Spring Framework源代码解析之IOC容器(二)
2012-05-22 16:06 飘扬的红领巾 阅读(1984) 评论(1) 编辑 收藏 举报在上文(Spring Framework源代码解析之IOC容器(一))中,我们简单了解了Spring的IOC特性,但对Spring相关源码没有做详细的分析,本文将对支持IOC特性的重要代码进行分析,有不对的地方请指正。
水桶的标准——BeanFactory
我们说Spring中包含了IOC的容器,倒不如说它包含了一系列容器的集合,因为IOC容器不只一个,像ConfigurableBeanFactory、XmlBeanFactory、ApplicationContext都是IOC容器。它们就像一个个水桶,都能够装水(放置Java Bean),但外观、样式、使用场景可能有所不同,使用者可以根据自己的需求使用不同的“水桶”。但不管是哪个“水桶”,它们都会一些基本的功能,比如装水。所以我们发现这些容器它们都实现了一个相同的接口—— BeanFactory。BeanFactory定义了这些容器基本的功能,比如getBean、containsBean、isSingleton等等。
getBean是BeanFactory最重要一个方法,作用是从IOC容器中取得指定的Bean,它还有一个重载方法可以指定类型来获取Bean。
containsBean是用来判断容器中是否包含指定的Bean。
isSingleton是用来判断指定的Bean是否是单例类型的Bean。
……
这些方法指定了每一个容器都必须实现的一些功能,也是支持IOC容器的最基本功能。
BeanFactory源码清单:
public interface BeanFactory {
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
T getBean(String name, Class requiredType) throws BeansException;
T getBean(Class requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
boolean containsBean(String name);
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> targetType) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
说完水桶的标准,我们眼前出现各式各样的“水桶”,但有些水桶功能过于复杂,有些又实用性不好,我们得选一个经济实用的水桶来研究,XmlBeanFactory就是这样的水桶。
屌丝版水桶——XmlBeanFactory
之所以称为屌丝版,是因为XmlBeanFactory只提供了最基本的IOC容器的功能,从名字来看,这个IOC容器可以读取XML文件定义的BeanDefinition(XML文件中对bean的描述)。什么是BeanDefinition呢,我们说IOC容器是用来装对象的,而具体描述装了哪些对象,对象之间的依赖关系又是什么?则是用BeanDefinition来描述,可以结合XML文件来理解它。
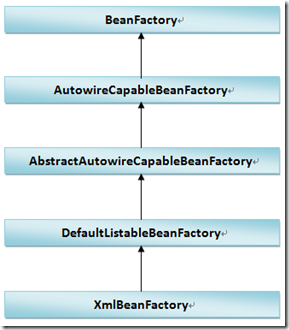
我们看一下XmlBeanFactory的继承关系:
BeanFactory不用说了,AutowireCapableBeanFactory、AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory最主要的功能就是实现bean创建方法createBean()。
T createBean(Class beanClass) throws BeansException;
接下来是DefaultListableBeanFactory,它很重要,很多容器都会继承它。从名字上看,它应该是一个默认的功能完备的BeanFactory,我们可以把它当做为水桶的半成品,功能健全,但使用的时候还需要包装。XmlBeanFactory就是包装它实现的一个基本容器。XmlBeanFactory除了包含DefaultListableBeanFactory的功能外,最重要的它支持以XML目录文件方式定义BeanDefinition。
XmlBeanFactory怎么读取Xml文件?
XmlBeanFactory源文件中,并看到读取Xml文件的具体实现,可见读取Xml文件并不是由XmlBeanFactory直接完成的。
XmlBeanFactory.java
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
/**
* Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given resource,
* which must be parsable using DOM.
* @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from
* @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
/**
* Create a new XmlBeanFactory with the given input stream,
* which must be parsable using DOM.
* @param resource XML resource to load bean definitions from
* @param parentBeanFactory parent bean factory
* @throws BeansException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}
我们注意到XmlBeanFactory.java开始实例化了一个XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象reader。实际上Xml文件的处理就是由这个reader来完成的。接着往下看XmlBeanFactory构造函数中需要一个Resource对象,它包含了BeanDefinition的信息,也就是在Xml配置文件当中的定义的Bean信息。Spring需要把它封装成Resource对象进行处理。
从XML文件读取Bean信息保存在Resource对象当中的方法:
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource( "application-context.xml");
有了Resource对象,reader执行loadBeanDefinitions方法。
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
就是这个方法从Resource载入BeanDefinition到读取器(XmlBeanDefinitionReader)中。
我们再来梳理一下XmlBeanFactory的整个流程:
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource( "application-context.xml"); DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory); reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
1)根据Xml配置文件创建Resource资源对象,该对象中包含了BeanDefinition的信息。
2)创建DefaultListableBeanFactory。
3)创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader读取器,用于载入BeanDefinition。之所以需要BeanFactory作为参数,是因为会将读取的信息回调配置给factory。
4)XmlBeanDefinitionReader执行载入BeanDefinition的方法,最后会完成Bean的载入和注册。完成后Bean就成功的放置到IOC容器当中,以后我们就可以从中取得Bean来使用。
水桶中的高帅富——ApplicationContext
如果说XmlBeanFactory是容器中的屌丝,ApplicationContext应该算容器中的高帅富,浏览一下ApplicationContext。
ApplicationContext.java
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
/**
* Return the unique id of this application context.
* @return the unique id of the context, or null if none
*/
String getId();
/**
* Return a friendly name for this context.
* @return a display name for this context (never null)
*/
String getDisplayName();
/**
* Return the timestamp when this context was first loaded.
* @return the timestamp (ms) when this context was first loaded
*/
long getStartupDate();
/**
* Return the parent context, or null if there is no parent
* and this is the root of the context hierarchy.
* @return the parent context, or null if there is no parent
*/
ApplicationContext getParent();
/**
* Expose AutowireCapableBeanFactory functionality for this context.
* This is not typically used by application code, except for the purpose
* of initializing bean instances that live outside the application context,
* applying the Spring bean lifecycle (fully or partly) to them.
* Alternatively, the internal BeanFactory exposed by the
* {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext} interface offers access to the
* AutowireCapableBeanFactory interface too. The present method mainly
* serves as convenient, specific facility on the ApplicationContext
* interface itself.
* @return the AutowireCapableBeanFactory for this context
* @throws IllegalStateException if the context does not support
* the AutowireCapableBeanFactory interface or does not hold an autowire-capable
* bean factory yet (usually if refresh() has never been called)
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#getBeanFactory()
*/
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
ApplicationContext是一个接口,它定义了一组实现高级IOC容器的标准,看看它的配置:
public interface ApplicationContext extends
EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {……}
比较XmlBeanFactory只继承DefaultListableBeanFactory,它显得豪华得多。可以看到它继承MessageSource,这样他支持不同的信息源,国际化实现也依赖它。它还继承ApplicationEventPublisher,这让它支持事件机制,可以利用它根据生命周期做更多的事……
总之ApplicationContext是一个高级形式的IOC容器,再以后的学习中它的出场率会很高,我们慢慢了解它。
小结
本问介绍了与IOC容器相关的基础类,主要为后面学习依赖注入做铺垫,下文将重点介绍依赖注入的详细实现。