[LeetCode] 407. Trapping Rain Water II 收集雨水 II
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map: [ [1,4,3,1,3,2], [3,2,1,3,2,4], [2,3,3,2,3,1] ] Return 4.
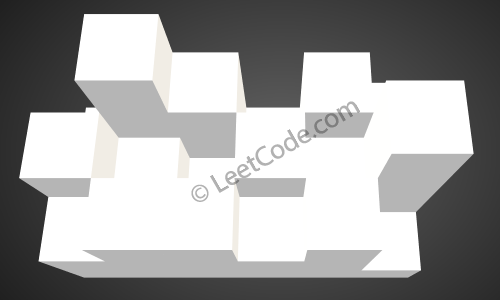
The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before the rain.
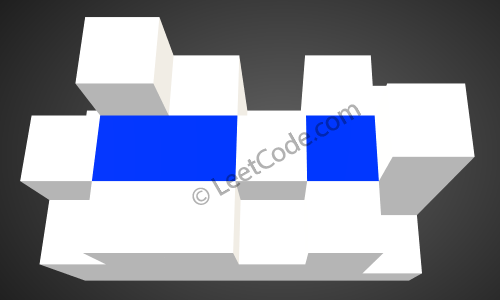
After the rain, water is trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
42. Trapping Rain Water的拓展,由2D变3D了。解法跟之前的完全不同了,之前那道题由于是二维的,我们可以用双指针来做,而这道三维的,我们需要用BFS来做。
Java: Priority Queue
public class Solution {
public class Cell {
int row;
int col;
int height;
public Cell(int row, int col, int height) {
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
this.height = height;
}
}
public int trapRainWater(int[][] heights) {
if (heights == null || heights.length == 0 || heights[0].length == 0)
return 0;
PriorityQueue<Cell> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(1, new Comparator<Cell>(){
public int compare(Cell a, Cell b) {
return a.height - b.height;
}
});
int m = heights.length;
int n = heights[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
// Initially, add all the Cells which are on borders to the queue.
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
visited[i][0] = true;
visited[i][n - 1] = true;
queue.offer(new Cell(i, 0, heights[i][0]));
queue.offer(new Cell(i, n - 1, heights[i][n - 1]));
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
visited[0][i] = true;
visited[m - 1][i] = true;
queue.offer(new Cell(0, i, heights[0][i]));
queue.offer(new Cell(m - 1, i, heights[m - 1][i]));
}
// from the borders, pick the shortest cell visited and check its neighbors:
// if the neighbor is shorter, collect the water it can trap and update its height as its height plus the water trapped
// add all its neighbors to the queue.
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
int res = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Cell cell = queue.poll();
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int row = cell.row + dir[0];
int col = cell.col + dir[1];
if (row >= 0 && row < m && col >= 0 && col < n && !visited[row][col]) {
visited[row][col] = true;
res += Math.max(0, cell.height - heights[row][col]);
queue.offer(new Cell(row, col, Math.max(heights[row][col], cell.height)));
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
Python:
from heapq import heappush, heappop
class Solution(object):
def trapRainWater(self, heightMap):
"""
:type heightMap: List[List[int]]
:rtype: int
"""
m = len(heightMap)
if not m:
return 0
n = len(heightMap[0])
if not n:
return 0
is_visited = [[False for i in xrange(n)] for j in xrange(m)]
heap = []
for i in xrange(m):
heappush(heap, [heightMap[i][0], i, 0])
is_visited[i][0] = True
heappush(heap, [heightMap[i][n-1], i, n-1])
is_visited[i][n-1] = True
for j in xrange(n):
heappush(heap, [heightMap[0][j], 0, j])
is_visited[0][j] = True
heappush(heap, [heightMap[m-1][j], m-1, j])
is_visited[m-1][j] = True
trap = 0
while heap:
height, i, j = heappop(heap)
for (dx, dy) in [(1,0), (-1,0), (0,1), (0,-1)]:
x, y = i+dx, j+dy
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n and not is_visited[x][y]:
trap += max(0, height - heightMap[x][y])
heappush(heap, [max(height, heightMap[x][y]), x, y])
is_visited[x][y] = True
return trap
C++:
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
if (heightMap.empty()) return 0;
int m = heightMap.size(), n = heightMap[0].size(), res = 0, mx = INT_MIN;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> q;
vector<vector<bool>> visited(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
vector<vector<int>> dir{{0,-1},{-1,0},{0,1},{1,0}};
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1) {
q.push({heightMap[i][j], i * n + j});
visited[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
auto t = q.top(); q.pop();
int h = t.first, r = t.second / n, c = t.second % n;
mx = max(mx, h);
for (int i = 0; i < dir.size(); ++i) {
int x = r + dir[i][0], y = c + dir[i][1];
if (x < 0 || x >= m || y < 0 || y >= n || visited[x][y]) continue;
visited[x][y] = true;
if (heightMap[x][y] < mx) res += mx - heightMap[x][y];
q.push({heightMap[x][y], x * n + y});
}
}
return res;
}
};
类似题目:
[LeetCode] 42. Trapping Rain Water 收集雨水
All LeetCode Questions List 题目汇总



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号