服务网关zuul----zuul中的动态刷新路由配置
Spring Cloud实战小贴士:Zuul处理Cookie和重定向
所以解决该问题的思路也很简单,我们只需要通过设置sensitiveHeaders即可,设置方法分为两种:
- 全局设置:
zuul.sensitive-headers=
- 指定路由设置:
zuul.routes.<routeName>.sensitive-headers=zuul.routes.<routeName>.custom-sensitive-headers=true
重定向问题
在使用Spring Cloud Zuul对接Web网站的时候,处理完了会话控制问题之后。往往我们还会碰到如下图所示的问题,我们在浏览器中通过Zuul发起了登录请求,该请求会被路由到某WebSite服务,该服务在完成了登录处理之后,会进行重定向到某个主页或欢迎页面。此时,仔细的开发者会发现,在登录完成之后,我们浏览器中URL的HOST部分发生的改变,该地址变成了具体WebSite服务的地址了。这就是在这一节,我们将分析和解决的重定向问题!

出现该问题的根源是Spring Cloud Zuul没有正确的处理HTTP请求头信息中的Host导致。在Brixton版本中,Spring Cloud Zuul的PreDecorationFilter过滤器实现时完全没有考虑这一问题,它更多的定位于REST API的网关。所以如果要在Brixton版本中增加这一特性就相对较为复杂,不过好在Camden版本之后,Spring Cloud Netflix 1.2.x版本的Zuul增强了该功能,我们只需要通过配置属性zuul.add-host-header=true就能让原本有问题的重定向操作得到正确的处理。关于更多Host头信息的处理,读者可以参考本文之前的分析思路,可以通过查看PreDecorationFilter过滤器的源码来详细更多实现细节。
http://blog.didispace.com/spring-cloud-zuul-cookie-redirect/
一 介绍
很多场景下,需要在运行期间动态调整配置。如果配置发生了修改,微服务也应该实现配置的刷新。
下面实现配置的手动刷新。
二 新建项目microservice-config-client-refresh
三 为项目添加spring-boot-starter-actuator依赖,该依赖包含了/refresh端点,用于配置的刷新。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
四 在Controller上添加注解@RefreshScope。添加@RefreshScope的类会在配置更改时得到特殊处理。
package com.itmuch.cloud.study.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RefreshScope
public class ConfigClientController {
@Value("${profile}")
private String profile;
@GetMapping("/profile")
public String hello() {
return this.profile;
}
}
五 测试
1 启动microservice-config-server
2 启动microservice-config-client-refresh
3 访问http://localhost:8081/profile,获得结果
dev-1.0
4 修改Git仓库中microservice-foo-dev.properties的文件内容为:
profile=dev-1.0-change
5 重新访问http://localhost:8081/profile,获得结果依然是:
dev-1.0
6 发送post请求到http://localhost:8081/refresh,结果返回
[
"config.client.version",
"profile"
]
7 再次访问http://localhost:8081/profile,返回结果为:
dev-1.0-change
说明配置已经刷新
---------------------
作者:chengqiuming
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/chengqiuming/article/details/80872615
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
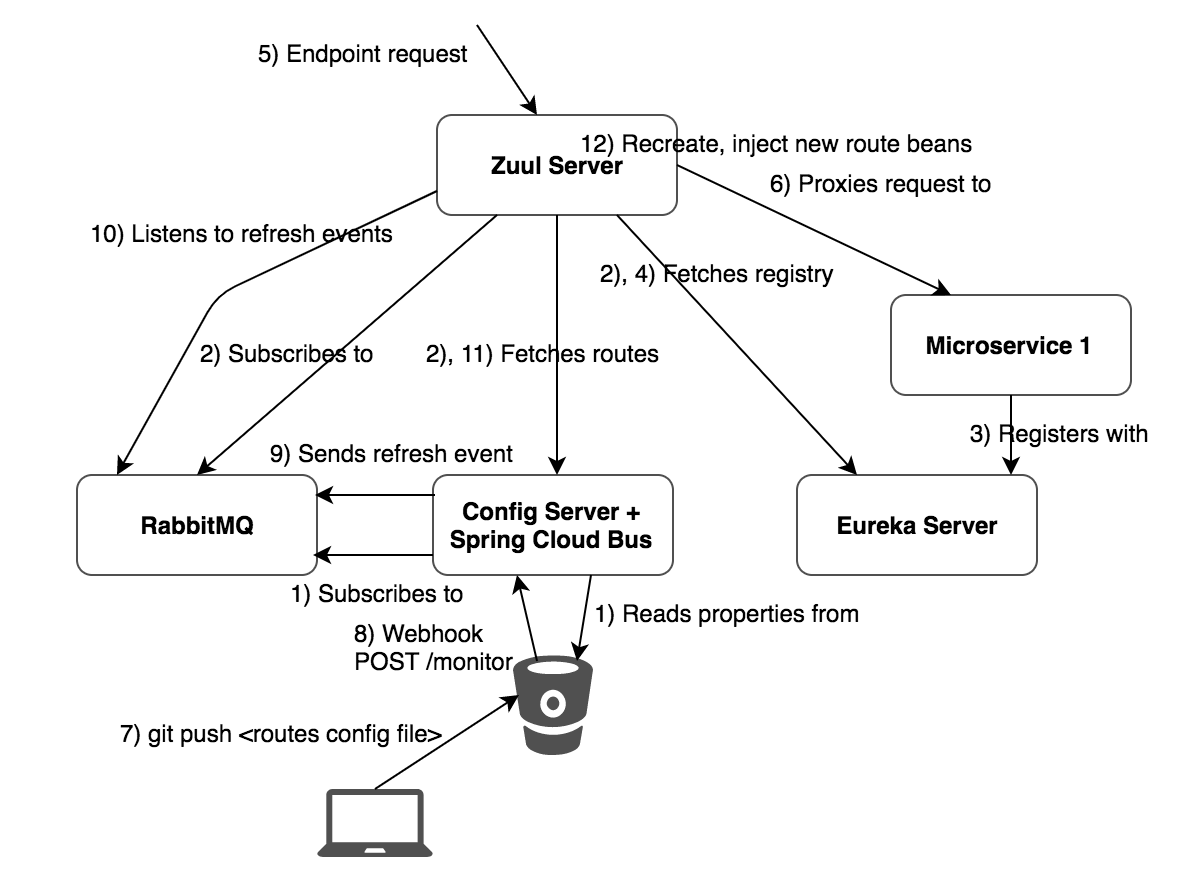
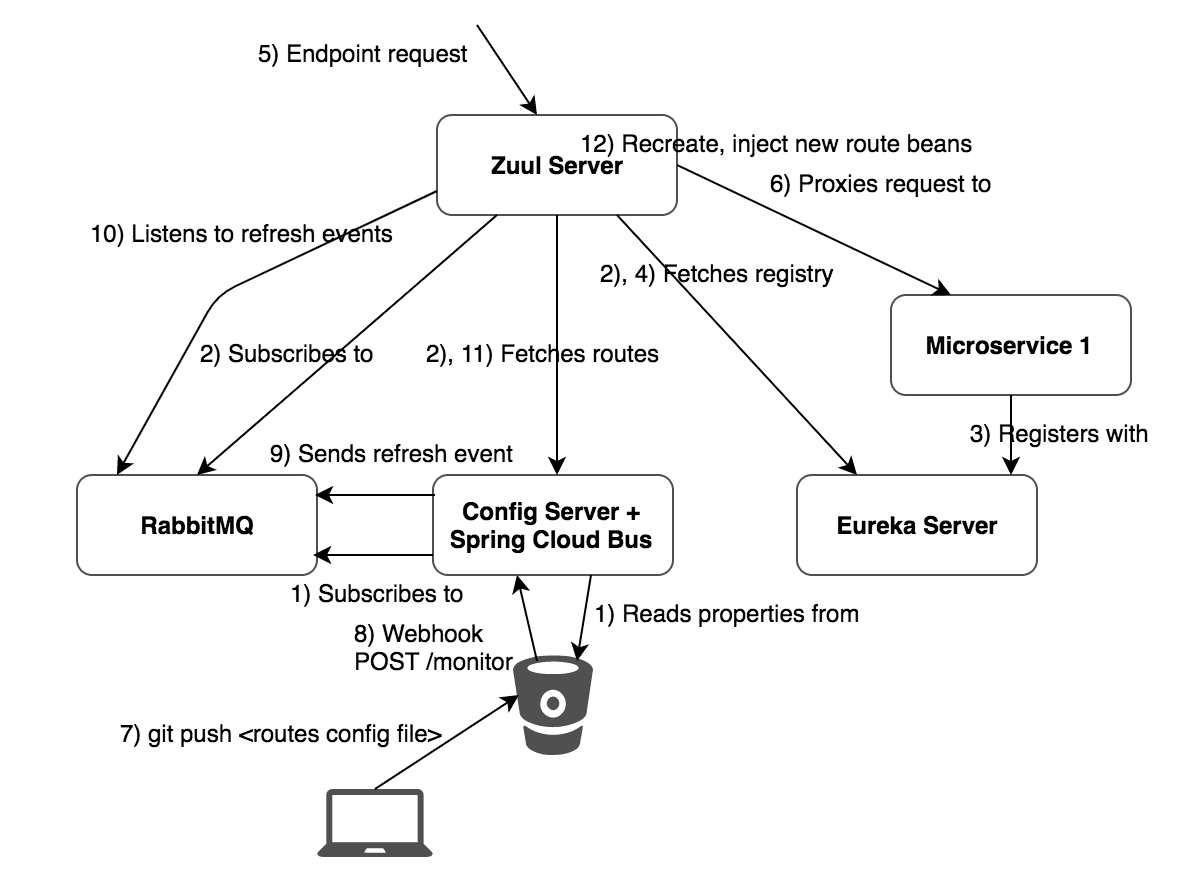
https://tech.asimio.net/2017/10/10/Routing-requests-and-dynamically-refreshing-routes-using-Spring-Cloud-Zuul-Server.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/flying607/p/8459397.html
《spring扩展点之三:Spring 的监听事件 ApplicationListener 和 ApplicationEvent 用法,在spring启动后做些事情》
在spring-cloud-netflix-core-1.4.4.RELEASE.jar中org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.RoutesRefreshedEvent.java
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class RoutesRefreshedEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private RouteLocator locator;
public RoutesRefreshedEvent(RouteLocator locator) {
super(locator);
this.locator = locator;
}
public RouteLocator getLocator() {
return this.locator;
}
}
在spring-cloud-netflix-core-1.4.4.RELEASE-sources.jar中的org.springframework.cloud.netflix.zuul.zuulZuulServerAutoConfiguration.java配置了监听事件。
private static class ZuulRefreshListener
implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
@Autowired
private ZuulHandlerMapping zuulHandlerMapping;
private HeartbeatMonitor heartbeatMonitor = new HeartbeatMonitor();
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent
|| event instanceof RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent
|| event instanceof RoutesRefreshedEvent) {
this.zuulHandlerMapping.setDirty(true);
}
else if (event instanceof HeartbeatEvent) {
if (this.heartbeatMonitor.update(((HeartbeatEvent) event).getValue())) {
this.zuulHandlerMapping.setDirty(true);
}
}
}
}</pre>
关于spring的ApplicationEvent见《spring扩展点之三:Spring 的监听事件 ApplicationListener 和 ApplicationEvent 用法,在spring启动后做些事情》
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34267123/article/details/86021770
java配置
@Configuration
public class ZuulConfig {
<span class="hljs-meta"><span class="hljs-meta">@Bean</span>(name=<span class="hljs-string"><span class="hljs-string">"zuul.CONFIGURATION_PROPERTIES"</span>)
<span class="hljs-meta"><span class="hljs-meta">@RefreshScope</span>
<span class="hljs-meta"><span class="hljs-meta">@ConfigurationProperties</span>(<span class="hljs-string"><span class="hljs-string">"zuul"</span>)
<span class="hljs-meta"><span class="hljs-meta">@Primary</span>
<span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-keyword"><span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-keyword">public</span> ZuulProperties </span><span class="hljs-title"><span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-title">zuulProperties</span></span><span class="hljs-params"><span class="hljs-function"><span class="hljs-params">()</span> </span>{
<span class="hljs-keyword"><span class="hljs-keyword">return</span> <span class="hljs-keyword"><span class="hljs-keyword">new</span> ZuulProperties();
}
}
修改路由
到git config server,修改zuul的路由,比如
zuul:
host:
socket-timeout-millis: 60000
connect-timeout-millis: 30000
proxy:
addProxyHeaders: true
routes:
baidu:
path: /baidu
url: http://baidu.com
刷新
curl -i -X POST localhost:10000/refresh
验证
curl -i localhost:10000/routes作者:go4it
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a9332b111002
來源:简书
简书著作权归作者所有,任何形式的转载都请联系作者获得授权并注明出处。
我们知道在SpringCloud中,当配置变更时,我们通过访问http://xxxx/refresh,可以在不启动服务的情况下获取最新的配置,那么它是如何做到的呢,当我们更改数据库配置并刷新后,如何能获取最新的数据源对象呢?下面我们看SpringCloud如何做到的。
一、环境变化
1.1、关于ContextRefresher
当我们访问/refresh时,会被RefreshEndpoint类所处理。我们来看源代码:

/* * Copyright 2013-2014 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */package org.springframework.cloud.endpoint;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Set;import org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.AbstractEndpoint;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.refresh.ContextRefresher;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedOperation;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedResource;/**
-
@author Dave Syer
-
@author Venil Noronha
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "endpoints.refresh", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
@ManagedResource
public class RefreshEndpoint extends AbstractEndpoint<Collection<String>> {private ContextRefresher contextRefresher;
public RefreshEndpoint(ContextRefresher contextRefresher) {
super("refresh");
this.contextRefresher = contextRefresher;
}@ManagedOperation
public String[] refresh() {
Set<String> keys = contextRefresher.refresh();
return keys.toArray(new String[keys.size()]);
}@Override
public Collection<String> invoke() {
return Arrays.asList(refresh());
}
}
通过源代码我们了解到:当访问refresh端点时,实际上执行的是ContextRefresher的refresh方法,那么我们继续追踪源代码,找到其refresh方法:
public synchronized Set<String> refresh() {
Map<String, Object> before = extract(
this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources());
addConfigFilesToEnvironment();
Set<String> keys = changes(before,
extract(this.context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources())).keySet();
this.context.publishEvent(new EnvironmentChangeEvent(context, keys));
this.scope.refreshAll();
return keys;
}
我们可以看到refresh方法做了如下几件事情:
1)获取刷新之前的所有PropertySource
2) 调用addConfigFilesToEnvironment方法获取最新的配置
3) 调用changes方法更新配置信息
4) 发布EnvironmentChangeEnvent事件
5)调用refreshScope的refreshAll方法刷新范围
我们重点关注一下2,3,4步骤
1.2、addConfigFilesToEnvironment方法
我们先来看看这个方法是怎么实现的:

/* for testing */ ConfigurableApplicationContext addConfigFilesToEnvironment() {
ConfigurableApplicationContext capture = null;
try {
StandardEnvironment environment = copyEnvironment(
this.context.getEnvironment());
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder(Empty.class)
.bannerMode(Mode.OFF).web(false).environment(environment);
// Just the listeners that affect the environment (e.g. excluding logging
// listener because it has side effects)
builder.application()
.setListeners(Arrays.asList(new BootstrapApplicationListener(),
new ConfigFileApplicationListener()));
capture = builder.run();
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE)) {
environment.getPropertySources().remove(REFRESH_ARGS_PROPERTY_SOURCE);
}
MutablePropertySources target = this.context.getEnvironment()
.getPropertySources();
String targetName = null;
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {
String name = source.getName();
if (target.contains(name)) {
targetName = name;
}
if (!this.standardSources.contains(name)) {
if (target.contains(name)) {
target.replace(name, source);
}
else {
if (targetName != null) {
target.addAfter(targetName, source);
}
else {
// targetName was null so we are at the start of the list
target.addFirst(source);
targetName = name;
}
}
}
}
}
finally {
ConfigurableApplicationContext closeable = capture;
while (closeable != null) {
try {
closeable.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore;
}
if (closeable.getParent() instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
closeable = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) closeable.getParent();
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
return capture;
}
1) 该方法首先拷贝当前的Environment
2) 通过SpringApplicationBuilder构建了一个简单的SpringBoot启动程序并启动
builder.application().setListeners(Arrays.asList(new BootstrapApplicationListener(),
new ConfigFileApplicationListener()));
这里面会添加两个监听器分别为:BootstrapApplicationListener与ConfigFileApplicationListener,通过先前的学习,我们知道BootstrapApplicationListener是引导程序的核心监听器,而ConfigFileApplicationListener也是非常重要的类:

/* * Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */package org.springframework.boot.context.config;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Set;import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.CachedIntrospectionResults;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertiesConfigurationFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues;
import org.springframework.boot.bind.RelaxedDataBinder;
import org.springframework.boot.bind.RelaxedPropertyResolver;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationPreparedEvent;
import org.springframework.boot.env.EnumerableCompositePropertySource;
import org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourcesLoader;
import org.springframework.boot.logging.DeferredLog;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.event.SmartApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.convert.support.DefaultConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.EnumerablePropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.MutablePropertySources;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySources;
import org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ResourceUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.validation.BindException;/**
-
{@link EnvironmentPostProcessor} that configures the context environment by loading
-
properties from well known file locations. By default properties will be loaded from
-
'application.properties' and/or 'application.yml' files in the following locations:
-
<ul>
-
<li>classpath:</li>
-
<li>file:./</li>
-
<li>classpath:config/</li>
-
<li>file:./config/:</li>
-
</ul>
-
<p>
-
Alternative search locations and names can be specified using
-
{@link #setSearchLocations(String)} and {@link #setSearchNames(String)}.
-
<p>
-
Additional files will also be loaded based on active profiles. For example if a 'web'
-
profile is active 'application-web.properties' and 'application-web.yml' will be
-
considered.
-
<p>
-
The 'spring.config.name' property can be used to specify an alternative name to load
-
and the 'spring.config.location' property can be used to specify alternative search
-
locations or specific files.
-
<p>
-
Configuration properties are also bound to the {@link SpringApplication}. This makes it
-
possible to set {@link SpringApplication} properties dynamically, like the sources
-
("spring.main.sources" - a CSV list) the flag to indicate a web environment
-
("spring.main.web_environment=true") or the flag to switch off the banner
-
("spring.main.show_banner=false").
-
@author Dave Syer
-
@author Phillip Webb
-
@author Stephane Nicoll
-
@author Andy Wilkinson
-
@author Eddú Meléndez
*/
public class ConfigFileApplicationListener
implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, SmartApplicationListener, Ordered {private static final String DEFAULT_PROPERTIES = "defaultProperties";
// Note the order is from least to most specific (last one wins)
private static final String DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = "classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/";private static final String DEFAULT_NAMES = "application";
/**
- The "active profiles" property name.
*/
public static final String ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY = "spring.profiles.active";
/**
- The "includes profiles" property name.
*/
public static final String INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY = "spring.profiles.include";
/**
- The "config name" property name.
*/
public static final String CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY = "spring.config.name";
/**
- The "config location" property name.
*/
public static final String CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY = "spring.config.location";
/**
- The default order for the processor.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10;
/**
- Name of the application configuration {@link PropertySource}.
*/
public static final String APPLICATION_CONFIGURATION_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "applicationConfigurationProperties";
private final DeferredLog logger = new DeferredLog();
private String searchLocations;
private String names;
private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER;
private final ConversionService conversionService = new DefaultConversionService();
@Override
public boolean supportsEventType(Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventType) {
return ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType)
|| ApplicationPreparedEvent.class.isAssignableFrom(eventType);
}@Override
public boolean supportsSourceType(Class<?> aClass) {
return true;
}@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(),
event.getSpringApplication());
}
}List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> loadPostProcessors() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(EnvironmentPostProcessor.class,
getClass().getClassLoader());
}@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment, application);
}private void configureIgnoreBeanInfo(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
if (System.getProperty(
CachedIntrospectionResults.IGNORE_BEANINFO_PROPERTY_NAME) == null) {
RelaxedPropertyResolver resolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(environment,
"spring.beaninfo.");
Boolean ignore = resolver.getProperty("ignore", Boolean.class, Boolean.TRUE);
System.setProperty(CachedIntrospectionResults.IGNORE_BEANINFO_PROPERTY_NAME,
ignore.toString());
}
}private void onApplicationPreparedEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
this.logger.replayTo(ConfigFileApplicationListener.class);
addPostProcessors(((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event).getApplicationContext());
}/**
- Add config file property sources to the specified environment.
- @param environment the environment to add source to
- @param resourceLoader the resource loader
- @see #addPostProcessors(ConfigurableApplicationContext)
*/
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
/**
- Bind the environment to the {@link SpringApplication}.
- @param environment the environment to bind
- @param application the application to bind to
*/
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
PropertiesConfigurationFactory<SpringApplication> binder = new PropertiesConfigurationFactory<SpringApplication>(
application);
binder.setTargetName("spring.main");
binder.setConversionService(this.conversionService);
binder.setPropertySources(environment.getPropertySources());
try {
binder.bindPropertiesToTarget();
}
catch (BindException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", ex);
}
}
/**
- Add appropriate post-processors to post-configure the property-sources.
- @param context the context to configure
*/
protected void addPostProcessors(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(
new PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor(context));
}
public void setOrder(int order) {
this.order = order;
}@Override
public int getOrder() {
return this.order;
}/**
- Set the search locations that will be considered as a comma-separated list. Each
- search location should be a directory path (ending in "/") and it will be prefixed
- by the file names constructed from {@link #setSearchNames(String) search names} and
- profiles (if any) plus file extensions supported by the properties loaders.
- Locations are considered in the order specified, with later items taking precedence
- (like a map merge).
- @param locations the search locations
*/
public void setSearchLocations(String locations) {
Assert.hasLength(locations, "Locations must not be empty");
this.searchLocations = locations;
}
/**
- Sets the names of the files that should be loaded (excluding file extension) as a
- comma-separated list.
- @param names the names to load
*/
public void setSearchNames(String names) {
Assert.hasLength(names, "Names must not be empty");
this.names = names;
}
/**
-
{@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} to re-order our property sources below any
-
{@code @PropertySource} items added by the {@link ConfigurationClassPostProcessor}.
*/
private class PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor
implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered {private ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
this.context = context;
}@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE;
}@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
reorderSources(this.context.getEnvironment());
}private void reorderSources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
ConfigurationPropertySources
.finishAndRelocate(environment.getPropertySources());
PropertySource<?> defaultProperties = environment.getPropertySources()
.remove(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES);
if (defaultProperties != null) {
environment.getPropertySources().addLast(defaultProperties);
}
}
}
/**
-
Loads candidate property sources and configures the active profiles.
*/
private class Loader {private final Log logger = ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.logger;
private final ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private PropertySourcesLoader propertiesLoader;
private Queue<Profile> profiles;
private List<Profile> processedProfiles;
private boolean activatedProfiles;
Loader(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.environment = environment;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader == null ? new DefaultResourceLoader()
: resourceLoader;
}public void load() {
this.propertiesLoader = new PropertySourcesLoader();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.profiles = Collections.asLifoQueue(new LinkedList<Profile>());
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<Profile>();// Pre-existing active profiles set via Environment.setActiveProfiles() // are additional profiles and config files are allowed to add more if // they want to, so don't call addActiveProfiles() here. Set<Profile> initialActiveProfiles = initializeActiveProfiles(); this.profiles.addAll(getUnprocessedActiveProfiles(initialActiveProfiles)); if (this.profiles.isEmpty()) { for (String defaultProfileName : this.environment.getDefaultProfiles()) { Profile defaultProfile = new Profile(defaultProfileName, true); if (!this.profiles.contains(defaultProfile)) { this.profiles.add(defaultProfile); } } } // The default profile for these purposes is represented as null. We add it // last so that it is first out of the queue (active profiles will then // override any settings in the defaults when the list is reversed later). this.profiles.add(null); while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) { Profile profile = this.profiles.poll(); for (String location : getSearchLocations()) { if (!location.endsWith("/")) { // location is a filename already, so don't search for more // filenames load(location, null, profile); } else { for (String name : getSearchNames()) { load(location, name, profile); } } } this.processedProfiles.add(profile); } addConfigurationProperties(this.propertiesLoader.getPropertySources());}
private Set<Profile> initializeActiveProfiles() {
if (!this.environment.containsProperty(ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY)
&& !this.environment.containsProperty(INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY)) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
// Any pre-existing active profiles set via property sources (e.g. System
// properties) take precedence over those added in config files.
SpringProfiles springProfiles = bindSpringProfiles(
this.environment.getPropertySources());
Set<Profile> activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<Profile>(
springProfiles.getActiveProfiles());
activeProfiles.addAll(springProfiles.getIncludeProfiles());
maybeActivateProfiles(activeProfiles);
return activeProfiles;
}/**
- Return the active profiles that have not been processed yet. If a profile is
- enabled via both {@link #ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY} and
- {@link ConfigurableEnvironment#addActiveProfile(String)} it needs to be
- filtered so that the {@link #ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY} value takes precedence.
- <p>
- Concretely, if the "cloud" profile is enabled via the environment, it will take
- less precedence that any profile set via the {@link #ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY}.
- @param initialActiveProfiles the profiles that have been enabled via
- @return the unprocessed active profiles from the environment to enable
*/
private List<Profile> getUnprocessedActiveProfiles(
Set<Profile> initialActiveProfiles) {
List<Profile> unprocessedActiveProfiles = new ArrayList<Profile>();
for (String profileName : this.environment.getActiveProfiles()) {
Profile profile = new Profile(profileName);
if (!initialActiveProfiles.contains(profile)) {
unprocessedActiveProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
// Reverse them so the order is the same as from getProfilesForValue()
// (last one wins when properties are eventually resolved)
Collections.reverse(unprocessedActiveProfiles);
return unprocessedActiveProfiles;
}
private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile) {
String group = "profile=" + (profile == null ? "" : profile);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
// Try to load directly from the location
loadIntoGroup(group, location, profile);
}
else {
// Search for a file with the given name
for (String ext : this.propertiesLoader.getAllFileExtensions()) {
if (profile != null) {
// Try the profile-specific file
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "-" + profile + "." + ext,
null);
for (Profile processedProfile : this.processedProfiles) {
if (processedProfile != null) {
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "-"
+ processedProfile + "." + ext, profile);
}
}
// Sometimes people put "spring.profiles: dev" in
// application-dev.yml (gh-340). Arguably we should try and error
// out on that, but we can be kind and load it anyway.
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "-" + profile + "." + ext,
profile);
}
// Also try the profile-specific section (if any) of the normal file
loadIntoGroup(group, location + name + "." + ext, profile);
}
}
}private PropertySource<?> loadIntoGroup(String identifier, String location,
Profile profile) {
try {
return doLoadIntoGroup(identifier, location, profile);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Failed to load property source from location '" + location + "'",
ex);
}
}private PropertySource<?> doLoadIntoGroup(String identifier, String location,
Profile profile) throws IOException {
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(location);
PropertySource<?> propertySource = null;
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
if (resource != null && resource.exists()) {
String name = "applicationConfig: [" + location + "]";
String group = "applicationConfig: [" + identifier + "]";
propertySource = this.propertiesLoader.load(resource, group, name,
(profile == null ? null : profile.getName()));
if (propertySource != null) {
msg.append("Loaded ");
handleProfileProperties(propertySource);
}
else {
msg.append("Skipped (empty) ");
}
}
else {
msg.append("Skipped ");
}
msg.append("config file ");
msg.append(getResourceDescription(location, resource));
if (profile != null) {
msg.append(" for profile ").append(profile);
}
if (resource == null || !resource.exists()) {
msg.append(" resource not found");
this.logger.trace(msg);
}
else {
this.logger.debug(msg);
}
return propertySource;
}private String getResourceDescription(String location, Resource resource) {
String resourceDescription = "'" + location + "'";
if (resource != null) {
try {
resourceDescription = String.format("'%s' (%s)",
resource.getURI().toASCIIString(), location);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
// Use the location as the description
}
}
return resourceDescription;
}private void handleProfileProperties(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
SpringProfiles springProfiles = bindSpringProfiles(propertySource);
maybeActivateProfiles(springProfiles.getActiveProfiles());
addProfiles(springProfiles.getIncludeProfiles());
}private SpringProfiles bindSpringProfiles(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();
propertySources.addFirst(propertySource);
return bindSpringProfiles(propertySources);
}private SpringProfiles bindSpringProfiles(PropertySources propertySources) {
SpringProfiles springProfiles = new SpringProfiles();
RelaxedDataBinder dataBinder = new RelaxedDataBinder(springProfiles,
"spring.profiles");
dataBinder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(propertySources, false));
springProfiles.setActive(resolvePlaceholders(springProfiles.getActive()));
springProfiles.setInclude(resolvePlaceholders(springProfiles.getInclude()));
return springProfiles;
}private List<String> resolvePlaceholders(List<String> values) {
List<String> resolved = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String value : values) {
resolved.add(this.environment.resolvePlaceholders(value));
}
return resolved;
}private void maybeActivateProfiles(Set<Profile> profiles) {
if (this.activatedProfiles) {
if (!profiles.isEmpty()) {
this.logger.debug("Profiles already activated, '" + profiles
+ "' will not be applied");
}
return;
}
if (!profiles.isEmpty()) {
addProfiles(profiles);
this.logger.debug("Activated profiles "
+ StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(profiles));
this.activatedProfiles = true;
removeUnprocessedDefaultProfiles();
}
}private void removeUnprocessedDefaultProfiles() {
for (Iterator<Profile> iterator = this.profiles.iterator(); iterator
.hasNext()😉 {
if (iterator.next().isDefaultProfile()) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
}private void addProfiles(Set<Profile> profiles) {
for (Profile profile : profiles) {
this.profiles.add(profile);
if (!environmentHasActiveProfile(profile.getName())) {
// If it's already accepted we assume the order was set
// intentionally
prependProfile(this.environment, profile);
}
}
}private boolean environmentHasActiveProfile(String profile) {
for (String activeProfile : this.environment.getActiveProfiles()) {
if (activeProfile.equals(profile)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}private void prependProfile(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
Profile profile) {
Set<String> profiles = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
environment.getActiveProfiles(); // ensure they are initialized
// But this one should go first (last wins in a property key clash)
profiles.add(profile.getName());
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
environment.setActiveProfiles(profiles.toArray(new String[profiles.size()]));
}private Set<String> getSearchLocations() {
Set<String> locations = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// User-configured settings take precedence, so we do them first
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY)) {
for (String path : asResolvedSet(
this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY), null)) {
if (!path.contains("$")) {
path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
if (!ResourceUtils.isUrl(path)) {
path = ResourceUtils.FILE_URL_PREFIX + path;
}
}
locations.add(path);
}
}
locations.addAll(
asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.searchLocations,
DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS));
return locations;
}private Set<String> getSearchNames() {
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY)) {
return asResolvedSet(this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY),
null);
}
return asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.names, DEFAULT_NAMES);
}private Set<String> asResolvedSet(String value, String fallback) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(StringUtils.trimArrayElements(
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value != null
? this.environment.resolvePlaceholders(value) : fallback)));
Collections.reverse(list);
return new LinkedHashSet<String>(list);
}private void addConfigurationProperties(MutablePropertySources sources) {
List<PropertySource<?>> reorderedSources = new ArrayList<PropertySource<?>>();
for (PropertySource<?> item : sources) {
reorderedSources.add(item);
}
addConfigurationProperties(
new ConfigurationPropertySources(reorderedSources));
}private void addConfigurationProperties(
ConfigurationPropertySources configurationSources) {
MutablePropertySources existingSources = this.environment
.getPropertySources();
if (existingSources.contains(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES)) {
existingSources.addBefore(DEFAULT_PROPERTIES, configurationSources);
}
else {
existingSources.addLast(configurationSources);
}
}
}
private static class Profile {
private final String name; private final boolean defaultProfile; Profile(String name) { this(name, false); } Profile(String name, boolean defaultProfile) { Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null"); this.name = name; this.defaultProfile = defaultProfile; } public String getName() { return this.name; } public boolean isDefaultProfile() { return this.defaultProfile; } @Override public String toString() { return this.name; } @Override public int hashCode() { return this.name.hashCode(); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (obj == this) { return true; } if (obj == null || obj.getClass() != getClass()) { return false; } return ((Profile) obj).name.equals(this.name); }}
/**
-
Holds the configuration {@link PropertySource}s as they are loaded can relocate
-
them once configuration classes have been processed.
*/
static class ConfigurationPropertySources
extends EnumerablePropertySource<Collection<PropertySource<?>>> {private final Collection<PropertySource<?>> sources;
private final String[] names;
ConfigurationPropertySources(Collection<PropertySource<?>> sources) {
super(APPLICATION_CONFIGURATION_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, sources);
this.sources = sources;
List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
for (PropertySource<?> source : sources) {
if (source instanceof EnumerablePropertySource) {
names.addAll(Arrays.asList(
((EnumerablePropertySource<?>) source).getPropertyNames()));
}
}
this.names = names.toArray(new String[names.size()]);
}@Override
public Object getProperty(String name) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.sources) {
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(name);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
}
return null;
}public static void finishAndRelocate(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
String name = APPLICATION_CONFIGURATION_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
ConfigurationPropertySources removed = (ConfigurationPropertySources) propertySources
.get(name);
if (removed != null) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : removed.sources) {
if (propertySource instanceof EnumerableCompositePropertySource) {
EnumerableCompositePropertySource composite = (EnumerableCompositePropertySource) propertySource;
for (PropertySource<?> nested : composite.getSource()) {
propertySources.addAfter(name, nested);
name = nested.getName();
}
}
else {
propertySources.addAfter(name, propertySource);
}
}
propertySources.remove(APPLICATION_CONFIGURATION_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
}
}@Override
public String[] getPropertyNames() {
return this.names;
}
}
/**
-
Holder for {@code spring.profiles} properties.
*/
static final class SpringProfiles {private List<String> active = new ArrayList<String>();
private List<String> include = new ArrayList<String>();
public List<String> getActive() {
return this.active;
}public void setActive(List<String> active) {
this.active = active;
}public List<String> getInclude() {
return this.include;
}public void setInclude(List<String> include) {
this.include = include;
}Set<Profile> getActiveProfiles() {
return asProfileSet(this.active);
}Set<Profile> getIncludeProfiles() {
return asProfileSet(this.include);
}private Set<Profile> asProfileSet(List<String> profileNames) {
List<Profile> profiles = new ArrayList<Profile>();
for (String profileName : profileNames) {
profiles.add(new Profile(profileName));
}
Collections.reverse(profiles);
return new LinkedHashSet<Profile>(profiles);
}
}
- The "active profiles" property name.
}
根据javadoc注释的说明,这个类会从指定的位置加载application.properties或者application.yml并将它们的属性读到Envrionment当中,其中这几个方法大家关注下:
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(
(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
当springboot程序启动时一定会触发该事件监听,如果当前是 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件就会调用 onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent方法,最终该方法会执行:
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment, application);
}
其中 bindToSpringApplication方法为:
/**
* Bind the environment to the {@link SpringApplication}.
* @param environment the environment to bind
* @param application the application to bind to
*/
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
PropertiesConfigurationFactory<SpringApplication> binder = new PropertiesConfigurationFactory<SpringApplication>(
application);
binder.setTargetName("spring.main");
binder.setConversionService(this.conversionService);
binder.setPropertySources(environment.getPropertySources());
try {
binder.bindPropertiesToTarget();
}
catch (BindException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", ex);
}
}
很明显该方法是将Environment绑定到对应SpringApplication上,通过这个类就可以获取到我们更改过后的配置了
1.3、changes方法
private Map<String, Object> changes(Map<String, Object> before,
Map<String, Object> after) {
Map<String, Object> result = new HashMap<String, Object>();
for (String key : before.keySet()) {
if (!after.containsKey(key)) {
result.put(key, null);
}
else if (!equal(before.get(key), after.get(key))) {
result.put(key, after.get(key));
}
}
for (String key : after.keySet()) {
if (!before.containsKey(key)) {
result.put(key, after.get(key));
}
}
return result;
}
changes方法其实就是处理配置变更信息的,分以下几种情况:
1)如果刷新过后配置文件新增配置就添加到Map里
2) 如果有配置变更就添加变更后的配置
3) 如果删除了原先的配置,就把原先的key对应的值设置为null
至此经过changes方法后,上下文环境已经拥有最新的配置了。
1.4、发布事件
当上述步骤都执行完毕后,紧接着会发布EnvrionmentChangeEvent事件,可是这个事件谁来监听呢?在这里我贴出官网的一段描述:
应用程序将收听EnvironmentChangeEvent,并以几种标准方式进行更改(用户可以以常规方式添加ApplicationListeners附加ApplicationListeners)。当观察到EnvironmentChangeEvent时,它将有一个已更改的键值列表,应用程序将使用以下内容:1.重新绑定上下文中的任何@ConfigurationProperties bean
2.为logging.level.*中的任何属性设置记录器级别
根据官网描述我们知道将变更一下操作行为@ConfigurationProperties的bean与更改日志level,那么如何做到的呢?结合官网文档我们来关注以下两个类:
ConfigurationPropertiesRebinder:
 View Code
View Code我们可以看到该类监听了ChangeEnvrionmentEvent事件,它最主要作用是拿到更新的配置以后,重新绑定@ConfigurationProperties标记的类使之能够读取最新的属性
LoggingRebinder:
 View Code
View Code该类也是监听了ChangeEnvrionmentEvent事件,用于重新绑定日志级别
二、刷新范围
我们考虑如下场景,当我们变更数据库配置后,通过refresh刷新,虽然能获取到最新的配置,可是我们的DataSource对象早就被初始化好了,换句话说即便配置刷新了我们拿到的依然是配置刷新前的对象。怎么解决这个问题呢?
我们继续看ContextRefresher的refresh方法,最后有一处代码值得我们关注一下this.scope.refreshAll(),此处scope对象是RefreshScope类型,那么这个类有什么作用呢?那么我们先要关注一下@RefreshScope注解。在这里我在贴出官网一段解释:
当配置更改时,标有@RefreshScope的Spring @Bean将得到特殊处理。这解决了状态bean在初始化时只注入配置的问题。例如,如果通过Environment更改数据库URL时DataSource有开放连接,那么我们可能希望这些连接的持有人能够完成他们正在做的工作。然后下一次有人从游泳池借用一个连接,他得到一个新的URL
刷新范围bean是在使用时初始化的懒惰代理(即当调用一个方法时),并且作用域作为初始值的缓存。要强制bean重新初始化下一个方法调用,您只需要使其缓存条目无效。RefreshScope是上下文中的一个bean,它有一个公共方法refreshAll()来清除目标缓存中的范围内的所有bean。还有一个refresh(String)方法可以按名称刷新单个bean。此功能在/refresh端点(通过HTTP或JMX)中公开。
这里我贴出@RefreshScope源码:
 View Code
View Code在这个注解上我们关注一下此处标记了@Scope("refresh"),我们知道Spring的Bean属性有个叫scope的,它定义了bean的作用范围,常见的有singleon,prototype,session等。此处新定义了一个范围叫做refresh,在此我贴出RefreshScope的源代码来分析一下:
 View Code
View Code该类继承了GenericScope:
 View Code
View Code
这里面我们先看一下RefreshScope的构造函数:
/**
* Create a scope instance and give it the default name: "refresh".
*/
public RefreshScope() {
super.setName("refresh");
}
这里面创建了一个名字为refresh的scope。
紧接着在它的父类里我们可以看一下这个方法:
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
beanFactory.registerScope(this.name, this);
setSerializationId(beanFactory);
}
此方法中使用BeanFactory注册了一个refresh的范围,使得scope为refresh的bean生效。@RefreshScope标注的类还有一个特点:会使用代理对象并进行延迟加载。我们来看一下postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeansException {
for (String name : registry.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition definition = registry.getBeanDefinition(name);
if (definition instanceof RootBeanDefinition) {
RootBeanDefinition root = (RootBeanDefinition) definition;
if (root.getDecoratedDefinition() != null && root.hasBeanClass()
&& root.getBeanClass() == ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class) {
if (getName().equals(root.getDecoratedDefinition().getBeanDefinition()
.getScope())) {
root.setBeanClass(LockedScopedProxyFactoryBean.class);
}
}
}
}
}
该方法遍历所有的bean定义 如果当前的bean的scope为refresh,那么就把当前的bean设置为 LockedScopedProxyFactoryBean的代理对象。
RefreshScope还会监听一个ContextRefreshedEvent,该事件会在ApplicationContext初始化或者refreshed时触发,我们来看一下代码:
@EventListener
public void start(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
if (event.getApplicationContext() == this.context && this.eager
&& this.registry != null) {
eagerlyInitialize();
}
}
private void eagerlyInitialize() {
for (String name : this.context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition definition = this.registry.getBeanDefinition(name);
if (this.getName().equals(definition.getScope()) && !definition.isLazyInit()) {
Object bean = this.context.getBean(name);
if (bean != null) {
bean.getClass();
}
}
}
}</pre>
注意此处获取refreshscope的bean,其中getBean是一个复杂而又繁琐的过程,此处我们先不在这里讨论,只不过经过这个方法以后,其通过代理机制会在GernericScope的BeanLifecycleWrapperCache缓存里把这个@RefreshScope标记的bean添加进去。
最后我们回过头来看一看RefreshScope的refreshAll方法:
@ManagedOperation(description = "Dispose of the current instance of all beans in this scope and force a refresh on next method execution.")
public void refreshAll() {
super.destroy();
this.context.publishEvent(new RefreshScopeRefreshedEvent());
}
//.......GernericScope的destroy方法
@Override
public void destroy() {
List<Throwable> errors = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
Collection<BeanLifecycleWrapper> wrappers = this.cache.clear();
for (BeanLifecycleWrapper wrapper : wrappers) {
try {
Lock lock = locks.get(wrapper.getName()).writeLock();
lock.lock();
try {
wrapper.destroy();
}
finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
errors.add(e);
}
}
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
throw wrapIfNecessary(errors.get(0));
}
this.errors.clear();
}</pre>
这里的代码逻辑很简单清除与释放缓存里被@RefreshScope标记的bean 。
当我们要获取对象时,我们可以关注如下方法:
@Override
public Object get(String name, ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
BeanLifecycleWrapper value = this.cache.put(name,
new BeanLifecycleWrapper(name, objectFactory));
locks.putIfAbsent(name, new ReentrantReadWriteLock());
try {
return value.getBean();
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
this.errors.put(name, e);
throw e;
}
}
//..... BeanLifecycleWrapper的方法
public Object getBean() {
if (this.bean == null) {
synchronized (this.name) {
if (this.bean == null) {
this.bean = this.objectFactory.getObject();
}
}
}
return this.bean;
} </pre>
BeanLifecycleWrapper这个是@RefreshScope标记bean的一个包装类,会被存储到缓存里,在这里取不到值的话就会从objectFactory里去拿
三、示例与总结
3.1、示例
创建AppConfig类代码如下:

package com.bdqn.lyrk.refresh.scope.server;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(StudentConfig.class)
public class AppConfig {@RefreshScope @Bean public Student student(StudentConfig config) { Student student = new Student(); student.setName(config.getName()); return student; }}
在这里,将Student设置为@RefreshScope 那么刷新以后会获取最新的Bean
启动类:

package com.bdqn.lyrk.refresh.scope.server;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
public class RefreshScopeApplication {@Autowired private Student student; @GetMapping public String student() { return student.getName(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { SpringApplication.run(RefreshScopeApplication.class, args); }}
application.yml文件:

spring:
application:
name: refresh-scope-server
endpoints:
refresh:
sensitive: false
server:
port: 8089
student:
name: admin
这里把refresh端点开放出来,然后变更配置后就可以获取最新的对象了
3.2、总结
1) 当配置更新并通过refresh端点刷新后,会执行ContextRefresher的refresh方法,该方法会记录当前的Environment,而后构建一个简易的SpringApplicationBuilder并执行其run方法,此时ConfigFileApplicationListener会读取我们修改过后的配置并绑定到SpringApplication对象上,最后进行changes操作来变更已有的PropertySource
2) @RefreshScope最好配合@Bean使用,当且仅当变更配置后,需要重新获取最新的bean时使用。加上该注解的Bean会被代理并且延迟加载,所有的scope属性为Refresh的bean会被包装成BeanLifecycleWrapper存入缓存(ConcurrentHashMap)中,所有的读取,修改,删除都是基于该缓存的
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/10427041.html




