映射文件,用于告诉NHibernate数据库里的表、列于.Net程序中的类的关系。因此映射文件的配置非常重要。
一、一对一
NHibernate一对一关系的配置方式使用<one-to-one>配置节点。
当我们两个表拥有相同的主键字段,主键值相同的需要关联在一起。比较典型的一个例子是,一个对象的属性太多,常用的和不常用的分开存放。例如一个文章表,我们将文章内容字段,提取出来作为一个单独的字段,因为比较长。
下面我们来新建两张表如下:
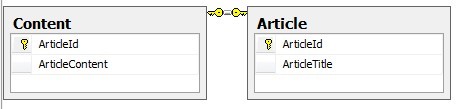
本来, Article表还有很多字段,比如添加时间,所属栏目,是否高亮,是否置顶等等,但是本处仅仅做示范NHibernate一对多一配置之使用。因此简略了。
Article.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2"> <class name="Model.ArticleModel,Model" table="Article"> <id name="Id" column="ArticleId" type="Int32"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <one-to-one name="Content" cascade="all" /> <property name="Title" column="ArticleTitle" type="String"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
Content.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2"> <class name="Model.ContentModel,Model" table="Content"> <id name="Id" column="ArticleId" type="Int32"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <one-to-one name="Article" cascade="all" /> <property name="Content" column="ArticleContent" type="String"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
ArticleModel.cs
public class ArticleModel { public virtual int Id { get; set; } public virtual string Title { get; set; } public virtual ContentModel Content { get; set; } }
ContentModel.cs
public class ContentModel { public virtual int Id { get; set; } public virtual string Content { get; set; } public virtual ArticleModel Article { get; set; } }
Program.cs
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ISessionFactory sessionFactory = new Configuration().Configure().BuildSessionFactory(); using (ISession session = sessionFactory.OpenSession()) { ArticleModel art = session.Get<ArticleModel>(1); Console.WriteLine(art.Id); Console.WriteLine(art.Title); Console.WriteLine(art.Content.Content); } Console.ReadKey(); } }
输出结果如下:
2016-05-16:今天对一对一又有新理解。
像上面这种主键关联一对一,可以设置两种方式。
<one-to-one name="ArtContent" cascade="none" constrained="true"/> 对象1配置方式 <one-to-one name="Article" cascade="all" constrained="true" /> 对象2配置方式
这样设置有什么好处呢?
1、cascade="none"那个,是不关联。不需要关联的操作,选择上面这个对象来Add,Select,Update。SELECT是个严重的问题,数据多了以后,如果不需要Join的情况下Join了,资源浪费,很慢。
2、cascade="all",需要关联的操作,使用下面这个对象来操作。
之前弄错了,配置成这样。
<one-to-one name="ArtContent" /> 对象1配置方式 <one-to-one name="Article" cascade="all" constrained="true" /> 对象2配置方式
因为,如果你什么关联都不写,有可能会是级联操作,即使你不希望关联,NHibernate也会关联,查询的时候默认关联查询出了你不需要的对象。所以会造成资源浪费的问题。
当然,整个NHibernate外层还可以配置默认的default-cascade关联操作。
有时间还是要多跟跟SQL语句,才能明白怎样配置才是最优的。
二、一对多
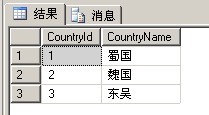
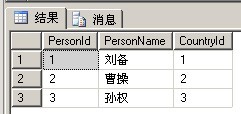
来看以下两张表,这是一个典型的一对多关系。人与国家:
Country表:
Person表:
NHibernate映射文件配置基础,一对多配置示例。先来看看映射文件:
Country.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2"> <class name="Model.CountryModel, Model" table="Country"> <id name="CountryId" column="CountryId" type="Int32"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="CountryName" column="CountryName" type="String"/> <!-- 一个Country里面有多个Person --> <set name="ListPerson" table="Person" generic="true" inverse="true"> <key column="CountryId" foreign-key="FK_Person_Country"/> <one-to-many class="Model.PersonModel,Model"/> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
Person.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2"> <class name="Model.PersonModel, Model" table="Person"> <id name="PersonId" column="PersonId" type="Int32"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="PersonName" column="PersonName" type="String"/> <!--多对一关系:Person属于一个Country name是Person实体类里的--> <many-to-one name="Country" column="CountryId" not-null="true" class="Model.CountryModel,Model" foreign-key="FK_Person_Country" /> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
CountryModel.cs
namespace Model { public class CountryModel { public virtual int CountryId { get; set; } public virtual string CountryName { get; set; } //N个PersonModel属于一个CountryModel public virtual ISet<PersonModel> ListPerson { get; set; } } }
PersonModel.cs
namespace Model { public class PersonModel { public virtual int PersonId { get; set; } public virtual string PersonName { get; set; } //要注意到一个PersonModel是属于一个CountryModel public virtual CountryModel Country { get; set; } } }
这里要说明以下,NHibernate巧妙地通过集合与实体解决了一对多、多对一关系。将延迟加载发挥到极限。
CountryDao.cs:
namespace Dao { public class CountryDao {public IList<CountryModel> GetCountyList() { ISession NSession = NHibernateHelper.GetSession(); return NSession.QueryOver<CountryModel>().List(); } } }
PersonDao.cs:
namespace Dao { public class PersonDao {public IList<PersonModel> GetPersonList() { ISession NSession = NHibernateHelper.GetSession(); return NSession.QueryOver<PersonModel>().List(); } } }
Program.cs:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { PersonDao pDao = new PersonDao(); IList<PersonModel> ListPerson = pDao.GetPersonList(); foreach (PersonModel p in ListPerson) {
//输出Person所属的国家名 Console.WriteLine(p.PersonId + " " + p.PersonName + " " + p.Country.CountryName); } CountryDao cDao = new CountryDao(); IList<CountryModel> ListCountry = cDao.GetCountyList(); foreach (CountryModel m in ListCountry) { Console.WriteLine(m.CountryName + ":");
//循环输出该国家的所有人名 foreach (PersonModel p1 in m.ListPerson) { Console.WriteLine("--" + p1.PersonName); } } Console.ReadKey(); } }
输出结果如下:

虽然你没有写过一句join,但是你直接就能够"."出来了相关的东西,感觉NHibernate非常强大。不过方便归方便,SQL语句可不能忘。
延迟加载小尝甜头
下面来玩点有趣的东西,在Dao里加如下一个方法:
public PersonModel GetPerson() { ISession NSession = NHibernateHelper.GetSession(); return NSession.Get<PersonModel>(1); }
Program.cs主程序改为如下:
static void Main(string[] args) { PersonDao dao = new PersonDao(); PersonModel p = dao.GetPerson(); Console.WriteLine(p.PersonId); Console.WriteLine(p.PersonName); Thread.Sleep(5000); //停止5秒钟后,再输出个人所属国家名 Console.WriteLine(p.Country.CountryName); }
对于输出结果我不关注,我关注的是NHibernate对SQLServer做了什么,我们来看看SQL Server Profiler监控到了什么?
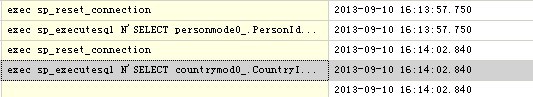
留意两条SQL语句的执行时间间隔,刚好是5秒,那么sql语句是什么呢?
exec sp_executesql N'SELECT personmode0_.PersonId as PersonId0_0_, personmode0_.PersonName as PersonName0_0_, personmode0_.CountryId as CountryId0_0_ FROM Person personmode0_ WHERE personmode0_.PersonId=@p0',N'@p0 int',@p0=1 --第一条:等价于 SELECT PersonId,PersonName,CountryId FROM Person WHERE PersonId = 1 exec sp_executesql N'SELECT countrymod0_.CountryId as CountryId1_0_, countrymod0_.CountryName as CountryN2_1_0_ FROM Country countrymod0_ WHERE countrymod0_.CountryId=@p0',N'@p0 int',@p0=1 --第二条:等价于 SELECT CountryId,CountryName FROM WHEE CountryId = 1
留意到NHibernate并没有采用inner join的语法,将Country的数据也一并从数据库读到程序中,而是当C#5秒后要用到CountryName这个东西的时候,它才去数据库读取。很明显的结论,如果C#不打算输出CountryName,NHibernate根本不会执行第二条SQL语句。
延迟加载 lazy:true
下面再来一点点变种,在Country.hbm.xml映射文件里的第一行加上一句 lazy="false"如下:
<class lazy="false" name="Model.CountryModel, Model" table="Country">
在执行显示结果上面,完全没变化,但是用SQL Server Profiler看的到SQL语句如下:
exec sp_executesql N'SELECT personmode0_.PersonId as PersonId0_1_, personmode0_.PersonName as PersonName0_1_, personmode0_.CountryId as CountryId0_1_, countrymod1_.CountryId as CountryId1_0_, countrymod1_.CountryName as CountryN2_1_0_ FROM Person personmode0_ inner join Country countrymod1_ on personmode0_.CountryId=countrymod1_.CountryId WHERE personmode0_.PersonId=@p0',N'@p0 int',@p0=1 --SQL语句等价于: SELECT p.PersonId,p.PersonName,p.CountryId,c.CountryId,c.CountryName FROM Person AS p INNER JOIN Country AS c ON P.CountryId = c.CountryId
可以看到,如果禁止Country表使用延迟加载,那么NHibernate就会被逼得使用Inner Join一次把所有的数据都读出来,无论你用没用到另外一张表中的数据。
不可变类,mutable="false"
还是利用这个例子,来看看不可变类是什么意思,我们将Person.hbm.xml的第一行加上一个mutable="false",变为:
<class name="Model.PersonModel, Model" table="Person" mutable="false">
PersonDao.cs写一个Delete方法如下:
public void Delete() { ISession NSession = NHibernateHelper.GetSession(); PersonModel p = NSession.Get<PersonModel>(1); Session.Delete(p); }
然后在Program.cs中调用它。
PersonDao dao = new PersonDao(); dao.Delete();
你希望看到什么?答案是:SQL Server Profiler显示没有任何SQL语句被执行。而再次查询也同样还有PersonId为1的Person数据在。
对于NHibernate的映射配置属性,非常多,不可能一一示例。如果需要查询比较详细的映射配置信息,可以到这里http://www.cnblogs.com/kissdodog/archive/2013/02/21/2919886.html。
三、多对多
还是以一个最简单的示例来说明,一个程序员可以开发多个软件,一个软件可以由多个程序员共同开发。典型的数据表如下:
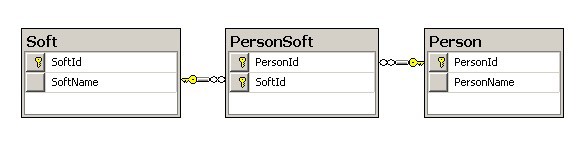
先来看Person.hbm.xml的映射文件配置如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2"> <class name="Model.PersonModel, Model" table="Person"> <id name="PersonId" column="PersonId" type="Int32"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="PersonName" column="PersonName" type="String"/> <!-- 多对多关系 对应多个软件 --> <bag name="Softs" generic="true" table="PersonSoft"> <key column="PersonId" foreign-key="FK_PersonSoft_Person"/> <many-to-many column="SoftId" class ="Model.SoftModel,Model" foreign-key="FK_PersonSoft_Soft"/> </bag> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
Soft.hbm.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2"> <class name="Model.SoftModel, Model" table="Soft"> <id name="SoftId" column="SoftId" type="Int32"> <generator class="native"/> </id> <property name="SoftName" column="SoftName" type="String"/> <!-- 多对多关系 对应多个程序员 name属性名,table中间表名 --> <bag name="Persons" generic="true" table="PersonSoft"> <key column="SoftId" foreign-key="FK_PersonSoft_Soft"/> <!--主键列,主键表的外键名称--> <many-to-many column="PersonId" class ="Model.PersonModel,Model" foreign-key="FK_PersonSoft_Person"/> <!--外键列,外键类,外键名称--> </bag> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
SoftModel.cs:
public class SoftModel { public virtual int SoftId { get; set; } public virtual string SoftName { get; set; } //多对多关系:一个软件由多个程序员开发 public virtual IList<PersonModel> Persons { get; set; } }
PersonModel.cs:
public class PersonModel { public virtual int PersonId{ get; set; } public virtual string PersonName{ get; set; } //多对多关系:一个程序员可以开发多个软件 public virtual IList<SoftModel> Softs { get; set; } }
现在我们来看一个基本的需求,我们现在知道一个人的Id,要求出这个人所开发的软件
public class PersonDao { public PersonModel GetPerson(int Id) { ISession NSession = NHibernateHelper.GetSession(); return NSession.Get<PersonModel>(Id); } }
上面代码实现的是根据Id,查询到人的实体对象。
Program.cs:
static void Main(string[] args) { PersonDao dao = new PersonDao(); PersonModel p = dao.GetPerson(1); Console.WriteLine(p.PersonName + "开发的软件有:"); foreach (SoftModel soft in p.Softs) //什么都没有干,纯粹是.出来的 { Console.WriteLine("--" + soft.SoftName); } }
但是到调用的时候,只要我们得到了PersonModel的对象,就能够直接点出它所开发出的软件列表。
以上代码显示结果如下:

你现在领略到NHibernate的恐怖之处的吧,也知道为什么配置那么复杂了吧,配置复杂了,写SQL语句的时间都省了。
第一步根据Id查出PersonModel实体类的对象,这个就忽略了。关键是第二步,当我们点(.)出Softs的时候,NHibernate做了什么呢?
exec sp_executesql N'SELECT softs0_.PersonId as PersonId1_, softs0_.SoftId as SoftId1_, softmodel1_.SoftId as SoftId3_0_, softmodel1_.SoftName as SoftName3_0_ FROM PersonSoft softs0_ left outer join Soft softmodel1_ on softs0_.SoftId=softmodel1_.SoftId WHERE softs0_.PersonId=@p0',N'@p0 int',@p0=1 --相当于下面的SQL语句 SELECT ps.PersonId,ps.SoftId,s.SoftId,S.SoftName FROM PersonSoft ps LEFT OUTER JOIN Soft s ON ps.SoftId = s.SoftId WHERE ps.PersonId = 1
NHibernate在我们点的时候,生成了SQL语句,并返回了结果。
以前要写一大坨SQL语句,现在只需要一个点(.),不过千万要记住,SQL语句不能忘。



