福大软工1816 · 第二次作业 - 个人项目
福大软工1816 · 第二次作业 - 个人项目
Github传送门
PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 10 | 30 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 10 | 10 |
| Development | 开发 | 60 | 60 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 120 | 120 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 30 | 30 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 30 | 30 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 30 | 30 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 30 | 30 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 240 | 600 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 30 | 60 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 15 | 15 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 60 |
| Test Repor | 测试报告 | 10 | 10 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 5 | 5 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 20 |
| | 合计 | 700|1110
解题思路
1.文件读写
既然是要从文件中读取单词并统计数量,并将它们按要求输出到指定的文件中,肯定要了解文件读写的过程和细节。主要用到的是C++的fstream类。
2.单词的统计
先将文件中的所有内容读入一个字符串,根据要求把他们分成各个单词,并判断单词是否符合要求,再把他们统一小写。如果符合要求,则将他们存入一个字典,如果在文本中重复出现一个单词,则它对应的个数+1。
3.行数的统计
忽略换行符、制表符等空白字符,进行行数统计。
实现过程
为了实现上述功能,我写了5个类
- Ascii //用于统计字符以及行数
int countAscii(string pth); //计算总字符数
int countLine(string pth); //计算总行数
- Check //用于检查字符和单词的有效性
bool check_isChar(char s1); //判断是否是字符
bool check_isVal(char s1); //判断是否是合法字符
bool check(string str); //判断是否是合法单词
void testfile(string str); //判断是否能够正确读入文件名并将之打开
- Word //用于统计单词数量
unordered_map<string, int> count_Word(string fname, unordered_map<string, int> strMap); //统计单词并将他们存入字典
- Frequency //用于统计所有单词的频率
unordered_map<string, int> count_Frequency(string strTmp, unordered_map<string, int> strMap); //统计单词频率并将它们存入字典
void output_Frequency(string fname, unordered_map<string, int> strMap); //按要求将前10的单词输出至文件
- File //将结果输出至指定文本
void file_output(string input_fname, string output_fname);
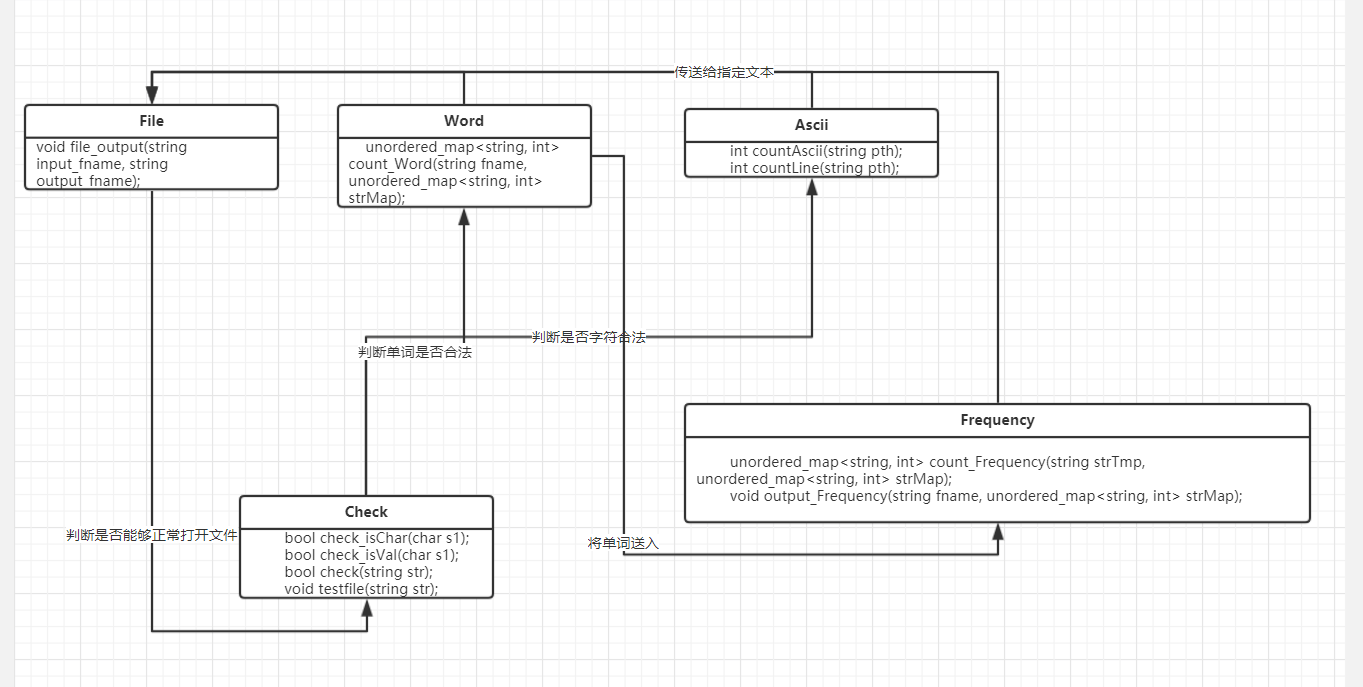
算法的关键
统计单词
while (getline(file, str)) //读入文本内容
{
strfile.append(str);
strfile.append(" ");
str.clear();
}
for (int i = 0; i < strfile.length(); i++)
{
if (!mycheck.check_isVal(strfile[i]))
strfile[i] = ' '; //符号位替换成为空格
}
transform(strfile.begin(), strfile.end(), strfile.begin(), ::tolower);
istringstream stream(strfile);
string word;
while (stream >> word) //从字节流中读取单词
{
if (mycheck.check(word))
{
strMap = myfrequence.count_Frequency(word, strMap);
}
}
用字典将有效的单词存起来,并根据要求写出排序的判断函数
typedef pair<string, int> PAIR;
unordered_map<string, int> strMap
static bool cmp_my_value(const PAIR& lhs, const PAIR& rhs)
{
if (lhs.second != rhs.second) //如果词频不一样,按照词频大优先
{
return lhs.second > rhs.second;
}
else //如果词频一样,按照字典序优先
{
return lhs.first < rhs.first;
}
}
unordered_map<string, int> Frequence::count_Frequency(string strTmp, unordered_map<string, int> strMap)
{
unordered_map<string, int>::iterator it = strMap.find(strTmp);
if (it == strMap.end()) //strMap中如果不存在当前单词则插入一个新键值对,出现频率为1
{
strMap.insert(unordered_map<string, int>::value_type(strTmp, 1));
}
else //如果存在则出现频率+1
strMap[strTmp]++;
return strMap;
}
计算模块接口部分的性能
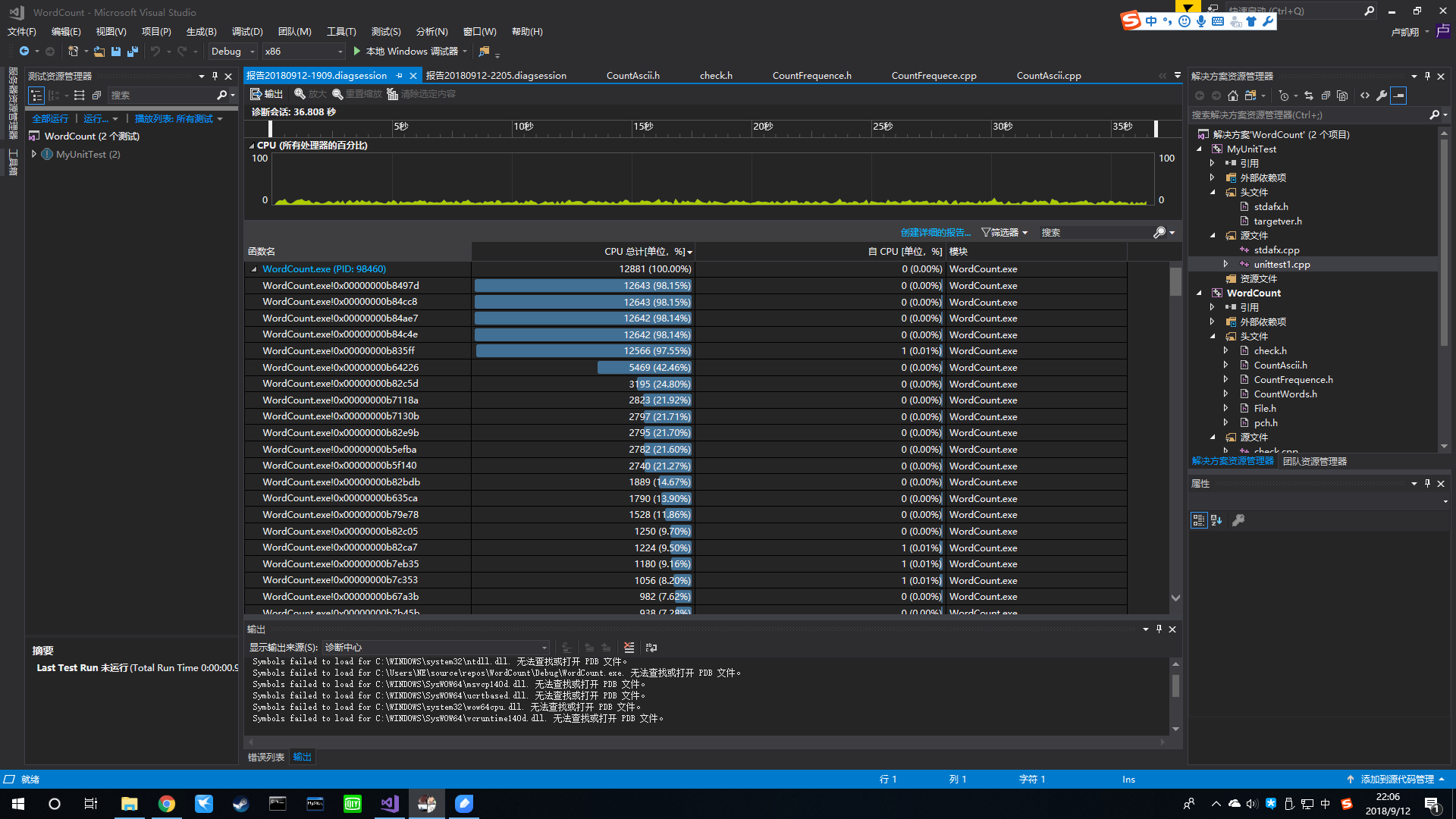
计算模块部分单元测试(部分)
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CppUnitTest.h"
#include "../WordCount/CountAscii.h"
#include "../WordCount/CountWords.h"
#include "../WordCount/File.h"
using namespace Microsoft::VisualStudio::CppUnitTestFramework;
namespace CountAsciiTest //用于对字符数量的统计
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
Ascii test_ascii;
int count = test_ascii.countAscii("countascii.txt");
Assert::IsTrue(count == 28);
}
};
}
namespace CountLineTest //用于测试对空白行的技术
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
Ascii test_ascii;
int count = test_ascii.countLine("countline.txt");
Assert::IsTrue(count == 0);
}
};
}
namespace FileTest //用于对空文件名的测试
{
TEST_CLASS(UnitTest1)
{
public:
TEST_METHOD(TestMethod1)
{
// TODO: 在此输入测试代码
Ascii test_ascii;
int count = test_ascii.countAscii("1.txt");
Assert::IsTrue(count == 0);
}
};
}
代码覆盖率
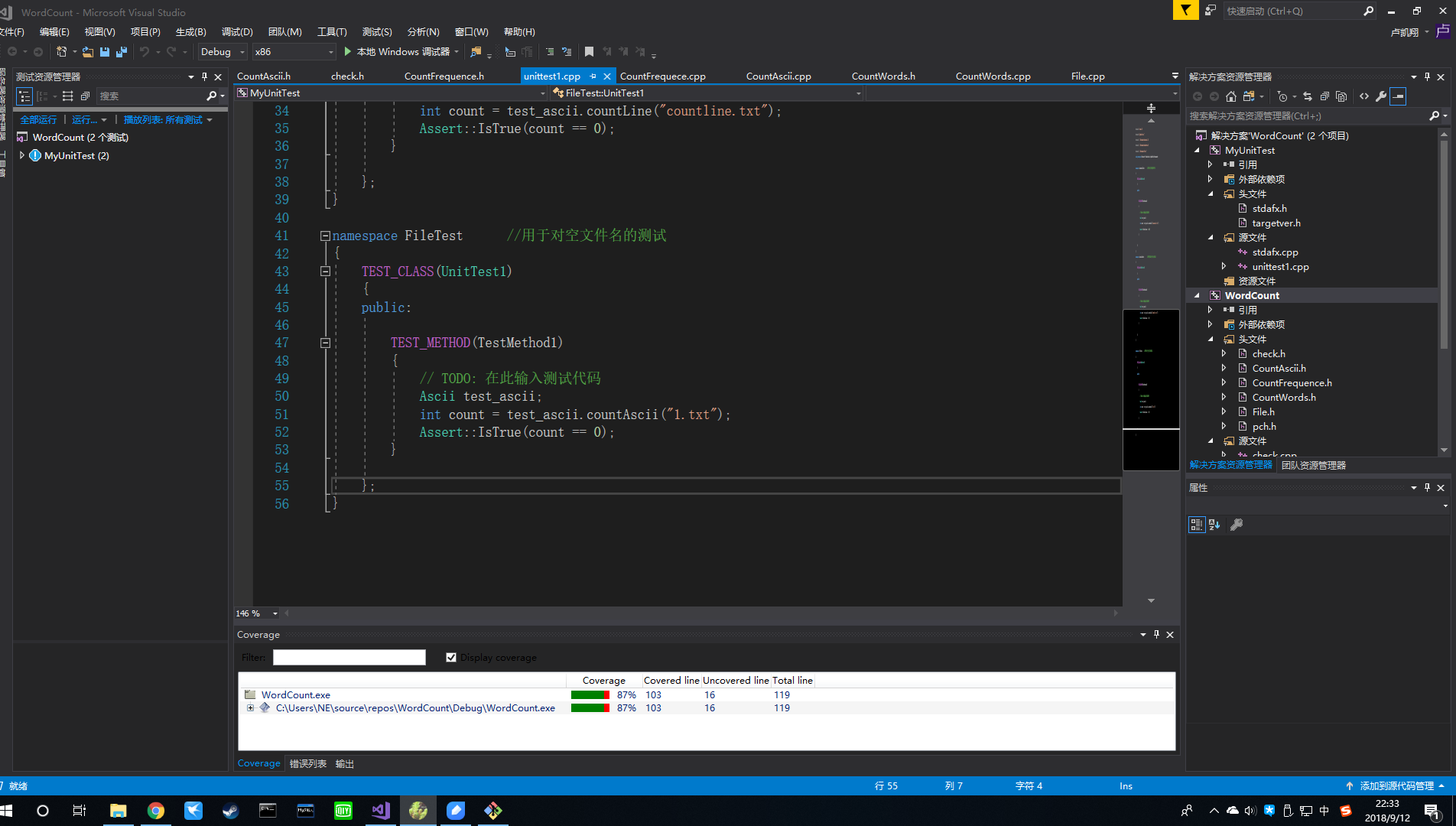
代码覆盖率为87%
异常处理说明
在文件读入失败的时候,会出现提示。
if (!file)
{
cout << "不存在这个文件或者文件未打开,请重新输入!" << endl;
exit(0);
}
作业心得
- 由于上半年都在使用python编程,对C++的编程已经有些生疏,有时甚至会忘记定义变量类型。导致编码速度较慢。
- 没有比较合理安排项目时间,导致时间有些紧张,以至于有些代码可读性不是很好。
- 在编码之前仔细地构想该如何实现,确实可以提高编码效率。



