sanic官方文档解析之Deploying(部署)和Extension(扩展)
1,Deploying(部署)

通过内置的websocket可以很简单的部署sanic项目,之后通过实例sanic.Sanic,我们可以运行run这个方法通过接下来的关键字参数
host(default"127.0.0.1"): Address to host the server on.- 默认的主机ip是127.0.0.1
port(default8000): Port to host the server on.- 默认的端口是8000
debug(defaultFalse): Enables debug output (slows server).- 调试模式(默认是False)可以输出degug
ssl(defaultNone):SSLContextfor SSL encryption of worker(s).- 在ssl加密中(参数默认是空)
sock(defaultNone): Socket for the server to accept connections from.- 接收连接数的socket是默认空
workers(default1): Number of worker processes to spawn.- 运行程序的进程默认是1
loop(defaultNone): Anasyncio-compatible event loop. If none is specified, Sanic creates its own event loop.- 异步兼容的事件循环,如果没有,sanic将会创建自己的时间循环
protocol(defaultHttpProtocol): Subclass of asyncio.protocol.- 异步协议默认是HTTPProtocol协议
1.1workers

通过默认值,Sanic仅仅使用一核CPU来监听主程序的进程,为了压榨出果汁,恰好一定特殊数量的工人用run参数
app.run(host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, workers=4)

Sanic能够自动的多线程旋转上升,且在他们之间有路由指示,我们推荐尽可能多核的运行
1.2,运行via命令
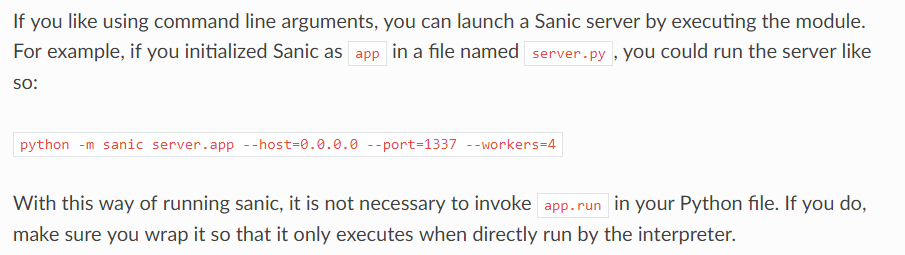
如果你喜欢使用命令模式参数,你可以启动Sanic服务端执行模块,,如果你初始化一个Sanic为一个app对象在一个文件中,你可以运行这个服务文件执行以下代码:
python -m sanic server.app --host=0.0.0.0 --port=1337 --workers=4
通过这样的方式运行sanic,也不是引用app.run在Python中不是必须的,如果存在,确定要包起来,当解释器跳转执行的时候,它会被执行
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host="0.0.0.0",port=1337, workers=4)
1.3,运行via Gunicorn
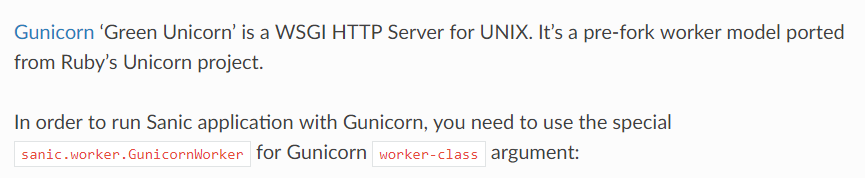
Gunicon'Green Unicorn' 是一个为UNIX服务的WSGI HTTP, 它是一个pre-fork 工作模块的端口,是从Ruby的Unicorn项目中来.
为了运行sanic应用,你需要从Gunicon的worker-class参数中使用特殊的sanic.worker.GunicornWorker
gunicorn myapp:app --bind 0.0.0.0:1337
--worker-class sanic.worker.GunicornWorker

如果您需要与其他应用程序(尤其是循环)共享SANIC过程,那么这是合适的。但是,请注意,此方法不支持使用多个进程,并且通常不是运行应用程序的首选方法
更多信息,查看Gunicorn 文档
1.4,禁止调试的日志
要提高性能,请在运行参数中添加debug=false和access_log=false
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=1337, workers=4, debug=False, access_log=False)
通过gunicorn运行,您可以设置环境变量sanic_access_log=“false”
env SANIC_ACCESS_LOG="False" gunicorn myapp:app --bind 0.0.0.0:1337
--worker-class sanic.worker.GunicornWorker --log-level warning
你也可以直接重写配置文件
app.config.ACCESS_LOG = False
1.5,支持异步

如果您需要与其他应用程序(尤其是循环)共享SANIC过程,那么这是合适的。但是,请注意,此方法不支持使用多个进程,并且通常不是运行应用程序的首选方法。
以下是一个不完整的示例(请参阅示例中的run_async.py了解更实用的内容)
server = app.create_server(host="0.0.0.0", port=8000)
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
task = asyncio.ensure_future(server)
loop.run_forever()


