ASP.NET性能优化之构建自定义文件缓存
ASP.NET的输出缓存(即静态HTML)在.NET4.0前一直是基于内存的。这意味着如果我们的站点含有大量的缓存,则很容易消耗掉本机内存。现在,借助于.NET4.0中的OutputCacheProvider,我们可以有多种选择创建自己的缓存。如,我们可以把HTML输出缓存存储到memcached分布式集群服务器,或者MongoDB中(一种常用的面向文档数据库,不妨阅读本篇http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/magazine/gg650661.aspx)。当然,我们也可以把缓存作为文件存储到硬盘上,考虑到可扩展性,这是一种最廉价的做法,本文就是介绍如果构建自定义文件缓存。
1:OutputCacheProvider
OutputCacheProvider是一个抽象基类,我们需要override其中的四个方法,它们分别是:
Add 方法,将指定项插入输出缓存中。
Get 方法,返回对输出缓存中指定项的引用。
Remove 方法,从输出缓存中移除指定项。
Set 方法,将指定项插入输出缓存中,如果该项已缓存,则覆盖该项。
2:创建自己的文件缓存处理类
该类型为FileCacheProvider,代码如下:
public class FileCacheProvider : OutputCacheProvider
{
private static readonly ILog log = LogManager.GetLogger(System.Reflection.MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod().DeclaringType);
public override void Initialize(string name, NameValueCollection attributes)
{
base.Initialize(name, attributes);
CachePath = HttpContext.Current.Server.MapPath(attributes["cachePath"]);
}
public override object Add(string key, object entry, DateTime utcExpiry)
{
Object obj = Get(key);
if (obj != null) //这一步很重要
{
return obj;
}
Set(key,entry,utcExpiry);
return entry;
}
public override object Get(string key)
{
string path = ConvertKeyToPath(key);
if (!File.Exists(path))
{
return null;
}
CacheItem item = null;
using (FileStream file = File.OpenRead(path))
{
var formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
item = (CacheItem)formatter.Deserialize(file);
}
if (item.ExpiryDate <= DateTime.Now.ToUniversalTime())
{
log.Info(item.ExpiryDate + "*" + key);
Remove(key);
return null;
}
return item.Item;
}
public override void Set(string key, object entry, DateTime utcExpiry)
{
CacheItem item = new CacheItem(entry, utcExpiry);
string path = ConvertKeyToPath(key);
using (FileStream file = File.OpenWrite(path))
{
BinaryFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
formatter.Serialize(file, item);
}
}
public override void Remove(string key)
{
string path = ConvertKeyToPath(key);
if (File.Exists(path))
File.Delete(path);
}
public string CachePath
{
get;
set;
}
private string ConvertKeyToPath(string key)
{
string file = key.Replace('/', '-');
file += ".txt";
return Path.Combine(CachePath, file);
}
}
[Serializable]
public class CacheItem
{
public DateTime ExpiryDate;
public object Item;
public CacheItem(object entry, DateTime utcExpiry)
{
Item = entry;
ExpiryDate = utcExpiry;
}
}
有两个地方需要特别说明:
在Add方法中,有一个条件判断,必须做出这样的处理,否则缓存机制将会缓存第一次的结果,过了有效期后缓存讲失效并不再重建;
在示例程序中,我们简单的将缓存放到了Cache目录下,在实际的项目实践中,考虑到缓存的页面将是成千上万的,所以我们必须要做目录分级,否则寻找并读取缓存文件将会成为效率瓶颈,这会耗尽CPU。
3:配置文件
我们需要在Web.config中配置缓存处理程序是自定义的FileCacheProvider,即在 <system.web>下添加节点:
<caching>
<outputCache defaultProvider="FileCache">
<providers>
<add name="FileCache" type="MvcApplication2.Common.FileCacheProvider" cachePath="~/Cache" />
</providers>
</outputCache>
</caching>
4:缓存的使用
我们假设在MVC的控制中使用(如果要在ASP.NET页面中使用,则在页面中包含<%@OutputCache VaryByParam="none" Duration="10" %>),可以看到,Index是未进行输出缓存的,而Index2进行了输出缓存,缓存时间为10秒。
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private static readonly ILog log = LogManager.GetLogger(System.Reflection.MethodBase.GetCurrentMethod().DeclaringType);
static string s_conn = "Data Source=192.168.0.77;Initial Catalog=luminjidb;User Id=sa;Password=sa;";
public ActionResult Index()
{
using (DataSet ds = Common.SqlHelper.ExecuteDataset(s_conn, CommandType.Text, "select top 1* from NameTb a, DepTb b where a.DepID = b.ID ORDER BY NEWID()"))
{
ViewBag.Message = ds.Tables[0].Rows[0]["name"].ToString();
}
return View();
}
[OutputCache(Duration = 10, VaryByParam = "none")]
public ActionResult Index2()
{
using (DataSet ds = Common.SqlHelper.ExecuteDataset(s_conn, CommandType.Text, "select top 1* from NameTb a, DepTb b where a.DepID = b.ID ORDER BY NEWID()"))
{
ViewBag.Message = ds.Tables[0].Rows[0]["name"].ToString();
}
return View();
}
}
5:查看下效果
上面的代码,在访问了Index2后,将会在Cache文件夹下产生缓存文件,如下:
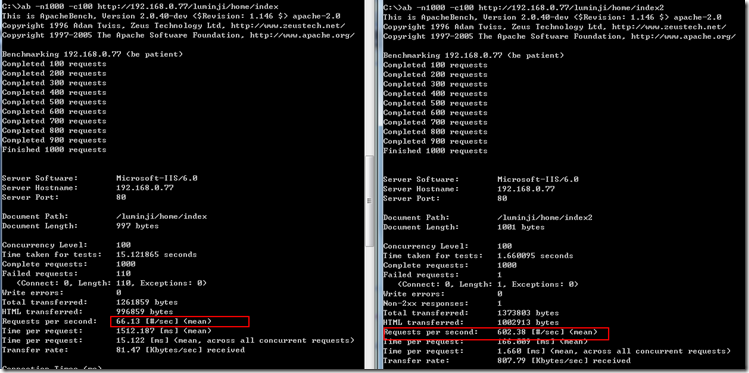
现在,我们开始评价下有输出缓存和无输出缓存的性能对比,模拟100个用户并发1000次请求如下:
可以看到,有输出缓存后,吞吐率明显提高了10倍。
6:代码下载
FileCacheProvider的原始代码来自于网络,我修改了其中的BUG,全部代码下载如下:MvcApplication20110907.rar