数据同步那些事儿(优化过程分享)
简介
很久之前就想写这篇文章了,主要是介绍一下我做数据同步的过程中遇到的一些有意思的内容,和提升效率的过程。
当前在数据处理的过程中,数据同步如同血液一般充满全过程,如图:

数据同步开源产品对比:
DataX,是淘宝的开源项目,可惜不支持Postgresql
Sqoop,Apache开源项目,同步过程中字段需要严格一致,不方便扩展,不易于二次开发
整体设计思路:
使用生产者消费者模型,中间使用内存,数据不落地,直接插入目标数据

优化过程:
1、插入数据部分:
首先生产者通过Jdbc获取源数据内容,放入固定大小的缓存队列,同时消费者不断的从缓存读取数据,根据不同的数据类型分别读取出来,并逐条插入目标数据库。
速度每秒300条,每分钟1.8W条。
这样做表面上看起来非常美好,流水式的处理,来一条处理一下,可是发现插入的速度远远赶不上读取的速度,所以为了提升写入的速度,决定采用批量处理的方法,事例代码:
@Override public Boolean call() { long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); this.isRunning.set(true); try { cyclicBarrier.await(); int lineNum = 0; int commitCount = 0; // 缓存数量 List<RowData> tmpRowDataList = new ArrayList<RowData>();// 缓存数组 while (this.isGetDataRunning.get() || this.queue.size() > 0) { // 从队列获取一条数据 RowData rowData = this.queue.poll(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); if (rowData == null) { logger.info("this.isGetDataRunning:" + this.isGetDataRunning + ";this.queue.size():" + this.queue.size()); Thread.sleep(10000); continue; } // 添加到缓存数组 tmpRowDataList.add(rowData); lineNum++; commitCount++; if (commitCount == SyncConstant.INSERT_SIZE) { this.insertContractAch(tmpRowDataList); // 批量写入 tmpRowDataList.clear(); // 清空缓存 commitCount = 0; } if (lineNum % SyncConstant.LOGGER_SIZE == 0) { logger.info(" commit line: " + lineNum + "; queue size: " + queue.size()); } } this.insertContractAch(tmpRowDataList); // 批量写入 tmpRowDataList.clear();// 清空缓存 logger.info(" commit line end: " + lineNum); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error(" submit data error" , e); } finally { this.isRunning.set(false); } logger.info(String.format("SubmitDataToDatabase used %s second times", (System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTime) / 1000.00)); return true; } /** * 批量插入数据 * * @param rowDatas * @return */ public int insertContractAch(List<RowData> rowDatas) { final List<RowData> tmpObjects = rowDatas; String sql = SqlService.createInsertPreparedSql(tableMetaData); // 获取sql try { int[] index = this.jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, new PreparedStatementSetter(tmpObjects, this.columnMetaDataList)); return index.length; } catch (Exception e) { logger.error(" insertContractAch error: " , e); } return 0; } /** * 处理批量插入的回调类 */ private class PreparedStatementSetter implements BatchPreparedStatementSetter { private List<RowData> rowDatas; private List<ColumnMetaData> columnMetaDataList; /** * 通过构造函数把要插入的数据传递进来处理 */ public PreparedStatementSetter(List<RowData> rowDatas, List<ColumnMetaData> columnList) { this.rowDatas = rowDatas; this.columnMetaDataList = columnList; } @Override public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, int i) throws SQLException { RowData rowData = this.rowDatas.get(i); for (int j = 0; j < rowData.getColumnObjects().length; j++) { // 类型转换 try { ColumnAdapterService.setParameterValue(ps, j + 1, rowData.getColumnObjects()[j], this.columnMetaDataList.get(j).getType()); } catch (Exception e) { ps.setObject(j + 1, null); } } } }
咱们不是需要讲解代码,所以这里截取了代码片段,全部的代码github上有,感兴趣的同学可以看看。PreparedStatement的好处,可以参考文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/liqiu/p/3825544.html
由于增加批量插入的功能,终于速度提升到每秒1000条
2、多线程优化
每秒1000条,速度依然不理想,特别是写的速度跟不上读取的速度,队列是满的,如图:

所以只能提升消费者的数量,采用了多消费者的模式:

速度提升到每秒3000条。
3、升级读取方式
这时候观察,随着消费者的增加,观察缓存队列经常有空的情况,也就是说生产跟不上消费者速度,如果增加生产者的线程,那么也会增加程序的复杂性,因为势必要将读取的数据进行分割。所以采用Pgdump的方式直接获取数据(并不是所有情况都适用,比如数据中有特殊的分隔符与设定的分隔符一样,或者有分号,单引号之类的)
代码片段如下:
/** * 将数据放入缓存队列 */ public void putCopyData() { DataSourceMetaData dataSource = dataSourceService.getDataSource(syncOptions.getSrcDataSourceName()); String copyCommand = this.getCopyCommand(dataSource, querySql); //获取copy命令 ShellExecuter.execute(copyCommand, queue,columnMetaDatas); } /** * 执行copy的shell命令 * @param dataSource * @param sql * @return */ public String getCopyCommand(DataSourceMetaData dataSource, String sql){ String host = dataSource.getIp(); String user = dataSource.getUserName(); String dataBaseName = dataSource.getDatabaseName(); //String psqlPath = "/Library/PostgreSQL/9.3/bin/psql"; String psqlPath = "/opt/pg93/bin/psql"; String execCopy = psqlPath + " -h " + host + " -U " + user + " " + dataBaseName +" -c \"COPY (" + sql + ") TO STDOUT WITH DELIMITER E'"+ HiveDivideConstant.COPY_COLUMN_DIVIDE+"' CSV NULL AS E'NULL'\" "; // 执行copy命令 LOGGER.info(execCopy); return execCopy; }
意思就是通过执行一个Shell程序,获取数据,然后读取进程的输出流,不断写入缓存。这样生产者的问题基本都解决了,速度完全取决于消费者写入数据库的速度了。下面是执行Shell的Java方法代码:
public static int execute(String shellPath, LinkedBlockingQueue<RowData> queue, List<ColumnMetaData> columnMetaDatas) { int success = -1; Process pid = null; String[] cmd; try { cmd = new String[]{"/bin/sh", "-c", shellPath}; // 执行Shell命令 pid = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd); if (pid != null) { BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(pid.getInputStream()), SyncConstant.SHELL_STREAM_BUFFER_SIZE); try { String line; while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { // LOGGER.info(String.format("shell info output [%s]", line)); String[] columnObjects = line.split(HiveDivideConstant.COPY_COLUMN_DIVIDE.toString(), -1); if (columnObjects.length != columnMetaDatas.size()) { LOGGER.error(" 待同步的表有特殊字符,不能使用copy [{}] ", line); throw new RuntimeException("待同步的表有特殊字符,不能使用copy " + line); } RowData rowData = new RowData(line.split(HiveDivideConstant.COPY_COLUMN_DIVIDE.toString(), -1)); queue.put(rowData); } } catch (Exception ioe) { LOGGER.error(" execute shell error", ioe); } finally { try { if (bufferedReader != null) { bufferedReader.close(); } } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("execute shell, get system.out error", e); } } success = pid.waitFor(); if (success != 0) { LOGGER.error("execute shell error "); } } else { LOGGER.error("there is not pid "); } } catch (Exception ioe) { LOGGER.error("execute shell error", ioe); } finally { if (null != pid) { try { //关闭错误输出流 pid.getErrorStream().close(); } catch (IOException e) { LOGGER.error("close error stream of process fail. ", e); } finally { try { //关闭标准输入流 pid.getInputStream().close(); } catch (IOException e) { LOGGER.error("close input stream of process fail.", e); } finally { try { pid.getOutputStream().close(); } catch (IOException e) { LOGGER.error(String.format("close output stream of process fail.", e)); } } } } } return success; }
4、内存优化
在上线一段时间之后,发现两个问题:1、使用Jdbc方式获取数据,如果这个数据表比较大,那么获取第一条数据的速度特别慢;2、这个进程还会占用非常大的内存,并且GC不掉。分析原因,是Postgresql的Jdbc获取数据的时候,会一次将所有数据放入到内存,如果同步的数据表非常大,那么甚至会将内存撑爆。
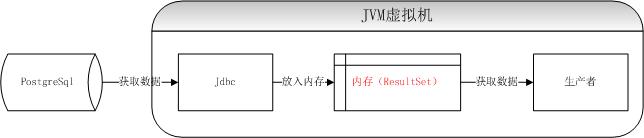
那么优化的方法是设置使Jdbc不是一次全部将数据拿到内存,而是批次获取,代码如下:
con.setAutoCommit(false); //并不是所有数据库都适用,比如hive就不支持,orcle不需要 stmt.setFetchSize(10000); //每次获取1万条记录
整体设计方案:

现在这个项目已经开源,代码放在:https://github.com/autumn-star/synchronous



