Expression.Constant("London"); Expression filter = Expression.Equal(left, right); Expression pred = Expression.Lambda(filter, param); //Where(c=>c.City=="London") MethodCallExpression whereCallExpression = Expression.Call( typeof(Queryable), "Where", new Type[] { typeof(Customer) }, Expression.Constant(custs), pred); //OrderBy(ContactName => ContactName) MethodCallExpression orderByCallExpression = Expression.Call( typeof(Queryable), "OrderBy", new Type[] { typeof(Customer), typeof(string) }, whereCallExpression, Expression.Lambda(Expression.Property (param, "ContactName"), param)); //生成动态查询 IQueryable<Customer> query = db.Customers.AsQueryable() .Provider.CreateQuery<Customer>(orderByCallExpression);
下面一张截图显示了怎么动态生成动态查询的过程
生成的SQL语句为:
SELECT [t0].[CustomerID], [t0].[CompanyName], [t0].[ContactName], [t0].[ContactTitle], [t0].[Address], [t0].[City], [t0].[Region], [t0].[PostalCode], [t0].[Country], [t0].[Phone], [t0].[Fax] FROM [dbo].[Customers] AS [t0] WHERE [t0].[City] = @p0 ORDER BY [t0].[ContactName] -- @p0: Input NVarChar (Size = 6; Prec = 0; Scale = 0) [London]
4.Union
下面的例子使用表达式树动态查询顾客和雇员同在的城市。
//e.City IQueryable<Customer> custs = db.Customers; ParameterExpression param1 = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Customer), "e"); Expression left1 = Expression.Property(param1, typeof(Customer).GetProperty("City")); Expression pred1 = Expression.Lambda(left1, param1); //c.City IQueryable<Employee> employees = db.Employees; ParameterExpression param2 = Expression.Parameter(typeof(Employee), "c"); Expression left2 = Expression.Property(param2, typeof(Employee).GetProperty("City")); Expression pred2 = Expression.Lambda(left2, param2); //Select(e=>e.City) Expression expr1 = Expression.Call(typeof(Queryable), "Select", new Type[] { typeof(Customer), typeof(string) }, Expression.Constant(custs), pred1); //Select(c=>c.City) Expression expr2 = Expression.Call(typeof(Queryable), "Select", new Type[] { typeof(Employee), typeof(string) }, Expression.Constant(employees), pred2); //生成动态查询 IQueryable<string> q1 = db.Customers.AsQueryable() .Provider.CreateQuery<string>(expr1); IQueryable<string> q2 = db.Employees.AsQueryable() .Provider.CreateQuery<string>(expr2); //并集 var q3 = q1.Union(q2);
生成的SQL语句为:
SELECT [t2].[City] FROM ( SELECT [t0].[City] FROM [dbo].[Customers] AS [t0] UNION SELECT [t1].[City] FROM [dbo].[Employees] AS [t1] ) AS [t2]
ID标识
在前面这一点没有说到,在这里作为高级特性单独说下ID标识。
这个例子说明我们存储一条新的记录时候,ContactID作为主键标识,系统自动分配,标识种子为1,所以每次自动加一。
//ContactID是主键ID,插入一条数据,系统自动分配ID Contact con = new Contact() { CompanyName = "New Era", Phone = "(123)-456-7890" }; db.Contacts.InsertOnSubmit(con); db.SubmitChanges();
本系列链接:LINQ体验系列文章导航
LINQ推荐资源
LINQ专题:http://kb.cnblogs.com/zt/linq/
关于LINQ方方面面的入门、进阶、深入的文章。
LINQ小组:http://space.cnblogs.com/group/linq/
学习中遇到什么问题或者疑问提问的好地方。