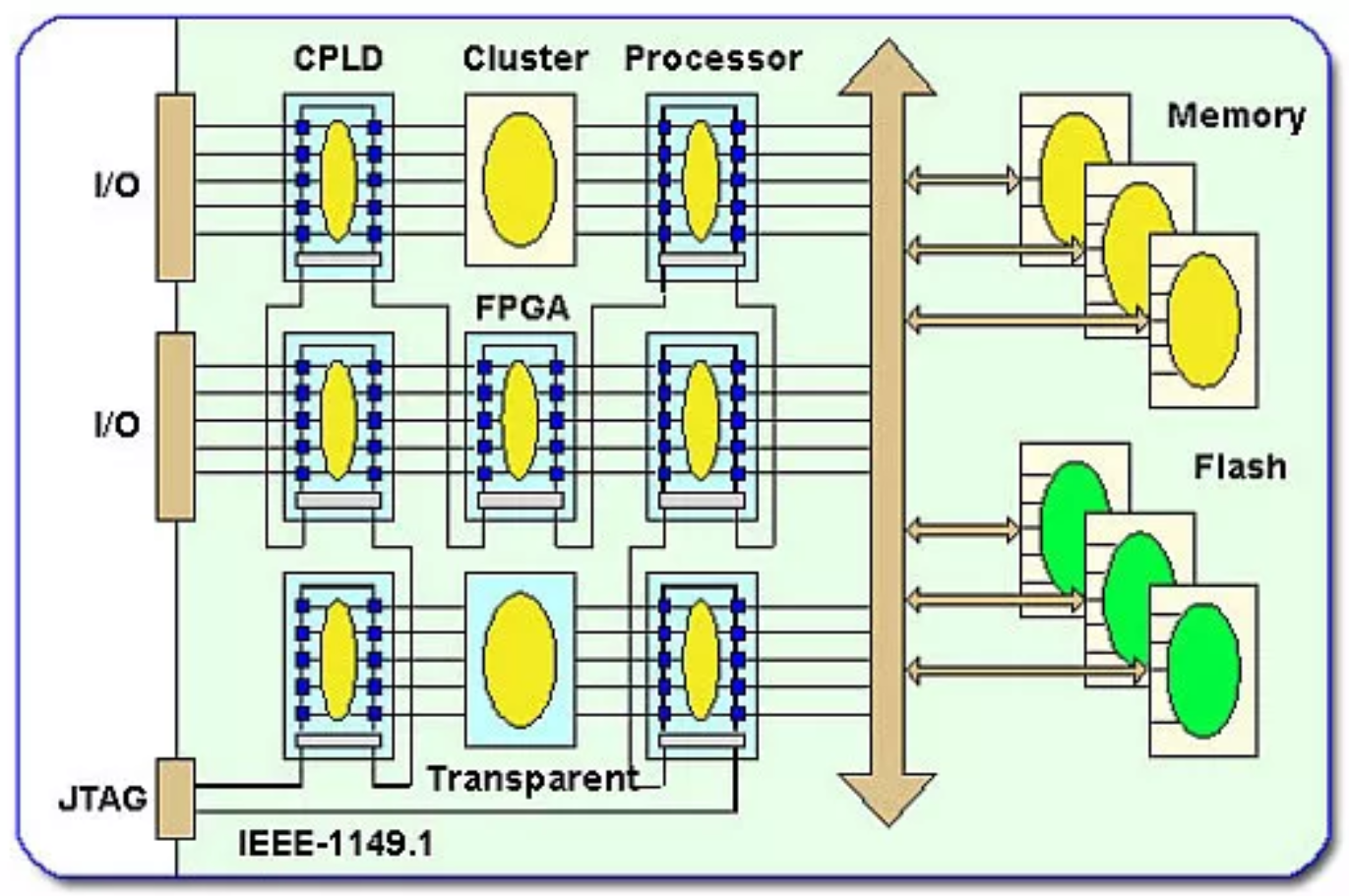
1. Boundary Scan
A:Boundary scan 顾名思义,是附加在芯片I/O 周边的扫描测试链,它通过专门的测试端口(TAP)访问。在测试模式下,边界扫描链会接管功能逻辑,对I/O进行灵活访问。边界扫描链的结构,测试端口,以及其控制器(TAP Controller),被IEEE定为标准协议(IEEE 1149), 也称做JTAG. 边界扫描链最早应用于印刷电路板上芯片间的互联测试, 后来也广泛应用于生产测试中对芯片管脚的测试。
MBIST Memory内建自测试:
A:MBIST是指在电路中加入针对Memory的自测试电路。在测试模式下,它会接管功能逻辑对memory的控制,依据特定算法,对memory进行读写测试操作,判断Memory是否有制造缺陷。至于面临的挑战,从以下几个方面来探讨:
-
对于Memory Vendor来说, 在新工艺下,memory可能会有新的失效机制,如何设计有效的MBIST 算法是一项重要的研究课题。
-
从EDA角度看,目前业界工具对常规memory (SRAM, ROM, Register File等)的支持已相对成熟。芯片公司对EDA 提供针对特殊类型的memory (如TCAM, DRAM )的测试方案的需求正日渐迫切。
-
从芯片实现的角度看,设计者需要考虑如何使得MBIST逻辑对芯片PPA的影响最小。对于使用带Redundacy Memory的design来说,要考虑自修复(self-repair),也会增加设计和验证的难度。
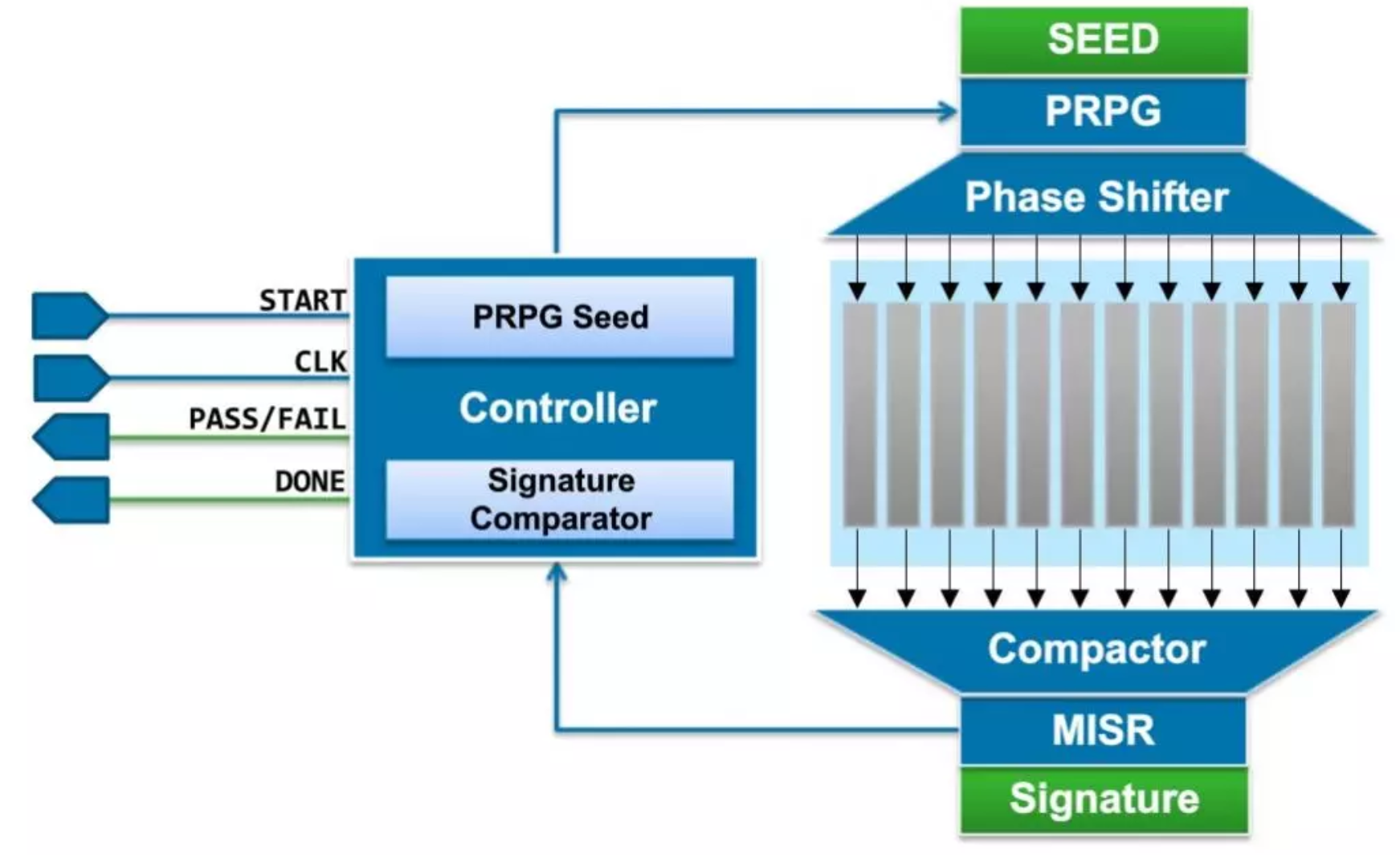
Logic Bist:
LBIST (Logic Built-In Self Test)是针对逻辑电路的自测试。测试激励由片上 PRPG (Pseudo-randompattern generation) 来产生。输出响应通过 MISR(Multiple Input Signature Register)来压缩,最后对得到的特征值进行比对。LBIST 多应用于对可靠性要求较高的芯片(如汽车电子,工业级应用)的系统自检测试。LBIST产生的激励是随机的,所以天生的缺陷是测试覆盖率不充分,通过在设计中增加测试点(Test Point Insertion)可以在一定程度上得到改善。
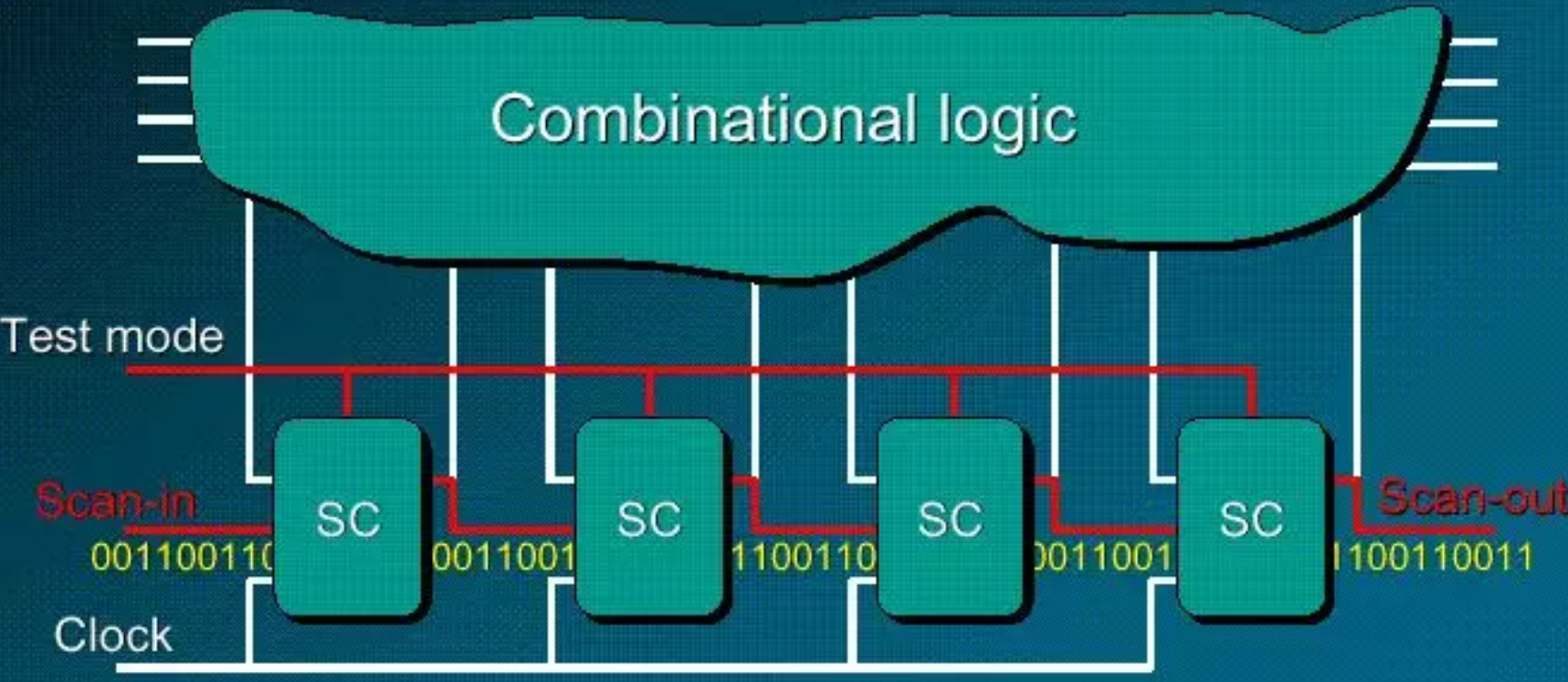
scan chain stuck-at, at-speed:
A:业界有两种 SCAN Style: LSSD 和MUX-D. 普遍使用的是MUX-D的扫描方式。所谓MUX-D, 是指在D触发器的数据端增加了一个MUX, 可以选择数据是从 D 输入,还是测试专用的SDI输入。 在测试模式下, MUX-D Flop 被配置成若干条移位寄存器,也就是扫描链。通过这些扫描链,内部寄存器可以被移位设置成想要的状态(scan load) ;同样的方式,内部寄存器的状态也可以被移位出来(scan unload),进行观测。
Stuck-at Test 也叫做Static Test, DC Test。它是针对制造工艺中 Stuck-at 类型失效机制的测试。Stuck-at是最基本的一种失效机制, 比如某个net短路到Ground,就叫做Stuck-at-0 Fault。某个net短路到VDD,就叫做Stuck-at-1Fault。
Transition fault 是对timing path 的 slow-to-rise 或 slow-to-fall失效机制的表诉。对其测试时需要至少两个at-speed 时钟,一个是Lauch clock, 另一个是Capture clock,At-speed测试在工艺进到90nm以下被广泛使用。
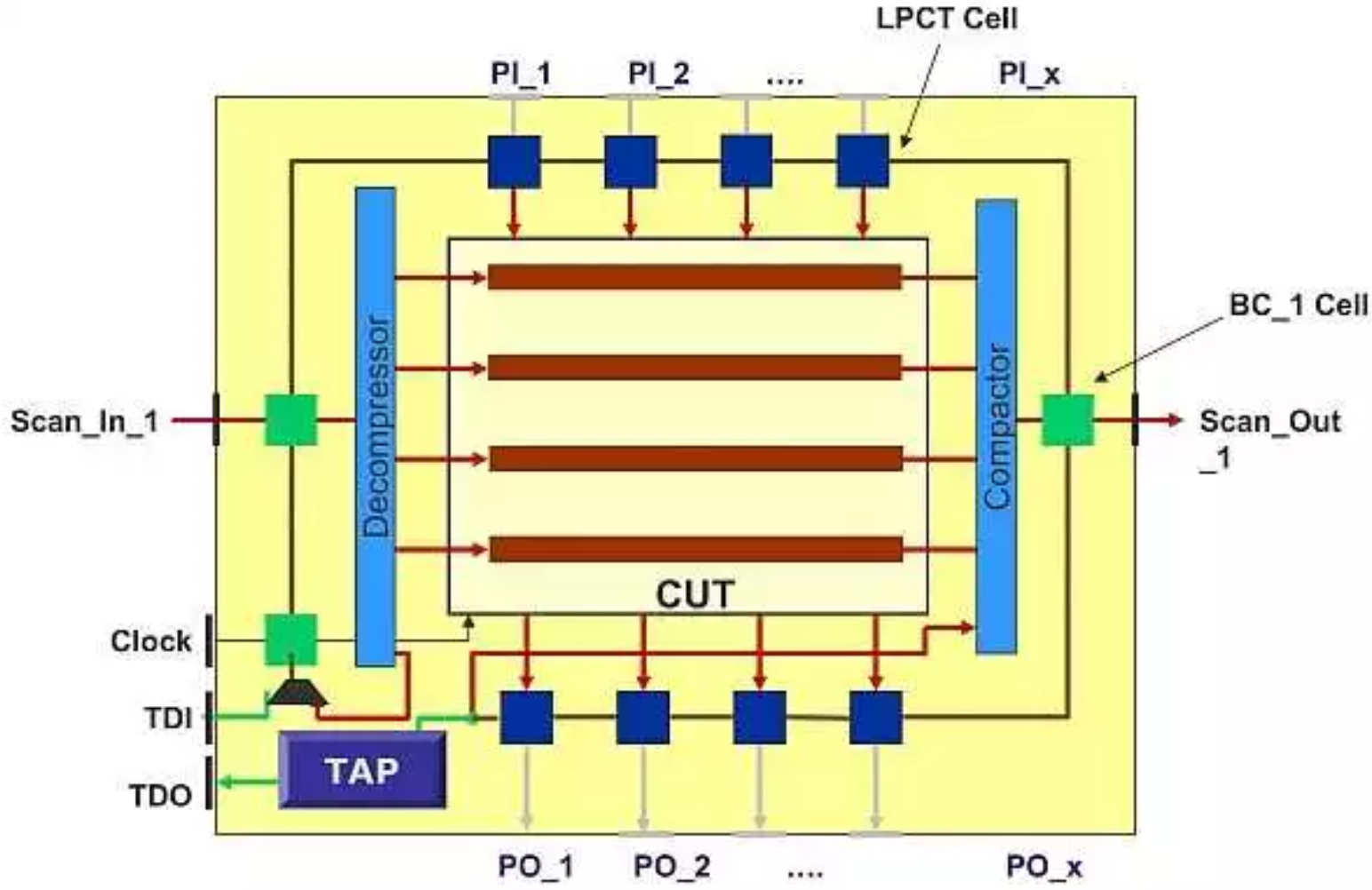
压缩和解压缩:
芯片设计规模愈来愈大,受到管脚数目的限制,传统的扫描链变得越来越长,导致测试时间无法承受。缩短扫描链, 增加扫描链的数目,是减少测试时间的根本手段,由此压缩解压缩技术应运而生。
但单方面地增加压缩率,并不意味着测试时间的线性递减。过高的压缩率反而会使得覆盖率降低,测试时间变长,得不尝失。压缩比的高低受到 compression 架构的限制,目前业界卓越的 compression 架构可以做到几百甚至上千的压缩比。但为什么绝大多数设计公司止步于100-200X的压缩比?
更重要的一个因素是过高的压缩比会带来严重的绕线拥堵,对物理实现带来挑战。
Cadence的Physcial Aware Compression 技术对此提供了完美的解决方案。
ATPG:
ATPG (AutomaticTest Pattern Generation) 指工具应用相应算法产生测试向量的过程,它广泛应用于生产测试中对逻辑电路的测试。ATPG算法研究的是,针对电路中的故障,如何激发故障、观测故障效应等。教科书级别的算法有D算法和PODEM等。各EDA厂商ATPG算法的差异性主要是由不同的 Compression 架构导致。不同的工具竞相追逐的主要目标是在达到相同测试覆盖率的前提下,谁的测试时间最短,从而为客户节省成本。ATPG工具的runtime也是评价ATPG工具的重要指标之一。
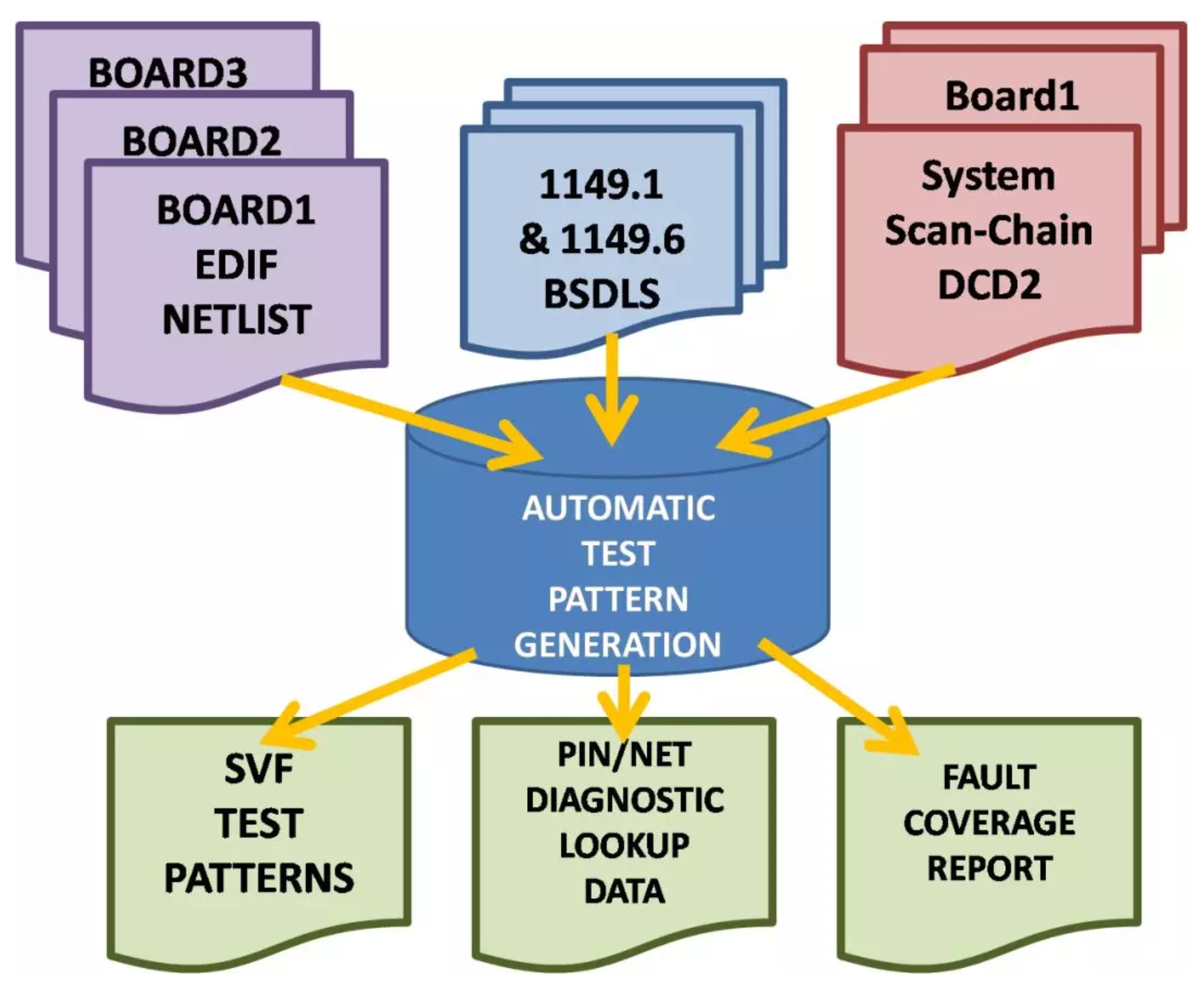
测试时间:
A:ATE测试程序会分别针对芯片IO, 逻辑电路, Memory 以及模拟电路进行全面的测试。测试数据量的大小, 测试向量运行频率,如何最大限度的并行测试,都是影响测试时间的重要因素。同时,在测试机台上尽可能做Multi-site 测试, 即多块芯片同时测试,也是缩短平均测试时间,降低成本的重要手段。
OCC/OPCG/scan clock mux:
A:芯片的运行速度愈来愈快,从几十兆赫兹,到几百兆赫兹,再到几个Giga赫兹。但测试机台的发展却相对滞后(一般在一两百兆左右), 这就需要利用片上PLL提供at-speed测试时钟。
OCC (On-Chip Clock) 或 OPCG (On-Product Clock Gating)是为了做at-speed测试,在设计中增加的时钟控制模块。它的基本原理是在 scan shift 模式下, 选通慢速的ATE 时钟,load 或 unload 扫描链; 在 capture 模式下,对 free-running PLL clock 过滤筛选出 lauch 和 capture clock 进行at-speed 测试
MBIST RTL vs Gate:
A:很多芯片设计公司都偏爱 MBIST RTL flow, 其中很重要的一个原因,就是在设计早期,可以在 RTL Level 做MBIST的快速验证。
Gate Level MBIST flow 则可以提供很高的自动化程度 。综合工具可以对设计中用到的所有 Memory 有一个全局把控,根据时钟域,Floorplan, power domain, memory power consuption等因素合理地对Memory分组, 自动制定Test plan。
DFT 标准:
IEEE1149:Standard Test Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture
The IEEE 1149.1 standard defines test logic that can be included in an integrated circuit to provide standardized approaches to
-
testing the interconnections between integrated circuits once they have been assembled onto a printed circuit board or other substrate;
-
testing the integrated circuit itself;
-
observing or modifying circuit activity during the component's normal operation.
The test logic consists of a boundary-scan register and other building blocks and is accessed through a Test Access Port (TAP).
IEEE1500:Standard for Embedded Core Test
IEEE Std 1500 is a scalable standard architecture for enabling test reuse and integration for embedded cores and associated circuitry. It foregoes addressing analog circuits and focuses on facilitating efficient test of digital aspects of systems on chip (SoCs). IEEE Std 1500 has serial and parallel test access mechanisms (TAMs) and a rich set of instructions suitable for testing cores, SoC interconnect, and circuitry. In addition, IEEE Std 1500 defines features that enable core isolation and protection. IEEE Std 1500 will reduce test cost through improved automation, promote good design-for-test (DFT) technique, and improve test quality through improved access.
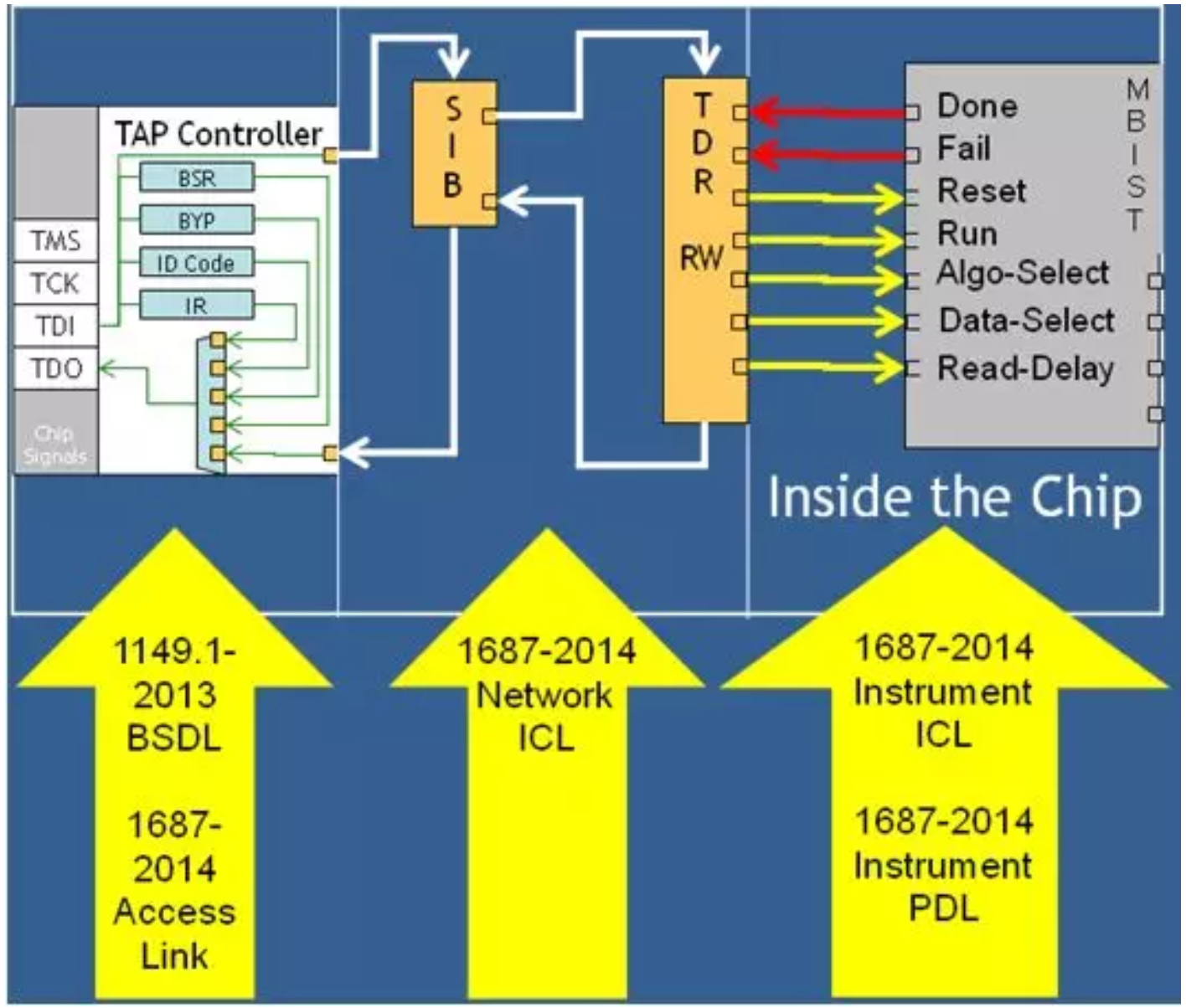
IEEE1687:Standard for Access and Control of Instrumentation Embedded within a Semiconductor Device.
This standard develops a methodology for access to embedded instrumentation, without defining the instruments or their features themselves, via the IEEE 1149.1(TM) test access port (TAP) and additional signals that may be required. The elements of the methodology include a description language for the characteristics of the features and for communication with the features, and requirements for interfacing to the features.
IEEE1838:Standard for Test Access Architecture for 3-D Stacked Integrated Circuits.
For 3D-SICs, three parties are involved: Die Maker(s), Stack Maker(s), and Stack User(s). All circuit features of the stack are included in the individual die designs. Design and integration of test access features needs to be done by the Die Maker(s), not only to serve their own (pre-stacking) test objectives, but also to serve test objectives of Stack Maker and Stack User. After stacking, test (control and data) signals need to be able to travel from the stack's external I/Os up and down through the stack. Hence, the test access features in the various dies of the stack need to function in a concerted and interoperable fashion. Different dies might have their own technologies, design set-up, and test and design-for-test approaches; the standard should not modify those. The standard defines test access features for a die that enable the transportation of test stimuli and responses both for testing THIS DIE and its inter-die connections, as well as for testing OTHER DIES in the stack and their inter-die connections.
DFT 发展趋势:
A:取决于芯片的应用领域,DFT 发展趋势、侧重点会有所不同。
-
对于Mix-signal 的设计, 受到芯片管脚较少的限制, 如何做 low-Pin-Count Test是一个挑战;
-
对于汽车电子而言,出于安全考虑,设计者考虑更多的则是如何将测试覆盖率做到极致;
-
消费电子的规模愈来愈大,受到芯片管脚数目,ATPG runtime 以及测试功耗等因素的约束,传统的 Flat-ATPG 已不再适用。 层次化测试 (Hierarchical Test) 成为主流。 层次化测试不仅可以允许不同模块灵活分组测试,而且在block level 产生的测试向量可以在顶层复用,减少ATPG的 runtime;
-
另外,一些新技术的出现,如3D Stack Die, 如何做 TSV test, 也给DFT带来新的课题。
新工艺挑战:
A:当工艺进步到28nm以下时,业内有不少声音指出 Cell Aware Model 可以帮助减少testescape,提升DPPM。通常的Fault Model是在Standard Cell level 对fault 建模, 所谓的 Cell Aware Model 是指在 transistor level 对fault 建模。 至于在最新工艺10nm, 7nm及以下,需要什么样的fault model, 还是需要大数据说话,让我们拭目以待。



