ORB-SLAM(三)地图初始化
单目SLAM地图初始化的目标是构建初始的三维点云。由于不能仅仅从单帧得到深度信息,因此需要从图像序列中选取两帧以上的图像,估计摄像机姿态并重建出初始的三维点云。
ORB-SLAM中提到,地图初始化常见的方法有三种。
方法一
追踪一个已知物体。单帧图像的每一个点都对应于空间的一条射线。通过不同角度不同位置扫描同一个物体,期望能够将三维点的不确定性缩小到可接受的范围。
方法二
基于假设空间存在一个平面物体,选取两帧不同位置的图像,通过计算Homography来估计位姿。这类方法在视差较小或者平面上的点靠近某个主点时效果不好。
参考文献Faugeras et al, Motion and structure from motion in a piecewise planar environment. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 1988.
方法三
根据两帧之间的特征点匹配计算Fundamental matrix,进一步估计位姿。这种方法要求存在不共面的特征点。
参考文献Hartley, Richard, and Andrew Zisserman. Multiple view geometry in computer vision. Cambridge university press, 2003.
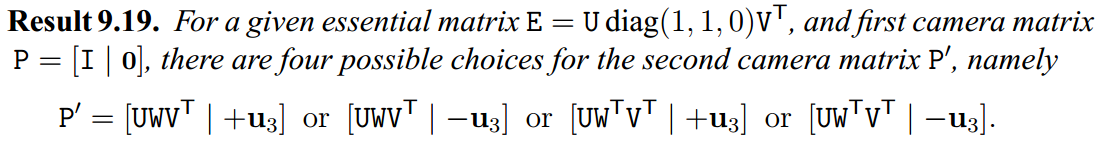
ORB-SLAM的作者提出了一种基于统计的模型选择方法。该方法优先选择第三种方法,并期望在场景退化情形下自动选择第二种方法。如果选取的两帧不满足要求,放弃这两帧并重新初始化。
第一步
提取特征点并匹配,若匹配点足够多,尝试第二步。
第二步
利用匹配的特征点分别计算方法二和方法三。
对每个模型,首先归一化所有的特征点。然后,在每步迭代中,
1. 根据特征点对计算homography或者fundamental matrix。Homography的计算方法为normalized DLT,fundamental matrix的计算方法为normalized 8 points。
2. 计算每个点对的symmetric transfer errors,和卡方分布的对应值比较,由此判定该点是否为内点。累计内点的总得分。
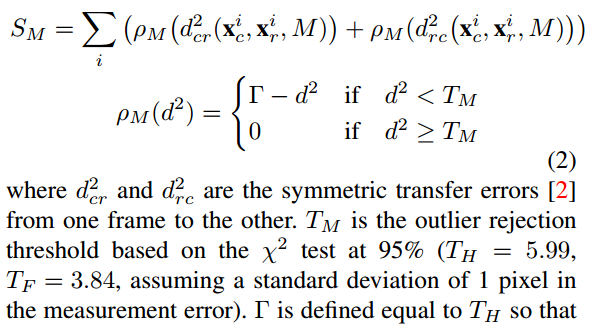
模型选择方法参考4.7.1 RANSAC in Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision。
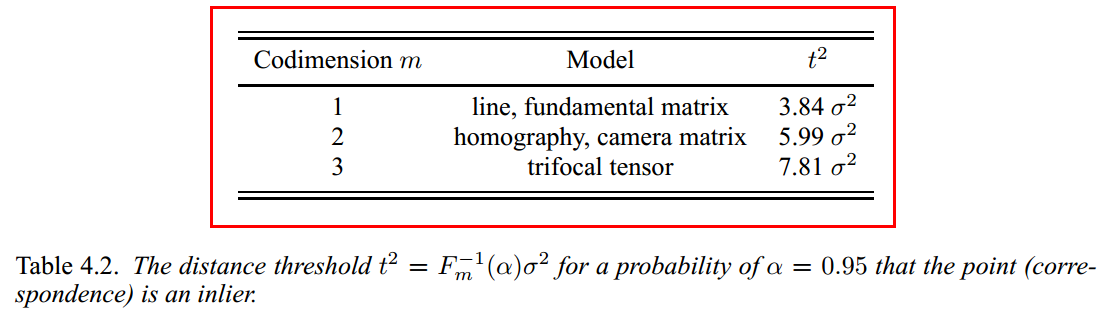
3. 比较本次得分和历史得分,取最高分并记录相应参数。
第三步
根据一定的准则选择模型。用SH表示homography的得分,SF表示fundamental matrix的得分。如果SH / (SH + SF) > 0.4,那么选择homography,反之选择fundamental matrix。
第四步
根据选择的模型计算位姿。参考方法二和方法三。
第五步
Full bundle adjustment。
由于ORB-SLAM对初始化的要求较高,因此初始化时可以选择一个特征丰富的场景,移动摄像机给它提供足够的视差。另外,由于坐标系会附着在初始化成功的那帧图像的位置,因此每次初始化不能保证在同一个位置。
下面结合源代码进一步说明一下。

1 /** 2 * This file is part of ORB-SLAM2. 3 * 4 * Copyright (C) 2014-2016 Raúl Mur-Artal <raulmur at unizar dot es> (University of Zaragoza) 5 * For more information see <https://github.com/raulmur/ORB_SLAM2> 6 * 7 * ORB-SLAM2 is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify 8 * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by 9 * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or 10 * (at your option) any later version. 11 * 12 * ORB-SLAM2 is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, 13 * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of 14 * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the 15 * GNU General Public License for more details. 16 * 17 * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License 18 * along with ORB-SLAM2. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. 19 */ 20 21 #include "Initializer.h" 22 23 #include "Thirdparty/DBoW2/DUtils/Random.h" 24 25 #include "Optimizer.h" 26 #include "ORBmatcher.h" 27 28 #include<thread> 29 30 namespace ORB_SLAM2 { 31 32 Initializer::Initializer(const Frame &ReferenceFrame, float sigma, int iterations) { 33 mK = ReferenceFrame.mK.clone(); 34 35 mvKeys1 = ReferenceFrame.mvKeysUn; 36 37 mSigma = sigma; 38 mSigma2 = sigma * sigma; 39 mMaxIterations = iterations; 40 } 41 42 bool Initializer::Initialize(const Frame &CurrentFrame, const vector<int> &vMatches12, cv::Mat &R21, cv::Mat &t21, 43 vector<cv::Point3f> &vP3D, vector<bool> &vbTriangulated) { 44 // Fill structures with current keypoints and matches with reference frame 45 // Reference Frame: 1, Current Frame: 2 46 // Frame 2 特征点 47 mvKeys2 = CurrentFrame.mvKeysUn; 48 49 mvMatches12.clear(); 50 mvMatches12.reserve(mvKeys2.size()); 51 mvbMatched1.resize(mvKeys1.size()); 52 // 组织特征点对 53 for (size_t i = 0, iend = vMatches12.size(); i < iend; i++) { 54 if (vMatches12[i] >= 0) { 55 mvMatches12.push_back(make_pair(i, vMatches12[i])); 56 mvbMatched1[i] = true; 57 } else 58 mvbMatched1[i] = false; 59 } 60 61 const int N = mvMatches12.size(); 62 63 // Indices for minimum set selection 64 vector<size_t> vAllIndices; 65 vAllIndices.reserve(N); 66 vector<size_t> vAvailableIndices; 67 68 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 69 vAllIndices.push_back(i); 70 } 71 72 // Generate sets of 8 points for each RANSAC iteration 73 // 为每个iteration选取8个随机的index(在FindHomography和FindFundamental被调用) 74 mvSets = vector< vector<size_t> >(mMaxIterations, vector<size_t>(8, 0)); 75 76 DUtils::Random::SeedRandOnce(0); 77 78 for (int it = 0; it < mMaxIterations; it++) { 79 vAvailableIndices = vAllIndices; 80 81 // Select a minimum set 82 for (size_t j = 0; j < 8; j++) { 83 int randi = DUtils::Random::RandomInt(0, vAvailableIndices.size() - 1); 84 int idx = vAvailableIndices[randi]; 85 86 mvSets[it][j] = idx; 87 88 vAvailableIndices[randi] = vAvailableIndices.back(); 89 vAvailableIndices.pop_back(); 90 } 91 } 92 93 // Launch threads to compute in parallel a fundamental matrix and a homography 94 // 调起多线程分别用于计算fundamental matrix和homography 95 vector<bool> vbMatchesInliersH, vbMatchesInliersF; 96 float SH, SF; 97 cv::Mat H, F; 98 99 // 计算homograpy并打分 100 thread threadH(&Initializer::FindHomography, this, ref(vbMatchesInliersH), ref(SH), ref(H)); 101 // 计算fundamental matrix并打分 102 thread threadF(&Initializer::FindFundamental, this, ref(vbMatchesInliersF), ref(SF), ref(F)); 103 104 // Wait until both threads have finished 105 threadH.join(); 106 threadF.join(); 107 108 // Compute ratio of scores 109 // 计算比例,选取某个模型 110 float RH = SH / (SH + SF); 111 112 // Try to reconstruct from homography or fundamental depending on the ratio (0.40-0.45) 113 if (RH > 0.40) 114 return ReconstructH(vbMatchesInliersH, H, mK, R21, t21, vP3D, vbTriangulated, 1.0, 50); 115 else //if(pF_HF>0.6) 116 return ReconstructF(vbMatchesInliersF, F, mK, R21, t21, vP3D, vbTriangulated, 1.0, 50); 117 118 return false; 119 } 120 121 122 void Initializer::FindHomography(vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, float &score, cv::Mat &H21) { 123 // Number of putative matches 124 const int N = mvMatches12.size(); 125 126 // Normalize coordinates 127 vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1, vPn2; 128 cv::Mat T1, T2; 129 Normalize(mvKeys1, vPn1, T1); 130 Normalize(mvKeys2, vPn2, T2); 131 cv::Mat T2inv = T2.inv(); 132 133 // Best Results variables 134 score = 0.0; 135 vbMatchesInliers = vector<bool>(N, false); 136 137 // Iteration variables 138 vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1i(8); 139 vector<cv::Point2f> vPn2i(8); 140 cv::Mat H21i, H12i; 141 vector<bool> vbCurrentInliers(N, false); 142 float currentScore; 143 144 // Perform all RANSAC iterations and save the solution with highest score 145 for (int it = 0; it < mMaxIterations; it++) { 146 // Select a minimum set 147 for (size_t j = 0; j < 8; j++) { 148 int idx = mvSets[it][j]; 149 150 vPn1i[j] = vPn1[mvMatches12[idx].first]; 151 vPn2i[j] = vPn2[mvMatches12[idx].second]; 152 } 153 154 cv::Mat Hn = ComputeH21(vPn1i, vPn2i); 155 H21i = T2inv * Hn * T1; 156 H12i = H21i.inv(); 157 158 currentScore = CheckHomography(H21i, H12i, vbCurrentInliers, mSigma); 159 160 if (currentScore > score) { 161 H21 = H21i.clone(); 162 vbMatchesInliers = vbCurrentInliers; 163 score = currentScore; 164 } 165 } 166 } 167 168 169 void Initializer::FindFundamental(vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, float &score, cv::Mat &F21) { 170 // Number of putative matches 171 const int N = vbMatchesInliers.size(); 172 173 // Normalize coordinates 174 vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1, vPn2; 175 cv::Mat T1, T2; 176 Normalize(mvKeys1, vPn1, T1); 177 Normalize(mvKeys2, vPn2, T2); 178 cv::Mat T2t = T2.t(); 179 180 // Best Results variables 181 score = 0.0; 182 vbMatchesInliers = vector<bool>(N, false); 183 184 // Iteration variables 185 vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1i(8); 186 vector<cv::Point2f> vPn2i(8); 187 cv::Mat F21i; 188 vector<bool> vbCurrentInliers(N, false); 189 float currentScore; 190 191 // Perform all RANSAC iterations and save the solution with highest score 192 for (int it = 0; it < mMaxIterations; it++) { 193 // Select a minimum set 194 for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) { 195 int idx = mvSets[it][j]; 196 197 vPn1i[j] = vPn1[mvMatches12[idx].first]; 198 vPn2i[j] = vPn2[mvMatches12[idx].second]; 199 } 200 201 cv::Mat Fn = ComputeF21(vPn1i, vPn2i); 202 203 F21i = T2t * Fn * T1; 204 205 currentScore = CheckFundamental(F21i, vbCurrentInliers, mSigma); 206 207 if (currentScore > score) { 208 F21 = F21i.clone(); 209 vbMatchesInliers = vbCurrentInliers; 210 score = currentScore; 211 } 212 } 213 } 214 215 // 从特征点匹配求homography(normalized DLT) 216 // Algorithm 4.2 in Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. 217 cv::Mat Initializer::ComputeH21(const vector<cv::Point2f> &vP1, const vector<cv::Point2f> &vP2) { 218 const int N = vP1.size(); 219 220 cv::Mat A(2 * N, 9, CV_32F); 221 222 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 223 const float u1 = vP1[i].x; 224 const float v1 = vP1[i].y; 225 const float u2 = vP2[i].x; 226 const float v2 = vP2[i].y; 227 228 A.at<float>(2 * i, 0) = 0.0; 229 A.at<float>(2 * i, 1) = 0.0; 230 A.at<float>(2 * i, 2) = 0.0; 231 A.at<float>(2 * i, 3) = -u1; 232 A.at<float>(2 * i, 4) = -v1; 233 A.at<float>(2 * i, 5) = -1; 234 A.at<float>(2 * i, 6) = v2 * u1; 235 A.at<float>(2 * i, 7) = v2 * v1; 236 A.at<float>(2 * i, 8) = v2; 237 238 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 0) = u1; 239 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 1) = v1; 240 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 2) = 1; 241 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 3) = 0.0; 242 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 4) = 0.0; 243 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 5) = 0.0; 244 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 6) = -u2 * u1; 245 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 7) = -u2 * v1; 246 A.at<float>(2 * i + 1, 8) = -u2; 247 248 } 249 250 cv::Mat u, w, vt; 251 252 cv::SVDecomp(A, w, u, vt, cv::SVD::MODIFY_A | cv::SVD::FULL_UV); 253 254 return vt.row(8).reshape(0, 3); 255 } 256 // 从特征点匹配求fundamental matrix(8点法) 257 // Algorithm 11.1 in Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. 258 cv::Mat Initializer::ComputeF21(const vector<cv::Point2f> &vP1, const vector<cv::Point2f> &vP2) { 259 const int N = vP1.size(); 260 261 cv::Mat A(N, 9, CV_32F); 262 263 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 264 const float u1 = vP1[i].x; 265 const float v1 = vP1[i].y; 266 const float u2 = vP2[i].x; 267 const float v2 = vP2[i].y; 268 269 A.at<float>(i, 0) = u2 * u1; 270 A.at<float>(i, 1) = u2 * v1; 271 A.at<float>(i, 2) = u2; 272 A.at<float>(i, 3) = v2 * u1; 273 A.at<float>(i, 4) = v2 * v1; 274 A.at<float>(i, 5) = v2; 275 A.at<float>(i, 6) = u1; 276 A.at<float>(i, 7) = v1; 277 A.at<float>(i, 8) = 1; 278 } 279 280 cv::Mat u, w, vt; 281 282 cv::SVDecomp(A, w, u, vt, cv::SVD::MODIFY_A | cv::SVD::FULL_UV); 283 284 cv::Mat Fpre = vt.row(8).reshape(0, 3); 285 286 cv::SVDecomp(Fpre, w, u, vt, cv::SVD::MODIFY_A | cv::SVD::FULL_UV); 287 288 w.at<float>(2) = 0; 289 290 return u * cv::Mat::diag(w) * vt; 291 } 292 // 从homography计算symmetric transfer errors 293 // IV. AUTOMATIC MAP INITIALIZATION (2) in Author's paper 294 // symmetric transfer errors: 295 // 4.2.2 Geometric distance in Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. 296 // model selection 297 // 4.7.1 RANSAC in Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision 298 float Initializer::CheckHomography(const cv::Mat &H21, const cv::Mat &H12, vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, float sigma) { 299 const int N = mvMatches12.size(); 300 301 const float h11 = H21.at<float>(0, 0); 302 const float h12 = H21.at<float>(0, 1); 303 const float h13 = H21.at<float>(0, 2); 304 const float h21 = H21.at<float>(1, 0); 305 const float h22 = H21.at<float>(1, 1); 306 const float h23 = H21.at<float>(1, 2); 307 const float h31 = H21.at<float>(2, 0); 308 const float h32 = H21.at<float>(2, 1); 309 const float h33 = H21.at<float>(2, 2); 310 311 const float h11inv = H12.at<float>(0, 0); 312 const float h12inv = H12.at<float>(0, 1); 313 const float h13inv = H12.at<float>(0, 2); 314 const float h21inv = H12.at<float>(1, 0); 315 const float h22inv = H12.at<float>(1, 1); 316 const float h23inv = H12.at<float>(1, 2); 317 const float h31inv = H12.at<float>(2, 0); 318 const float h32inv = H12.at<float>(2, 1); 319 const float h33inv = H12.at<float>(2, 2); 320 321 vbMatchesInliers.resize(N); 322 323 float score = 0; 324 // 来源于卡方分布 325 const float th = 5.991; 326 327 const float invSigmaSquare = 1.0 / (sigma * sigma); 328 329 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 330 bool bIn = true; 331 332 const cv::KeyPoint &kp1 = mvKeys1[mvMatches12[i].first]; 333 const cv::KeyPoint &kp2 = mvKeys2[mvMatches12[i].second]; 334 335 const float u1 = kp1.pt.x; 336 const float v1 = kp1.pt.y; 337 const float u2 = kp2.pt.x; 338 const float v2 = kp2.pt.y; 339 340 // Reprojection error in first image 341 // x2in1 = H12*x2 342 343 const float w2in1inv = 1.0 / (h31inv * u2 + h32inv * v2 + h33inv); 344 const float u2in1 = (h11inv * u2 + h12inv * v2 + h13inv) * w2in1inv; 345 const float v2in1 = (h21inv * u2 + h22inv * v2 + h23inv) * w2in1inv; 346 347 const float squareDist1 = (u1 - u2in1) * (u1 - u2in1) + (v1 - v2in1) * (v1 - v2in1); 348 349 const float chiSquare1 = squareDist1 * invSigmaSquare; 350 351 if (chiSquare1 > th) 352 bIn = false; 353 else 354 score += th - chiSquare1; 355 356 // Reprojection error in second image 357 // x1in2 = H21*x1 358 359 const float w1in2inv = 1.0 / (h31 * u1 + h32 * v1 + h33); 360 const float u1in2 = (h11 * u1 + h12 * v1 + h13) * w1in2inv; 361 const float v1in2 = (h21 * u1 + h22 * v1 + h23) * w1in2inv; 362 363 const float squareDist2 = (u2 - u1in2) * (u2 - u1in2) + (v2 - v1in2) * (v2 - v1in2); 364 365 const float chiSquare2 = squareDist2 * invSigmaSquare; 366 367 if (chiSquare2 > th) 368 bIn = false; 369 else 370 score += th - chiSquare2; 371 372 if (bIn) 373 vbMatchesInliers[i] = true; 374 else 375 vbMatchesInliers[i] = false; 376 } 377 378 return score; 379 } 380 // 从fundamental matrix计算symmetric transfer errors 381 // IV. AUTOMATIC MAP INITIALIZATION (2) in Author's paper 382 // symmetric transfer errors: 383 // 4.2.2 Geometric distance in Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision. 384 // model selection 385 // 4.7.1 RANSAC in Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision 386 float Initializer::CheckFundamental(const cv::Mat &F21, vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, float sigma) { 387 const int N = mvMatches12.size(); 388 389 const float f11 = F21.at<float>(0, 0); 390 const float f12 = F21.at<float>(0, 1); 391 const float f13 = F21.at<float>(0, 2); 392 const float f21 = F21.at<float>(1, 0); 393 const float f22 = F21.at<float>(1, 1); 394 const float f23 = F21.at<float>(1, 2); 395 const float f31 = F21.at<float>(2, 0); 396 const float f32 = F21.at<float>(2, 1); 397 const float f33 = F21.at<float>(2, 2); 398 399 vbMatchesInliers.resize(N); 400 401 float score = 0; 402 403 const float th = 3.841; 404 const float thScore = 5.991; 405 406 const float invSigmaSquare = 1.0 / (sigma * sigma); 407 408 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 409 bool bIn = true; 410 411 const cv::KeyPoint &kp1 = mvKeys1[mvMatches12[i].first]; 412 const cv::KeyPoint &kp2 = mvKeys2[mvMatches12[i].second]; 413 414 const float u1 = kp1.pt.x; 415 const float v1 = kp1.pt.y; 416 const float u2 = kp2.pt.x; 417 const float v2 = kp2.pt.y; 418 419 // Reprojection error in second image 420 // l2=F21x1=(a2,b2,c2) 421 422 const float a2 = f11 * u1 + f12 * v1 + f13; 423 const float b2 = f21 * u1 + f22 * v1 + f23; 424 const float c2 = f31 * u1 + f32 * v1 + f33; 425 426 const float num2 = a2 * u2 + b2 * v2 + c2; 427 428 const float squareDist1 = num2 * num2 / (a2 * a2 + b2 * b2); 429 430 const float chiSquare1 = squareDist1 * invSigmaSquare; 431 432 if (chiSquare1 > th) 433 bIn = false; 434 else 435 score += thScore - chiSquare1; 436 437 // Reprojection error in second image 438 // l1 =x2tF21=(a1,b1,c1) 439 440 const float a1 = f11 * u2 + f21 * v2 + f31; 441 const float b1 = f12 * u2 + f22 * v2 + f32; 442 const float c1 = f13 * u2 + f23 * v2 + f33; 443 444 const float num1 = a1 * u1 + b1 * v1 + c1; 445 446 const float squareDist2 = num1 * num1 / (a1 * a1 + b1 * b1); 447 448 const float chiSquare2 = squareDist2 * invSigmaSquare; 449 450 if (chiSquare2 > th) 451 bIn = false; 452 else 453 score += thScore - chiSquare2; 454 455 if (bIn) 456 vbMatchesInliers[i] = true; 457 else 458 vbMatchesInliers[i] = false; 459 } 460 461 return score; 462 } 463 // 从F恢复P 464 // 参考文献: 465 // Result 9.19 in Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision 466 bool Initializer::ReconstructF(vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, cv::Mat &F21, cv::Mat &K, 467 cv::Mat &R21, cv::Mat &t21, vector<cv::Point3f> &vP3D, vector<bool> &vbTriangulated, float minParallax, int minTriangulated) { 468 int N = 0; 469 for (size_t i = 0, iend = vbMatchesInliers.size() ; i < iend; i++) 470 if (vbMatchesInliers[i]) 471 N++; 472 473 // Compute Essential Matrix from Fundamental Matrix 474 cv::Mat E21 = K.t() * F21 * K; 475 476 cv::Mat R1, R2, t; 477 478 // Recover the 4 motion hypotheses 479 DecomposeE(E21, R1, R2, t); 480 481 cv::Mat t1 = t; 482 cv::Mat t2 = -t; 483 484 // Reconstruct with the 4 hyphoteses and check 485 vector<cv::Point3f> vP3D1, vP3D2, vP3D3, vP3D4; 486 vector<bool> vbTriangulated1, vbTriangulated2, vbTriangulated3, vbTriangulated4; 487 float parallax1, parallax2, parallax3, parallax4; 488 489 int nGood1 = CheckRT(R1, t1, mvKeys1, mvKeys2, mvMatches12, vbMatchesInliers, K, vP3D1, 4.0 * mSigma2, vbTriangulated1, parallax1); 490 int nGood2 = CheckRT(R2, t1, mvKeys1, mvKeys2, mvMatches12, vbMatchesInliers, K, vP3D2, 4.0 * mSigma2, vbTriangulated2, parallax2); 491 int nGood3 = CheckRT(R1, t2, mvKeys1, mvKeys2, mvMatches12, vbMatchesInliers, K, vP3D3, 4.0 * mSigma2, vbTriangulated3, parallax3); 492 int nGood4 = CheckRT(R2, t2, mvKeys1, mvKeys2, mvMatches12, vbMatchesInliers, K, vP3D4, 4.0 * mSigma2, vbTriangulated4, parallax4); 493 494 int maxGood = max(nGood1, max(nGood2, max(nGood3, nGood4))); 495 496 R21 = cv::Mat(); 497 t21 = cv::Mat(); 498 499 int nMinGood = max(static_cast<int>(0.9 * N), minTriangulated); 500 501 int nsimilar = 0; 502 if (nGood1 > 0.7 * maxGood) 503 nsimilar++; 504 if (nGood2 > 0.7 * maxGood) 505 nsimilar++; 506 if (nGood3 > 0.7 * maxGood) 507 nsimilar++; 508 if (nGood4 > 0.7 * maxGood) 509 nsimilar++; 510 511 // If there is not a clear winner or not enough triangulated points reject initialization 512 if (maxGood < nMinGood || nsimilar > 1) { 513 return false; 514 } 515 516 // If best reconstruction has enough parallax initialize 517 if (maxGood == nGood1) { 518 if (parallax1 > minParallax) { 519 vP3D = vP3D1; 520 vbTriangulated = vbTriangulated1; 521 522 R1.copyTo(R21); 523 t1.copyTo(t21); 524 return true; 525 } 526 } else if (maxGood == nGood2) { 527 if (parallax2 > minParallax) { 528 vP3D = vP3D2; 529 vbTriangulated = vbTriangulated2; 530 531 R2.copyTo(R21); 532 t1.copyTo(t21); 533 return true; 534 } 535 } else if (maxGood == nGood3) { 536 if (parallax3 > minParallax) { 537 vP3D = vP3D3; 538 vbTriangulated = vbTriangulated3; 539 540 R1.copyTo(R21); 541 t2.copyTo(t21); 542 return true; 543 } 544 } else if (maxGood == nGood4) { 545 if (parallax4 > minParallax) { 546 vP3D = vP3D4; 547 vbTriangulated = vbTriangulated4; 548 549 R2.copyTo(R21); 550 t2.copyTo(t21); 551 return true; 552 } 553 } 554 555 return false; 556 } 557 // 从H恢复P 558 // 参考文献: 559 // Faugeras et al, Motion and structure from motion in a piecewise planar environment. International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 1988. 560 bool Initializer::ReconstructH(vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, cv::Mat &H21, cv::Mat &K, 561 cv::Mat &R21, cv::Mat &t21, vector<cv::Point3f> &vP3D, vector<bool> &vbTriangulated, float minParallax, int minTriangulated) { 562 int N = 0; 563 for (size_t i = 0, iend = vbMatchesInliers.size() ; i < iend; i++) 564 if (vbMatchesInliers[i]) 565 N++; 566 567 // We recover 8 motion hypotheses using the method of Faugeras et al. 568 // Motion and structure from motion in a piecewise planar environment. 569 // International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 1988 570 571 cv::Mat invK = K.inv(); 572 cv::Mat A = invK * H21 * K; 573 574 cv::Mat U, w, Vt, V; 575 cv::SVD::compute(A, w, U, Vt, cv::SVD::FULL_UV); 576 V = Vt.t(); 577 578 float s = cv::determinant(U) * cv::determinant(Vt); 579 580 float d1 = w.at<float>(0); 581 float d2 = w.at<float>(1); 582 float d3 = w.at<float>(2); 583 584 if (d1 / d2 < 1.00001 || d2 / d3 < 1.00001) { 585 return false; 586 } 587 588 vector<cv::Mat> vR, vt, vn; 589 vR.reserve(8); 590 vt.reserve(8); 591 vn.reserve(8); 592 593 //n'=[x1 0 x3] 4 posibilities e1=e3=1, e1=1 e3=-1, e1=-1 e3=1, e1=e3=-1 594 float aux1 = sqrt((d1 * d1 - d2 * d2) / (d1 * d1 - d3 * d3)); 595 float aux3 = sqrt((d2 * d2 - d3 * d3) / (d1 * d1 - d3 * d3)); 596 float x1[] = {aux1, aux1, -aux1, -aux1}; 597 float x3[] = {aux3, -aux3, aux3, -aux3}; 598 599 //case d'=d2 600 float aux_stheta = sqrt((d1 * d1 - d2 * d2) * (d2 * d2 - d3 * d3)) / ((d1 + d3) * d2); 601 602 float ctheta = (d2 * d2 + d1 * d3) / ((d1 + d3) * d2); 603 float stheta[] = {aux_stheta, -aux_stheta, -aux_stheta, aux_stheta}; 604 605 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 606 cv::Mat Rp = cv::Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_32F); 607 Rp.at<float>(0, 0) = ctheta; 608 Rp.at<float>(0, 2) = -stheta[i]; 609 Rp.at<float>(2, 0) = stheta[i]; 610 Rp.at<float>(2, 2) = ctheta; 611 612 cv::Mat R = s * U * Rp * Vt; 613 vR.push_back(R); 614 615 cv::Mat tp(3, 1, CV_32F); 616 tp.at<float>(0) = x1[i]; 617 tp.at<float>(1) = 0; 618 tp.at<float>(2) = -x3[i]; 619 tp *= d1 - d3; 620 621 cv::Mat t = U * tp; 622 vt.push_back(t / cv::norm(t)); 623 624 cv::Mat np(3, 1, CV_32F); 625 np.at<float>(0) = x1[i]; 626 np.at<float>(1) = 0; 627 np.at<float>(2) = x3[i]; 628 629 cv::Mat n = V * np; 630 if (n.at<float>(2) < 0) 631 n = -n; 632 vn.push_back(n); 633 } 634 635 //case d'=-d2 636 float aux_sphi = sqrt((d1 * d1 - d2 * d2) * (d2 * d2 - d3 * d3)) / ((d1 - d3) * d2); 637 638 float cphi = (d1 * d3 - d2 * d2) / ((d1 - d3) * d2); 639 float sphi[] = {aux_sphi, -aux_sphi, -aux_sphi, aux_sphi}; 640 641 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 642 cv::Mat Rp = cv::Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_32F); 643 Rp.at<float>(0, 0) = cphi; 644 Rp.at<float>(0, 2) = sphi[i]; 645 Rp.at<float>(1, 1) = -1; 646 Rp.at<float>(2, 0) = sphi[i]; 647 Rp.at<float>(2, 2) = -cphi; 648 649 cv::Mat R = s * U * Rp * Vt; 650 vR.push_back(R); 651 652 cv::Mat tp(3, 1, CV_32F); 653 tp.at<float>(0) = x1[i]; 654 tp.at<float>(1) = 0; 655 tp.at<float>(2) = x3[i]; 656 tp *= d1 + d3; 657 658 cv::Mat t = U * tp; 659 vt.push_back(t / cv::norm(t)); 660 661 cv::Mat np(3, 1, CV_32F); 662 np.at<float>(0) = x1[i]; 663 np.at<float>(1) = 0; 664 np.at<float>(2) = x3[i]; 665 666 cv::Mat n = V * np; 667 if (n.at<float>(2) < 0) 668 n = -n; 669 vn.push_back(n); 670 } 671 672 673 int bestGood = 0; 674 int secondBestGood = 0; 675 int bestSolutionIdx = -1; 676 float bestParallax = -1; 677 vector<cv::Point3f> bestP3D; 678 vector<bool> bestTriangulated; 679 680 // Instead of applying the visibility constraints proposed in the Faugeras' paper (which could fail for points seen with low parallax) 681 // We reconstruct all hypotheses and check in terms of triangulated points and parallax 682 for (size_t i = 0; i < 8; i++) { 683 float parallaxi; 684 vector<cv::Point3f> vP3Di; 685 vector<bool> vbTriangulatedi; 686 int nGood = CheckRT(vR[i], vt[i], mvKeys1, mvKeys2, mvMatches12, vbMatchesInliers, K, vP3Di, 4.0 * mSigma2, vbTriangulatedi, parallaxi); 687 688 if (nGood > bestGood) { 689 secondBestGood = bestGood; 690 bestGood = nGood; 691 bestSolutionIdx = i; 692 bestParallax = parallaxi; 693 bestP3D = vP3Di; 694 bestTriangulated = vbTriangulatedi; 695 } else if (nGood > secondBestGood) { 696 secondBestGood = nGood; 697 } 698 } 699 700 701 if (secondBestGood < 0.75 * bestGood && bestParallax >= minParallax && bestGood > minTriangulated && bestGood > 0.9 * N) { 702 vR[bestSolutionIdx].copyTo(R21); 703 vt[bestSolutionIdx].copyTo(t21); 704 vP3D = bestP3D; 705 vbTriangulated = bestTriangulated; 706 707 return true; 708 } 709 710 return false; 711 } 712 713 void Initializer::Triangulate(const cv::KeyPoint &kp1, const cv::KeyPoint &kp2, const cv::Mat &P1, const cv::Mat &P2, cv::Mat &x3D) { 714 cv::Mat A(4, 4, CV_32F); 715 716 A.row(0) = kp1.pt.x * P1.row(2) - P1.row(0); 717 A.row(1) = kp1.pt.y * P1.row(2) - P1.row(1); 718 A.row(2) = kp2.pt.x * P2.row(2) - P2.row(0); 719 A.row(3) = kp2.pt.y * P2.row(2) - P2.row(1); 720 721 cv::Mat u, w, vt; 722 cv::SVD::compute(A, w, u, vt, cv::SVD::MODIFY_A | cv::SVD::FULL_UV); 723 x3D = vt.row(3).t(); 724 x3D = x3D.rowRange(0, 3) / x3D.at<float>(3); 725 } 726 // 归一化特征点到同一尺度(作为normalize DLT的输入) 727 void Initializer::Normalize(const vector<cv::KeyPoint> &vKeys, vector<cv::Point2f> &vNormalizedPoints, cv::Mat &T) { 728 float meanX = 0; 729 float meanY = 0; 730 const int N = vKeys.size(); 731 732 vNormalizedPoints.resize(N); 733 734 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 735 meanX += vKeys[i].pt.x; 736 meanY += vKeys[i].pt.y; 737 } 738 739 meanX = meanX / N; 740 meanY = meanY / N; 741 742 float meanDevX = 0; 743 float meanDevY = 0; 744 745 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 746 vNormalizedPoints[i].x = vKeys[i].pt.x - meanX; 747 vNormalizedPoints[i].y = vKeys[i].pt.y - meanY; 748 749 meanDevX += fabs(vNormalizedPoints[i].x); 750 meanDevY += fabs(vNormalizedPoints[i].y); 751 } 752 753 meanDevX = meanDevX / N; 754 meanDevY = meanDevY / N; 755 756 float sX = 1.0 / meanDevX; 757 float sY = 1.0 / meanDevY; 758 759 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { 760 vNormalizedPoints[i].x = vNormalizedPoints[i].x * sX; 761 vNormalizedPoints[i].y = vNormalizedPoints[i].y * sY; 762 } 763 764 T = cv::Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_32F); 765 T.at<float>(0, 0) = sX; 766 T.at<float>(1, 1) = sY; 767 T.at<float>(0, 2) = -meanX * sX; 768 T.at<float>(1, 2) = -meanY * sY; 769 } 770 771 772 int Initializer::CheckRT(const cv::Mat &R, const cv::Mat &t, const vector<cv::KeyPoint> &vKeys1, const vector<cv::KeyPoint> &vKeys2, 773 const vector<Match> &vMatches12, vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, 774 const cv::Mat &K, vector<cv::Point3f> &vP3D, float th2, vector<bool> &vbGood, float ¶llax) { 775 // Calibration parameters 776 const float fx = K.at<float>(0, 0); 777 const float fy = K.at<float>(1, 1); 778 const float cx = K.at<float>(0, 2); 779 const float cy = K.at<float>(1, 2); 780 781 vbGood = vector<bool>(vKeys1.size(), false); 782 vP3D.resize(vKeys1.size()); 783 784 vector<float> vCosParallax; 785 vCosParallax.reserve(vKeys1.size()); 786 787 // Camera 1 Projection Matrix K[I|0] 788 cv::Mat P1(3, 4, CV_32F, cv::Scalar(0)); 789 K.copyTo(P1.rowRange(0, 3).colRange(0, 3)); 790 791 cv::Mat O1 = cv::Mat::zeros(3, 1, CV_32F); 792 793 // Camera 2 Projection Matrix K[R|t] 794 cv::Mat P2(3, 4, CV_32F); 795 R.copyTo(P2.rowRange(0, 3).colRange(0, 3)); 796 t.copyTo(P2.rowRange(0, 3).col(3)); 797 P2 = K * P2; 798 799 cv::Mat O2 = -R.t() * t; 800 801 int nGood = 0; 802 803 for (size_t i = 0, iend = vMatches12.size(); i < iend; i++) { 804 if (!vbMatchesInliers[i]) 805 continue; 806 807 const cv::KeyPoint &kp1 = vKeys1[vMatches12[i].first]; 808 const cv::KeyPoint &kp2 = vKeys2[vMatches12[i].second]; 809 cv::Mat p3dC1; 810 811 Triangulate(kp1, kp2, P1, P2, p3dC1); 812 813 if (!isfinite(p3dC1.at<float>(0)) || !isfinite(p3dC1.at<float>(1)) || !isfinite(p3dC1.at<float>(2))) { 814 vbGood[vMatches12[i].first] = false; 815 continue; 816 } 817 818 // Check parallax 819 cv::Mat normal1 = p3dC1 - O1; 820 float dist1 = cv::norm(normal1); 821 822 cv::Mat normal2 = p3dC1 - O2; 823 float dist2 = cv::norm(normal2); 824 825 float cosParallax = normal1.dot(normal2) / (dist1 * dist2); 826 827 // Check depth in front of first camera (only if enough parallax, as "infinite" points can easily go to negative depth) 828 if (p3dC1.at<float>(2) <= 0 && cosParallax < 0.99998) 829 continue; 830 831 // Check depth in front of second camera (only if enough parallax, as "infinite" points can easily go to negative depth) 832 cv::Mat p3dC2 = R * p3dC1 + t; 833 834 if (p3dC2.at<float>(2) <= 0 && cosParallax < 0.99998) 835 continue; 836 837 // Check reprojection error in first image 838 float im1x, im1y; 839 float invZ1 = 1.0 / p3dC1.at<float>(2); 840 im1x = fx * p3dC1.at<float>(0) * invZ1 + cx; 841 im1y = fy * p3dC1.at<float>(1) * invZ1 + cy; 842 843 float squareError1 = (im1x - kp1.pt.x) * (im1x - kp1.pt.x) + (im1y - kp1.pt.y) * (im1y - kp1.pt.y); 844 845 if (squareError1 > th2) 846 continue; 847 848 // Check reprojection error in second image 849 float im2x, im2y; 850 float invZ2 = 1.0 / p3dC2.at<float>(2); 851 im2x = fx * p3dC2.at<float>(0) * invZ2 + cx; 852 im2y = fy * p3dC2.at<float>(1) * invZ2 + cy; 853 854 float squareError2 = (im2x - kp2.pt.x) * (im2x - kp2.pt.x) + (im2y - kp2.pt.y) * (im2y - kp2.pt.y); 855 856 if (squareError2 > th2) 857 continue; 858 859 vCosParallax.push_back(cosParallax); 860 vP3D[vMatches12[i].first] = cv::Point3f(p3dC1.at<float>(0), p3dC1.at<float>(1), p3dC1.at<float>(2)); 861 nGood++; 862 863 if (cosParallax < 0.99998) 864 vbGood[vMatches12[i].first] = true; 865 } 866 867 if (nGood > 0) { 868 sort(vCosParallax.begin(), vCosParallax.end()); 869 870 size_t idx = min(50, int(vCosParallax.size() - 1)); 871 parallax = acos(vCosParallax[idx]) * 180 / CV_PI; 872 } else 873 parallax = 0; 874 875 return nGood; 876 } 877 878 void Initializer::DecomposeE(const cv::Mat &E, cv::Mat &R1, cv::Mat &R2, cv::Mat &t) { 879 cv::Mat u, w, vt; 880 cv::SVD::compute(E, w, u, vt); 881 882 u.col(2).copyTo(t); 883 t = t / cv::norm(t); 884 885 cv::Mat W(3, 3, CV_32F, cv::Scalar(0)); 886 W.at<float>(0, 1) = -1; 887 W.at<float>(1, 0) = 1; 888 W.at<float>(2, 2) = 1; 889 890 R1 = u * W * vt; 891 if (cv::determinant(R1) < 0) 892 R1 = -R1; 893 894 R2 = u * W.t() * vt; 895 if (cv::determinant(R2) < 0) 896 R2 = -R2; 897 } 898 899 } //namespace ORB_SLAM
该系列的其它文章:





【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步