AOP & 拦截器
https://www.cnblogs.com/boywwj/p/7502185.html
spring aop中@after-returning和@after,@afterThrowing,@Around,@Before注解执行顺序 try{ try{ //@Around //@Before method.invoke(..); //@Around }catch(){ throw.....; }finally{ //@After } //@AfterReturning }catch(){ //@AfterThrowing } 正常情况 @Around @Before 目标方法 @Around @After @AfterReturning; 异常情况 @Around @Before 目标方法 @After @AfterThrowing;
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
一:AOP的背景
面试的时候面试官让我解释一下什么是AOP,当时不懂,在路上就查了,AOP:面向切面的编程技术,困惑了,JAVA是OOP:面向对象的编程技术。那么自己就立刻查了几个为题:1、什么是面向切面的编程技术;2、为什么要面向切面的编程技术;3、与OOP是什么关系?
首先解释第二个问题:在我们平时的开发过程中,你肯定会遇到下面几个面:1)权限校验;2)业务的核心代码;3)记录日志。那么在@Service层采用代码累加的方法,那么结构就会如下。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
@Servicepublic class myService{@Resourceprivate CoreService coreService;@Resourceprivate LogService logService;@Resourceprivate PropertyService propertyService; // 权限校验代码//核心业务层代码//记录日志的代码 <br><br>// 异常的处理<br>} |
从上面的代码结构中我们可以看出以下几个问题:
1.1、代码混乱:核心业务模块与其他非核心的代码交织在一起,大大影响了代码的模块独立性能,不利于代码的维护,而且分工不明确造成代码混乱。
1.2、冗余代码:其实权限的校验,异常的处理,日志的记录可以独立在一个模块给所有的服务公用,写在一起导致代码的分散和冗余。
因此面向切面的编程技术应运而生。
解释第一个问题:什么是面向切面的编程技术。切面与切点是几何上面的术语,用在这里可以这样理解:将核心业务代码过程比作一个柱体,其他的日志记录,权限校验等就像是横切核心业务的面,这些面需要完成一些非核心的业务。如下图:

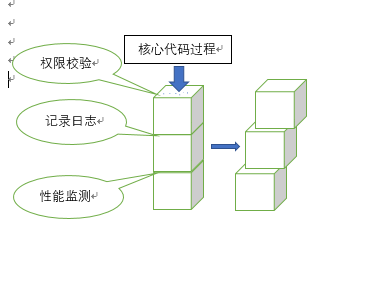
从图中可以看出我们定义了多个切面,每个切面都完成各自的非核心的业务,一个切面上还可以完成多个非核心的业务。
1.3、第三个问题:与OOP是什么关系?
AOP的实现技术有多种,其中与Java无缝对接的是一种称为AspectJ的技术,Spring AOP 与AspectJ 实现原理上并不完全一致,但功能上是相似的。AOP的出现确实解决外围业务代码与核心业务代码分离的问题,但它并不会替代OOP,如果说OOP的出现是把编码问题进行模块化,那么AOP就是把涉及到众多模块的某一类问题进行统一管理(参考:关于 Spring AOP (AspectJ) 你该知晓的一切;其实我也想到了他们的关系,但是感觉没有这篇博客总结的很好)
二:AOP的核心概念
从上右图可以可以很好看到切面(Aspect)包含了切点(PointCut)、连接点(JoinPoint);额外还有通知(Advice),织入(Weaving),引入(Introduce)。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
package springMVCmybatis.com.my.aop;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;@Aspect// 切面执行顺序@Order(3)public class MyAopTest { @Pointcut("execution(* springMVCmybatis..addController.addEmp(..))") private void pointCutMethod() { } @Pointcut("execution(* springMVCmybatis.com.my.aop.UserServiceImp.*(..))") private void testAOP() { } /* * 声明前置通知 ,JoinPont是srpring提供的静态变量, * 通过joinPoint参数可以获得目标方法的类名,方法参数,方法名等信息,这个参数可有可无。 */ @Before("pointCutMethod() || testAOP()") public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("@Before:开始添加--order=3"); } //声明后置通知 ,如果result的类型与proceed执行的方法返回的参数类型不匹配那么就不会执行这个方法 @AfterReturning(pointcut = "pointCutMethod() || testAOP()", returning = "result") public void doAfterReturning(String result) { System.out.println("@AfterReturning:后置通知--order=3"); System.out.println("---" + result + "---"); } //声明例外通知 @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "pointCutMethod() || testAOP()", throwing = "e") public void doAfterThrowing(Exception e) { System.out.println("@AfterThrowing:例外通知--order=3"); System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } //声明最终通知 @After("pointCutMethod() || testAOP()") public void doAfter() { System.out.println("@After:最终通知--order=3"); } /* * 声明环绕通知 * 参数必须是ProceedingJoinPoint,通过该对象的proceed()方法来执行目标函数, * proceed()的返回值就是环绕通知的返回值,proceedingJoinPoint是个接口, * implement JoinPoint,所以也可以获得目标函数的类名,方法名等参数。 */ @Around("pointCutMethod() || testAOP()") public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("@Around:进入方法---环绕通知--order=3"); Object o = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("@Around:退出方法---环绕通知--order=3"); return o; } } |
上面是我写的一个例子,结合例子我们来看看这些核心的概念:
2.1、切面(Aspect):是一个类,里面定义了通知与切点。
2.2、切点(PointCut):表达式。就是告诉程序要在执行哪些核心业务的时候,执行非核心的业务。
2.3、通知(advice):五种通知方式:
@Before:前置通知,在调用目标方法之前执行通知定义的任务@After:后置通知,在目标方法执行结束后,无论执行结果如何都执行通知定义的任务@After-returning:后置通知,在目标方法执行结束后,如果执行成功,则执行通知定义的任务@After-throwing:异常通知,如果目标方法执行过程中抛出异常,则执行通知定义的任务@Around:环绕通知,在目标方法执行前和执行后,都需要执行通知定义的任务。
五种通知方式的执行顺序:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
正常情况下的执行顺序:<br><br>@Around:进入方法---环绕通知--order=3@Before:开始添加--order=3============执行业务方法findUser,查找的用户是:张三=============@Around:退出方法---环绕通知--order=3@After:最终通知--order=3@AfterReturning:后置通知--order=3---张三---<br>异常情况下的执行顺序:@Around:进入方法---环绕通知--order=3@Before:开始添加--order=3============执行业务方法addUser=============@After:最终通知--order=3@AfterThrowing:例外通知--order=3null |
三:切点表达式。
这个表达式有很多种,如方法签名表达式,类型签名表达式,还有其他的表达式,我只用过前面两个,其他的没用过,也不做介绍,如果这两种表达式不能解决问题的可以参考我参考的博客。
|
1
2
|
execution(<修饰符模式>?<返回类型模式><方法所在类的完全限定名称模式>(<参数模式>)<异常模式>?)execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern fully-qualified-class-name (param-pattern) throws-pattern?) |
|
1
2
|
public String springMVCmybatic.com.my.aop.UserServiceImp(String a, int b) throw Exception{} |
- modifier-pattern?:表示方法的修饰符,可有可无;对应的就是 public
- ret-type-pattern:表示方法的返回值;对应的就是 String
- fully-qualified-class-name 方法所在类的完全限定名称;对应的就是 springMVCmybatic.com.my.aop.UserServiceImp
- param-pattern:表示方法的参数;对应的就是 String a, int b
- throws-pattern:表示方法抛出的异常,可有可无;对应的就是 throw Exception
3.2:&&,||,!
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@Around("pointCutMethod() || testAOP()") public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("@Around:进入方法---环绕通知"); Object o = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("@Around:退出方法---环绕通知"); return o; } |
表达式之间可以采用与,或,非的方式来过滤。
四:多个切点的执行顺序
上面的例子中,定义了order=3,重新创建一个切面,定义order=6,执行的结果是:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
@Around:进入方法---环绕通知--order=3@Before:开始添加--order=3@Around:进入方法---环绕通知--order=6@Before:开始添加--order=6============执行业务方法findUser,查找的用户是:张三=============@Around:退出方法---环绕通知--order=6@After:最终通知--order=6@AfterReturning:后置通知--order=6---张三---@Around:退出方法---环绕通知--order=3@After:最终通知--order=3@AfterReturning:后置通知--order=3---张三---@Around:进入方法---环绕通知--order=3@Before:开始添加--order=3@Around:进入方法---环绕通知--order=6@Before:开始添加--order=6============执行业务方法addUser=============@After:最终通知--order=6@AfterThrowing:例外通知--order=6null@After:最终通知--order=3@AfterThrowing:例外通知--order=3null |
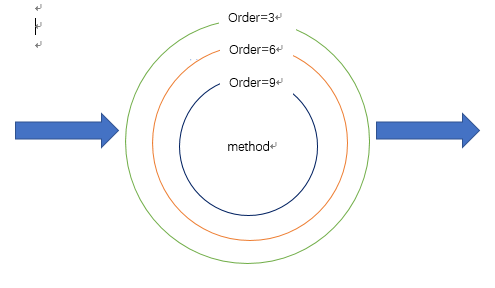
从结果中可以看出order越小越先执行,执行完了之后就order越小就越后推出。总结为下面的图:
【参考博客】
1、http://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/56267036/
2、http://blog.csdn.net/qqxhwwqwq/article/details/51678595
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
https://blog.csdn.net/u011974797/article/details/80591986
@Around是可以同时在所拦截方法的前后执行一段逻辑。
@Before是在所拦截方法执行之前执行一段逻辑。
@After 是在所拦截方法执行之后执行一段逻辑。
注意:不能拦截静态(static)方法
示例:
-
package com.abc.advice;
-
-
import java.util.Arrays;
-
-
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
-
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
-
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
-
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
-
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
-
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
-
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
-
-
@Aspect
-
public class AdviceTest {
-
@Around(
-
public Object process(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
-
System.out.println("@Around:执行目标方法之前...");
-
//访问目标方法的参数:
-
Object[] args = point.getArgs();
-
if (args != null && args.length > 0 && args[0].getClass() == String.class) {
-
args[0] = "改变后的参数1";
-
}
-
//用改变后的参数执行目标方法
-
Object returnValue = point.proceed(args);
-
System.out.println("@Around:执行目标方法之后...");
-
System.out.println("@Around:被织入的目标对象为:" + point.getTarget());
-
return "原返回值:" + returnValue + ",这是返回结果的后缀";
-
}
-
-
@Before(
-
public void permissionCheck(JoinPoint point) {
-
System.out.println("@Before:模拟权限检查...");
-
System.out.println("@Before:目标方法为:" +
-
point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() +
-
"." + point.getSignature().getName());
-
System.out.println("@Before:参数为:" + Arrays.toString(point.getArgs()));
-
System.out.println("@Before:被织入的目标对象为:" + point.getTarget());
-
}
-
-
@AfterReturning(pointcut=
-
returning=
-
public void log(JoinPoint point, Object returnValue) {
-
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:模拟日志记录功能...");
-
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:目标方法为:" +
-
point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() +
-
"." + point.getSignature().getName());
-
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:参数为:" +
-
Arrays.toString(point.getArgs()));
-
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:返回值为:" + returnValue);
-
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:被织入的目标对象为:" + point.getTarget());
-
-
}
-
-
@After(
-
public void releaseResource(JoinPoint point) {
-
System.out.println("@After:模拟释放资源...");
-
System.out.println("@After:目标方法为:" +
-
point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() +
-
"." + point.getSignature().getName());
-
System.out.println("@After:参数为:" + Arrays.toString(point.getArgs()));
-
System.out.println("@After:被织入的目标对象为:" + point.getTarget());
-
}
-
}
被拦截的方法
-
//将被AdviceTest的各种方法匹配
-
public String manyAdvices(String param1, String param2) {
-
System.out.println("方法:manyAdvices");
-
return param1 + " 、" + param2;
-
}
运行方法
-
String result = manager.manyAdvices("aa", "bb");
-
System.out.println("Test方法中调用切点方法的返回值:" + result);
结果
-
@Around:执行目标方法之前...
-
@Before:模拟权限检查...
-
@Before:目标方法为:com.abc.service.AdviceManager.manyAdvices
-
@Before:参数为:[改变后的参数1, bb]
-
@Before:被织入的目标对象为:com.abc.service.AdviceManager@1dfc617e
-
方法:manyAdvices
-
@Around:执行目标方法之后...
-
@Around:被织入的目标对象为:com.abc.service.AdviceManager@1dfc617e
-
@After:模拟释放资源...
-
@After:目标方法为:com.abc.service.AdviceManager.manyAdvices
-
@After:参数为:[改变后的参数1, bb]
-
@After:被织入的目标对象为:com.abc.service.AdviceManager@1dfc617e
-
@AfterReturning:模拟日志记录功能...
-
@AfterReturning:目标方法为:com.abc.service.AdviceManager.manyAdvices
-
@AfterReturning:参数为:[改变后的参数1, bb]
-
@AfterReturning:返回值为:原返回值:改变后的参数1 、 bb,这是返回结果的后缀
-
@AfterReturning:被织入的目标对象为:com.abc.service.AdviceManager@1dfc617e
-
Test方法中调用切点方法的返回值:原返回值:改变后的参数1 、bb,这是返回结果的后缀
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________
AspectJ 切面注解中五种通知注解:@Before、@After、@AfterRunning、@AfterThrowing、@Around
要在 Spring 中声明 AspectJ 切面, 只需要在 IOC 容器中将切面声明为 Bean 实例. 当在 Spring IOC 容器中初始化 AspectJ 切面之后, Spring IOC 容器就会为那些与 AspectJ 切面相匹配的 Bean 创建代理。
在切面类中需要定义切面方法用于响应响应的目标方法,切面方法即为通知方法,通知方法需要用注解标识,AspectJ 支持 5 种类型的通知注解:
- @Before: 前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行
- @After: 后置通知, 在方法执行之后执行 。
- @AfterRunning: 返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行
- @AfterThrowing: 异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后
- @Around: 环绕通知, 围绕着方法执行
下面分别举例5中通知方法的使用
首先建立一个目标接口ArithmeticCalculator:
package lzj.com.spring.aop;
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
}
然后创建接口的实现类ArithmeticCalculatorIml :
package lzj.com.spring.aop;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("arithmeticCalculator")
public class ArithmeticCalculatorIml implements ArithmeticCalculator {
@Override
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("add->result:" + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("div->result:" + result);
return result;
}
}
配置文件bean-aop.xml:
<context:component-scan base-package="lzj.com.spring.aop"></context:component-scan>
创建测试类:
package lzj.com.spring.aop;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-aop.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator arithmetic = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator");
arithmetic.add(3, 2);
arithmetic.div(4, 2);
}
}
运行结果:
add->result:5
div->result:2
上面的例子把目标类注入到IOC容器中,执行时从容器中获取目标类的bean,然后调用目标方法。
下面要在目标方法的前后等执行其它操作,打印日志,不需要改变任何目标方法,只需要增加切面类,新建切面类LogProxy,把切面类注入到IOC中,然后在切面类中定义要执行的切面方法即可。
在执行下面切面方法之前,需要先启动五种注解,配置文件中定义如下:
<context:component-scan base-package="lzj.com.spring.aop"></context:component-scan>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
一、@Before前置通知
用@Before标识的方法为前置方法,在目标方法的执行之前执行,即在连接点之前进行执行。
示例如下:
package lzj.com.spring.aop;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogProxy {
@Before("execution(public int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))")
public void beforMethod(JoinPoint point){
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(point.getArgs());
System.out.println("调用前连接点方法为:" + methodName + ",参数为:" + args);
}
}
执行测试类,输出结果如下:
调用前连接点方法为:add,参数为:[3, 2]
add->result:5
调用前连接点方法为:div,参数为:[4, 2]
div->result:2
在目标方法add和div之前分别执行了前置通知方法。
二、@After后置通知方法
后置方法在连接点方法完成之后执行,无论连接点方法执行成功还是出现异常,都将执行后置方法。示例如下:
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogProxy {
@After(("execution(public int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))"))
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint point){
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(point.getArgs());
System.out.println("调用后连接点方法为:" + methodName + ",参数为:" + args);
}
}
执行测试类,输出结果如下:
add->result:5
调用后连接点方法为:add,参数为:[3, 2]
div->result:2
调用后连接点方法为:div,参数为:[4, 2]
发现add和div两个连接点方法执行之后都调用了后置方法。如果目标连接点方法出现异常时,也会执行后置通知方法。把测试方法改成如下:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-aop.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator arithmetic = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator");
arithmetic.add(3, 2);
/*被除数为0,会抛出异常*/
arithmetic.div(4, 0);
}执行测试方法,输出结果如下:
add->result:5
调用后连接点方法为:add,参数为:[3, 2]
调用后连接点方法为:div,参数为:[4, 0]
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculatorIml.div(ArithmeticCalculatorIml.java:17)
……
从输出结果中可以看出,即使目标方法出现异常,后置通知方法依然执行。但后置通知拿不到目标方法执行后的结果,因为目标方法有可能出现异常。如果要拿目标方法的执行结果,要用下面的通知方法。
三、@AfterRunning返回通知方法
当连接点方法成功执行后,返回通知方法才会执行,如果连接点方法出现异常,则返回通知方法不执行。返回通知方法在目标方法执行成功后才会执行,所以,返回通知方法可以拿到目标方法(连接点方法)执行后的结果。切面类中定义返回通知方法,示例如下:
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogProxy {
/*通过returning属性指定连接点方法返回的结果放置在result变量中,在返回通知方法中可以从result变量中获取连接点方法的返回结果了。*/
@AfterReturning(value="execution(public int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))",
returning="result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint point, Object result){
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(point.getArgs());
System.out.println("连接点方法为:" + methodName + ",参数为:" + args + ",目标方法执行结果为:" + result);
}
}
运行测试方法,输出结果如下:
add->result:5
连接点方法为:add,参数为:[3, 2],目标方法执行结果为:5
div->result:2
连接点方法为:div,参数为:[4, 2],目标方法执行结果为:2
当连接点方法出现异常时,不执行返回通知方法,把测试方法该为如下:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-aop.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator arithmetic = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator");
arithmetic.add(3, 2);
arithmetic.div(4, 0);
}
}
运行测试方法,输出结果如下:
add->result:5
连接点方法为:add,参数为:[3, 2],目标方法执行结果为:5
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
……
从输出结果可以看出,div(4,0)出现异常,因此该连接点对应的返回通知方法也不执行。
四、@AfterThrowing异常通知
异常通知方法只在连接点方法出现异常后才会执行,否则不执行。在异常通知方法中可以获取连接点方法出现的异常。在切面类中异常通知方法,示例如下:
/*通过throwing属性指定连接点方法出现异常信息存储在ex变量中,在异常通知方法中就可以从ex变量中获取异常信息了*/
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(public int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))",
throwing="ex")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint point, Exception ex){
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(point.getArgs());
System.out.println("连接点方法为:" + methodName + ",参数为:" + args + ",异常为:" + ex);
}
测试方法为:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-aop.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator arithmetic = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator");
arithmetic.add(3, 2);
arithmetic.div(4, 0);
}
}
执行测试方法,输出结果如下:
add->result:5
连接点方法为:div,参数为:[4, 0],异常为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
从输出结果中可以看出,add方法没有异常,因此不执行异常通知方法,div方法出现异常,执行科异常通知方法。
上面的例子中,异常类型设置的是Exception,表示捕获连接点方法的所有异常信息,也可以指定捕获指定类型的信息,例如
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(public int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))",
throwing="ex")
/*只捕获连接点方法中的NullPointerException 类型的异常信息*/
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint point, NullPointerException ex){
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(point.getArgs());
System.out.println("连接点方法为:" + methodName + ",参数为:" + args + ",异常为:" + ex);
}五、@Around环绕通知
环绕通知方法可以包含上面四种通知方法,环绕通知的功能最全面。环绕通知需要携带 ProceedingJoinPoint 类型的参数,且环绕通知必须有返回值, 返回值即为目标方法的返回值。在切面类中创建环绕通知方法,示例如下:
@Around("execution(public int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pdj){
/*result为连接点的放回结果*/
Object result = null;
String methodName = pdj.getSignature().getName();
/*前置通知方法*/
System.out.println("前置通知方法>目标方法名:" + methodName + ",参数为:" + Arrays.asList(pdj.getArgs()));
/*执行目标方法*/
try {
result = pdj.proceed();
/*返回通知方法*/
System.out.println("返回通知方法>目标方法名" + methodName + ",返回结果为:" + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
/*异常通知方法*/
System.out.println("异常通知方法>目标方法名" + methodName + ",异常为:" + e);
}
/*后置通知*/
System.out.println("后置通知方法>目标方法名" + methodName);
return result;
}
}
测试方法为:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-aop.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator arithmetic = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator");
arithmetic.add(3, 2);
arithmetic.div(4, 0);
}
}
运行测试方法:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean-aop.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator arithmetic = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator");
arithmetic.add(3, 2);
arithmetic.div(4, 0);
}
}运行测试方法,输出结果:
前置通知方法>目标方法名:add,参数为:[3, 2]
add->result:5
返回通知方法>目标方法名add,返回结果为:5
后置通知方法>目标方法名add
前置通知方法>目标方法名:div,参数为:[4, 0]
异常通知方法>目标方法名div,异常为:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
后置通知方法>目标方法名div
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.aop.AopInvocationException: Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: public abstract int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.div(int,int)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke(JdkDynamicAopProxy.java:219)
at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy7.div(Unknown Source)
at lzj.com.spring.aop.Main.main(Main.java:12)
从输出结果中可以看出,环绕通知实现了上面几种通知的结合。
当div目标方法出现异常时,在环绕通知方法中已经用try…catch方法进行捕捉了,为什么最后输出结果中还出现了一个返回类型不匹配的错误:
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.aop.AopInvocationException: Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: public abstract int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.div(int,int)
at org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy.invoke(JdkDynamicAopProxy.java:219)
at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy7.div(Unknown Source)
at lzj.com.spring.aop.Main.main(Main.java:12)
那是因为在环绕通知方法中开始就定义了目标方法的返回结果Object result = null。当目标方法出现异常时,result = pdj.proceed();执行时出现异常,此时result中还是null,所以在环绕通知方法最后return result;时,返回的result就是null,但是环绕通知的返回类型我们定义的是Object类型的,null不能转化为Object类型,所以抛出了个类型转换的错误。我们可以在环绕通知方法中把异常抛出去,即为:
@Around("execution(public int lzj.com.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pdj){
/*result为连接点的放回结果*/
Object result = null;
String methodName = pdj.getSignature().getName();
/*前置通知方法*/
System.out.println("前置通知方法>目标方法名:" + methodName + ",参数为:" + Arrays.asList(pdj.getArgs()));
/*执行目标方法*/
try {
result = pdj.proceed();
/*返回通知方法*/
System.out.println("返回通知方法>目标方法名" + methodName + ",返回结果为:" + result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
/*异常通知方法*/
System.out.println("异常通知方法>目标方法名" + methodName + ",异常为:" + e);
/*当环绕通知方法本身还有其它异常时,非连接点方法出现的异常,此时抛出来*/
throw new RuntimeException();
}
/*后置通知*/
System.out.println("后置通知方法>目标方法名" + methodName);
return result;
}
}
在输出结果中会抛出一个运行时异常java.lang.RuntimeException
插曲:不可以在执行目标方法时在定义result变量:
……
/*执行目标方法*/
try {
Object result = pdj.proceed();
……
} catch (Throwable e) {
……
}
……
return result;这种方法是行不通的,在Object result = pdj.proceed();中,如果pdj.proceed()执行失败,就会被try …catch捕获到异常,而不会就不会执行定义result变量那一步了,即Object result不会执行,所以在return result;就会出现错误。




