《Java 程序设计》课堂实践一
题目要求MySort
模拟实现Linux下Sort -t : -k 2的功能。参考 Sort的实现。提交码云链接和代码运行截图。
知识点
选项
-b:忽略每行前面开始出的空格字符;
-c:检查文件是否已经按照顺序排序;
-d:排序时,处理英文字母、数字及空格字符外,忽略其他的字符;
-f:排序时,将小写字母视为大写字母;
-i:排序时,除了040至176之间的ASCII字符外,忽略其他的字符;
-m:将几个排序号的文件进行合并;
-M:将前面3个字母依照月份的缩写进行排序;
-n:依照数值的大小排序;
-o<输出文件>:
将排序后的结果存入制定的文件;
-r:以相反的顺序来排序;
-t<分隔字符>:指定排序时所用的栏位分隔字符; +<起始栏位>-<结束栏位>:以指定的栏位来排序,范围由起始栏位到结束栏位的前一栏位。
split() :把一个字符串分割成字符串数组
"2:3:4:5".split("😊 //将返回["2", "3", "4", "5"]
"hello".split("", 3) //可返回 ["h", "e", "l"]
实验代码
import java.util.*;
public class Mysort1 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
String [] toSort = {"aaa:10:1:1",
"ccc:30:3:4",
"bbb:50:4:5",
"ddd:20:5:3",
"eee:40:2:20"};
System.out.println("Before sort:");
for (String str: toSort)
System.out.println(str);
String [] s1 = new String[toSort.length];
for (int i = 0; i < toSort.length; i++) {
String list[] = toSort[i].split(":");
s1[i] = list[2];
}
Arrays.sort(s1);
String [] s2 = new String[toSort.length];
for (int i=0; i<s1.length;i++)
for (int j=0;j<toSort.length;j++)
if( toSort[j].charAt(7) == (s1[i].toCharArray()[0]))
s2[i] = toSort[j];
System.out.println("After sort:");
for(String str : s2 )
System.out.println(str);
}
}
程序截图
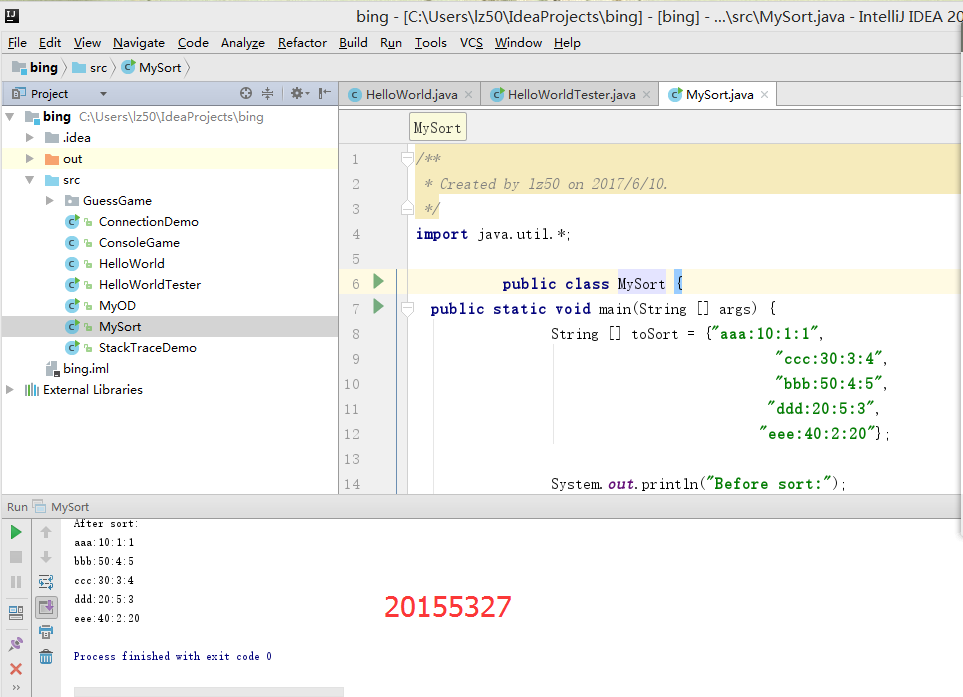
实践反思
1.对于转换字符串数组:调用Integer.parseInt()方法进行转换。
2.int与Integer的区别:
我本来以为是一样的,通过同学的博客了解到Integer类提供了多个方法,能在 int 类型和 String 类型之间互相转换,还提供了处理 int 类型时非常有用的其他一些常量和方法。如果需要调用Integer类的方法,查阅API文档


 posted on
posted on

【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步