Entity Framework 6 Recipes 2nd Edition(11-2)译 -> 用”模型定义”函数过滤实体集
11-2. 用”模型定义”函数过滤实体集
问题
想要创建一个”模型定义”函数来过滤一个实体集
解决方案
假设我们已有一个客户(Customer)和票据Invoice)模型,如Figure 11-2所示.
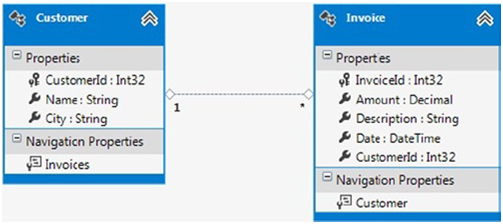
Figure 11-2. Customer and Invoice in a model
我们要想要创建一个”模型定义”函数获取invoice集并过滤出总数高于$300的invoice. 为了更有趣,让我们把一个"模型定义"函数用在一个查询中,这个查询进一步过滤出在5/1/2013之后创建的invoice. 当然,我们想要的是所有customer符合上述条件的invoice.
按下列步骤:
1.在解决方案中右击.edmx 文件,打开方式➤ XML编辑器.
2.在.edmx 文件中概念模型(conceptual models )小区里的<Schema> 标签下插入Listing 11-3所示的代码.
Listing 11-3. The GetInvoices() Model-Defined Function
<Function Name="GetInvoices" ReturnType="Collection(EFRecipesModel1102.Invoice)" >
<Parameter Name="invoices" Type="Collection(EFRecipesModel1102.Invoice)">
</Parameter>
<DefiningExpression>
Select VALUE i from invoices as i where i.Amount > 300M
</DefiningExpression>
</Function>
3.插入和查询模型的代码,如Listing 11-4所示的代码:
Listing 11-4.用eSQL 和LINQ两种方式用GetInvoices()方法(“模型定义”函数)来查询模型
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
RunExample();
}
static void RunExample()
{
using (var context = new EFRecipesEntities1102())
{
DateTime d1 = DateTime.Parse("8/8/2013");
DateTime d2 = DateTime.Parse("8/12/2012");
var c1 = new Customer { Name = "Jill Robinson", City = "Dallas" };
var c2 = new Customer { Name = "Jerry Jones", City = "Denver" };
var c3 = new Customer { Name = "Janis Brady", City = "Dallas" };
var c4 = new Customer { Name = "Steve Foster", City = "Dallas" };
context.Invoices.Add(new Invoice
{
Amount = 302.99M,
Description = "New Tires",
Date = d1,
Customer = c1
});
context.Invoices.Add(new Invoice
{
Amount = 430.39M,
Description = "Brakes and Shocks",
Date = d1,
Customer = c2
});
context.Invoices.Add(new Invoice
{
Amount = 102.28M,
Description = "Wheel Alignment",
Date = d1,
Customer = c3
});
context.Invoices.Add(new Invoice
{
Amount = 629.82M,
Description = "A/C Repair",
Date = d2,
Customer = c4
});
context.SaveChanges();
}
using (var context = new EFRecipesEntities1102())
{
Console.WriteLine("Using eSQL query...");
string sql = @"Select value i from
EFRecipesModel1102.GetInvoices(EFRecipesEntities1102.Invoices) as i
where i.Date > DATETIME'2013-05-1 00:00'
and i.Customer.City = @City";
var objectContext = (context as IObjectContextAdapter).ObjectContext;
var invoices = objectContext.CreateQuery<Invoice>(sql,
new ObjectParameter("City", "Dallas")).Include("Customer");
foreach (var invoice in invoices)
{
Console.WriteLine("Customer: {0}\tInvoice for: {1}, Amount: {2}",
invoice.Customer.Name, invoice.Description, invoice.Amount);
}
}
using (var context = new EFRecipesEntities1102())
{
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Using LINQ query...");
DateTime date = DateTime.Parse("5/1/2013");
var invoices = from invoice in
MyFunctions.GetInvoices(context.Invoices)
where invoice.Date > date
where invoice.Customer.City == "Dallas"
select invoice;
foreach (var invoice in ((DbQuery<Invoice>)invoices)
.Include("Customer"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Customer: {0}, Invoice for: {1}, Amount: {2}",
invoice.Customer.Name, invoice.Description, invoice.Amount);
}
}
Console.WriteLine("\nPress any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class MyFunctions
{
[EdmFunction("EFRecipesModel1102", "GetInvoices")]
public static IQueryable<Invoice> GetInvoices(IQueryable<Invoice> invoices)
{
return invoices.Provider.CreateQuery<Invoice>(
Expression.Call((MethodInfo)MethodInfo.GetCurrentMethod(),
Expression.Constant(invoices,typeof(IQueryable<Invoice>))));
}
}
代码Listing 11-4的输出结果如下:
Using eSQL for the query...
Customer: Jill Robinson Invoice for: New Tires, Amount: 302.99
Using LINQ for the query...
Customer: Jill Robinson, Invoice for: New Tires, Amount: 302.99
它是如何工作的?
从我们定义的Listing 11-3所示的GetInvoices()函数, 我们可以看到它接受一个Invoice集,并返回一个Invoice集.在运行时里,会解释为接受一个 IQueryable<Invoice> 并返回一个IQueryable<Invoice>.
在 eSQL表达式里, 我们把GetInvoices() 函数用在 from 子句里. 我们传递进去未过滤的Invoice集,然后我们的GetInvoices() 函数会返回一个过滤后的Invoice集. 我们进一步根据日期和Customer所有城市,用Where子句过滤这个集合. 接着我们用CreateQuery<Invoice>()来创建ObjectQuery<Invoice>类型. 在创建的查询里, 我们传递一个参数(客户所在的城市)来过滤并使用Include()方法来包含相关联的customer.一旦我们有了ObjectQuery<Invoice>, 我们遍历这个结果集并且过滤后符合条件的invoice打印出来.
用 LINQ 查询, 要有趣一些,我们把GetInvoices()方法放在了表达式的Form子句里,并把结果再根据日期和城市进行过滤(这点类似于eSQL表达式).然而,为了在LINQ查询中使用我们的函数,我们需要实现一个运行时方法,它接受一个IQueryable<Invoice> 并返回一个IQueryable<Invoice>.
与11-1小节里用”模型定义”函数返回一个标量值的方法存根不同,此处我们必须实现方法.创建该方法通常是参考引导程序
下面是引导程序的几个规则:
如果"模型定义"函数返回一个IQueryable<T>,必须使用引导程序
当一个函数返回一个IQueryable<T>,但不是接受一个IQueryable<T>, 引导方法必须实现为ObjectContext类的一部分
因为第二条规则,所以我们的ObjectContext在没有用一个IQueryable<T>开始的情况下,我们也不能返回一个IQueryable<T>.但我们可以传递进去一个IQueryable<T>, 接着在我们的引导方法里执行一些操作使它返回一个相关的IQueryable<T>. 尽管,我们不能在ObjectContext类以外手工创建一个IQueryable<T>,但像我们的例子里,我们接收一个IQueryable<T>作为参数后,可以为我们的ObjectContext在类外实现引导代码.
在我们实现的引导方法里,我们得到一个IQueryable<Invoice>.可以通过它的的Provider 属性得到一个IqueryProvider实例, IQueryProvider.CreateQuery<Invoice>()允许我们把IQueryable<T>加到表达树上
.当然此方法我们也使用了相关的”函数”特性来修饰,并传入一个invoice集.
kid1412声明:转载请把此段声明完整地置于文章页面明显处,并保留个人在博客园的链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/kid1412/(可点击跳转)。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号