Django的CBV与FBV
FBV
FBV(function base views) 就是在视图里使用函数处理请求。
在之前django的学习中,我们一直使用的是这种方式。
CBV

views.py from django.views import View class View: http_method_names = ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace'] @classmethod def as_view(cls, **initkwargs): def view(request, *args, **kwargs): # 实例化一个对象,对象名称为self,self是cls的对象,谁调用了cls # cls就是谁(当前调用cls的是BookView), # 所以,此时的self就是BookView的实例化对象 self = cls(**initkwargs) if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'): self.head = self.get # 此时的request对象指向原始的request对象 # 给self这个实例化对象赋值:原始的request self.request = request self.args = args self.kwargs = kwargs # 开始执行self.dispatch() return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) return view def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: # 通过getattr找到的属性,已经和对象绑定了,访问的时候不需要在指明对象了 # 不需要再:self.handler # 直接handler() handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed) else: handler = self.http_method_not_allowed return handler(request, *args, **kwargs) class BookView(View): def get(self, request): pass def post(self, request): pass urls.py from django.urls import path, include, re_path from classbasedview import views urlpatterns = [ re_path('books/$', views.BookView.as_view()), ] 1. 启动django:python manage.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8000 2. 加载settings 2.1 读取models.py 2.2 views.py 2.3 urls.py 2.3.1 开始执行as_views(): views.LoginView.as_view(), 返回view函数 2.3.2 此时url对应具体的某一个函数 2.4 开始等待用户请求(127.0.0.1:8000/books/) 2.5 开始执行view函数:view(request)
CBV(class base views) 就是在视图里使用类处理请求。
Python是一个面向对象的编程语言,如果只用函数来开发,有很多面向对象的优点就错失了(继承、封装、多态)。所以Django在后来加入了Class-Based-View。可以让我们用类写View。这样做的优点主要下面两种:
- 提高了代码的复用性,可以使用面向对象的技术,比如Mixin(多继承)
- 可以用不同的函数针对不同的HTTP方法处理,而不是通过很多if判断,提高代码可读性
使用class-based views
如果我们要写一个处理GET方法的view,用函数写的话是下面这样。
from django.http import HttpResponse
def my_view(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
return HttpResponse('OK')
如果用class-based view写的话,就是下面这样
from django.http import HttpResponse from django.views import View class MyView(View):
def get(self, request): return HttpResponse('OK')
Django的url是将一个请求分配给可调用的函数的,而不是一个class。针对这个问题,class-based view提供了一个as_view()静态方法(也就是类方法),调用这个方法,会创建一个类的实例,然后通过实例调用dispatch()方法,dispatch()方法会根据request的method的不同调用相应的方法来处理request(如get() , post()等)。到这里,这些方法和function-based view差不多了,要接收request,得到一个response返回。如果方法没有定义,会抛出HttpResponseNotAllowed异常。
在url中,就这么写:
# urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from myapp.views import MyView
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^index/$', MyView.as_view()),
]
类的属性可以通过两种方法设置,第一种是常见的Python的方法,可以被子类覆盖。
from django.http import HttpResponse
from django.views import View
class GreetingView(View):
name = "yuan"
def get(self, request):
return HttpResponse(self.name)
# You can override that in a subclass
class MorningGreetingView(GreetingView):
name= "alex"
第二种方法,你也可以在url中指定类的属性:
在url中设置类的属性Python
urlpatterns = [ url(r'^index/$', GreetingView.as_view(name="egon")), ]
使用Mixin
我觉得要理解django的class-based-view(以下简称cbv),首先要明白django引入cbv的目的是什么。在django1.3之前,generic view也就是所谓的通用视图,使用的是function-based-view(fbv),亦即基于函数的视图。有人认为fbv比cbv更pythonic,窃以为不然。python的一大重要的特性就是面向对象。而cbv更能体现python的面向对象。cbv是通过class的方式来实现视图方法的。class相对于function,更能利用多态的特定,因此更容易从宏观层面上将项目内的比较通用的功能抽象出来。关于多态,不多解释,有兴趣的同学自己Google。总之可以理解为一个东西具有多种形态(的特性)。cbv的实现原理通过看django的源码就很容易明白,大体就是由url路由到这个cbv之后,通过cbv内部的dispatch方法进行分发,将get请求分发给cbv.get方法处理,将post请求分发给cbv.post方法处理,其他方法类似。怎么利用多态呢?cbv里引入了mixin的概念。Mixin就是写好了的一些基础类,然后通过不同的Mixin组合成为最终想要的类。
所以,理解cbv的基础是,理解Mixin。Django中使用Mixin来重用代码,一个View Class可以继承多个Mixin,但是只能继承一个View(包括View的子类),推荐把View写在最右边,多个Mixin写在左边
CBV使用配置
路径url的配置
cbv 顾名知义就是通过类的方法来调用,我们在url中配置为如下路径
url(r'^cbv.html/', views.Cbv.as_view()),这里的Cbv是一个class 类,要想使用cbv方法,这个路径后面还得必须有一个as_view()这个是必须的固定格式
views里面函数的格式
在views里面配置类,需要导入一个模块
from django.views.generic import View #这个是导入的模块,原来的django版本从django.views 里面可以直接导入View,但是现在需要加一个generic才可以
class Cbv(View): #这里必须要继承View这个类,只有继承了这个url那里的as_view()才会有这个方法
def get(self,request):
return HttpResponse('cbv-get')
def post(self,request):
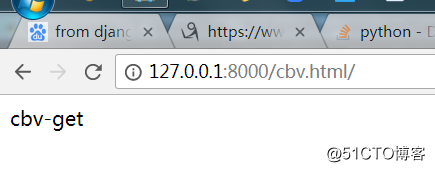
return HttpResponse('cbv-post')浏览器get方式访问
创建一个login登陆页面测试post方法
views配置
from django.views.generic import View
class Cbv(View):
def get(self,request):
# return HttpResponse('cbv-get')
return render(request,'login.html') #发送到login.html
def post(self,request):
return HttpResponse('cbv-post')login的页面配置代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>cbv学习</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/cbv.html/" method="post">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>浏览器访问查看点击提交后的结果
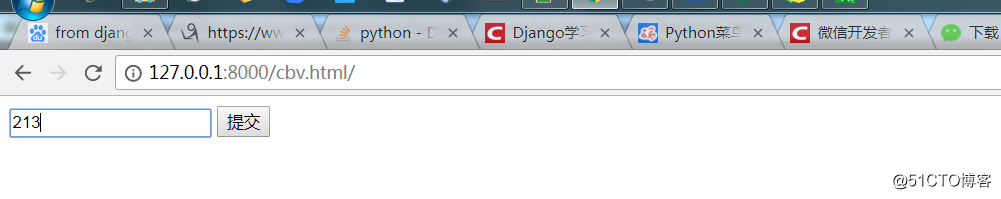
点击提交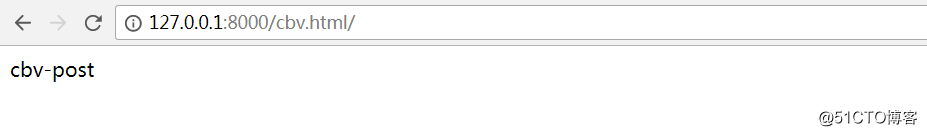
这里通过查看View的源码,可以看到里面会有很多种提交方法
http_method_names = ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace']
使用ajax的时候这些方法都是可以使用的。
另外继承类不光有View,还有很多的,查看源码就可以看到的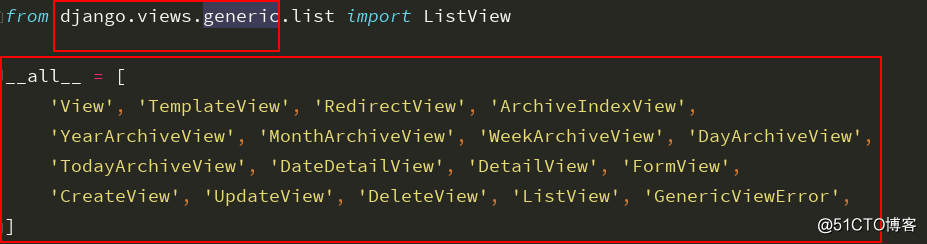
我的django版本号是
C:\Users\Tony>python3 -m django --version
1.9.13
cbv匹配原理
这种更具url来匹配方法的是通过反射方法(getattr)来做的。请求过来后先走dispatch这个方法,这个方法存在View类中。
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# Try to dispatch to the right method; if a method doesn't exist,
# defer to the error handler. Also defer to the error handler if the
# request method isn't on the approved list.
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
return handler(request, *args, **kwargs)定制dispatch
如果需要批量对方法,例如get,post等方法做一些操作的时候,这里我们可以手动写一个dispatch,这个dispatch就和装饰器的效果一样。因为请求来的时候总是先走的dispatch。
from django.views.generic import View
class Cbv(View):
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
print('操作前的操作')
obj = super(Cbv,self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
print('操作后的操作代码')
return obj
def get(self,request):
# return HttpResponse('cbv-get')
return render(request,'login.html')
def post(self,request):
return HttpResponse('cbv-post')这次我们在通过浏览器访问的时候,发现不管get或者post方法,都会走print代码,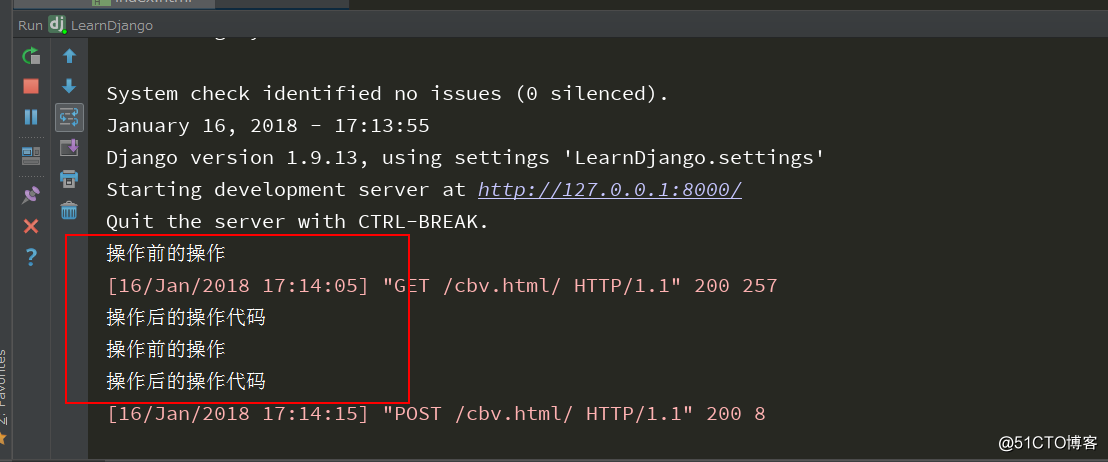
使用cbv实现视图

1 from django.views import View 2 from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator 3 4 5 class LoginView(View): 6 7 def get(self, request): 8 return render(request, "login.html") 9 10 def post(self, request): 11 user = request.POST.get("name") 12 pwd = request.POST.get("pwd") 13 if user == "safly" and pwd == "123": 14 # 登陆成功 15 # 写session 16 request.session["user2"] = user 17 request.session.set_expiry(5) 18 return redirect("/index/") 19 20 def index(request): 21 return render(request,"index.html")
CBV结合装饰器
直接加在视图类上,但method_decorator必须传 name 关键字参数

1 from django.views import View 2 from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator 3 4 5 def wrapper(func): 6 @wraps(func) 7 def inner(request, *args, **kwargs): 8 # 登录校验 9 cookie_k = request.session.get("user01", None) 10 if cookie_k: 11 # 表示已经登录的用户 12 ret = func(request, *args, **kwargs) 13 return ret 14 else: 15 # 滚去登录 16 return redirect("/login/") 17 18 return inner 19 20 21 class LoginView(View): 22 23 def get(self, request): 24 return render(request, "login.html") 25 26 def post(self, request): 27 user = request.POST.get("name") 28 pwd = request.POST.get("pwd") 29 if user == "safly" and pwd == "123": 30 # 登陆成功 31 # 写session 32 request.session["user01"] = user 33 # request.session.set_expiry(5) 34 return redirect("/index/") 35 36 37 @method_decorator(wrapper, name="get") 38 class IndexView(View): 39 def get(self, request): 40 user = request.session.get("user01", "游客") 41 return render(request, "index.html", {"user": user})
* 加在CBV视图的get或post方法上*

# @method_decorator(wrapper, name="get") class IndexView(View): @method_decorator(wrapper) def get(self, request): user = request.session.get("user02", "游客") return render(request, "index.html", {"user": user})
* 加在dispatch方法上*

1 # @method_decorator(wrapper, name="get") 2 class IndexView(View): 3 ## 这么写所有的请求方法都要做登录校验 4 @method_decorator(wrapper) 5 def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): 6 return super(IndexView,self).dispatch(request,*args,**kwargs) 7 8 # @method_decorator(wrapper) 9 def get(self, request): 10 user = request.session.get("user04", "游客") 11 return render(request, "index.html", {"user": user})
CSRF Token
CSRF Token相关装饰器在CBV只能加到dispatch方法上
备注:
csrf_protect,为当前函数强制设置防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings中没有设置全局中间件。
csrf_exempt,取消当前函数防跨站请求伪造功能,即便settings中设置了全局中间件

1 from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt, csrf_protect 2 3 4 class HomeView(View): 5 6 @method_decorator(csrf_exempt) 7 def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): 8 return super(HomeView, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) 9 10 def get(self, request): 11 return render(request, "home.html") 12 13 def post(self, request): 14 print("Home View POST method...") 15 return redirect("/index/")




