BZOJ1497 [NOI2006] 最大获利
题目链接:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1497
Description
新的技术正冲击着手机通讯市场,对于各大运营商来说,这既是机遇,更是挑战。THU集团旗下的CS&T通讯公司在新一代通讯技术血战的前夜,需要做太多的准备工作,仅就站址选择一项,就需要完成前期市场研究、站址勘测、最优化等项目。在前期市场调查和站址勘测之后,公司得到了一共N个可以作为通讯信号中转站的地址,而由于这些地址的地理位置差异,在不同的地方建造通讯中转站需要投入的成本也是不一样的,所幸在前期调查之后这些都是已知数据:建立第i个通讯中转站需要的成本为Pi(1≤i≤N)。另外公司调查得出了所有期望中的用户群,一共M个。关于第i个用户群的信息概括为Ai, Bi和Ci:这些用户会使用中转站Ai和中转站Bi进行通讯,公司可以获益Ci。(1≤i≤M, 1≤Ai, Bi≤N) THU集团的CS&T公司可以有选择的建立一些中转站(投入成本),为一些用户提供服务并获得收益(获益之和)。那么如何选择最终建立的中转站才能让公司的净获利最大呢?(净获利 = 获益之和 - 投入成本之和)
Input
输入文件中第一行有两个正整数N和M 。第二行中有N个整数描述每一个通讯中转站的建立成本,依次为P1, P2, …, PN 。以下M行,第(i + 2)行的三个数Ai, Bi和Ci描述第i个用户群的信息。所有变量的含义可以参见题目描述。
Output
你的程序只要向输出文件输出一个整数,表示公司可以得到的最大净获利。
最大权闭合子图,参见2007年国家集训队胡伯涛论文《最小割模型在信息学竞赛中的应用》,参照论文中的方法建图
源点向每一个中转站连流量为费用的边,用户向汇点连流量为收益的边,中转站向对应用户连流量为INF的边
关于效率:
参照这道题的实际表现改进了最大流模版的写法,BFS到汇点就跳出能快很多(这个图只有4层,且第三层的点很多),不同的当前弧优化姿势也能影响效率。最快的一份代码跑到了252ms。

效率对比:400+ms是另一种当前弧优化的姿势,1000+ms是BFS到汇点不跳出。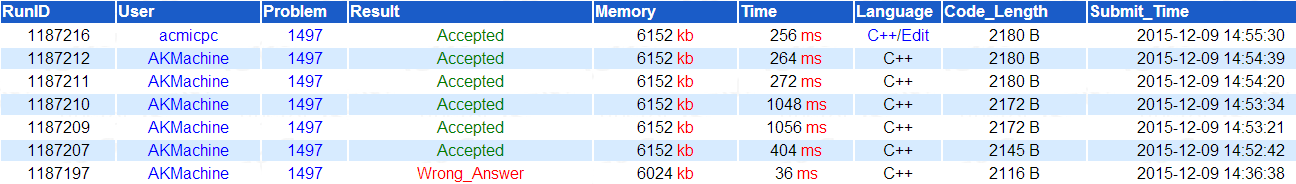
update: 后来对代码进行了几乎可以忽略的小修改,只快了4ms,要想提高效率估计只有写非递归DFS,或者干脆用ISAP了。但是单纯的提高效率并没有什么意义。


1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <queue> 6 #define rep(i,l,r) for(int i=l; i<=r; i++) 7 #define clr(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x)) 8 #define travel(x) for(int i=last[x]; i!=-1; i=edge[i].pre) 9 const int INF = 0x7fffffff; 10 const int maxn = 55010; 11 using namespace std; 12 struct Edge{ 13 int pre,to,cost; 14 }edge[350000]; 15 int n,m,x,y,z,s,t,now,tot=-1,ans=0,total=0,last[maxn],cur[maxn],d[maxn]; 16 queue <int> q; 17 inline int read(){ 18 int ans = 0, f = 1; 19 char c = getchar(); 20 while (!isdigit(c)){ 21 if (c == '-') f = -1; 22 c = getchar(); 23 } 24 while (isdigit(c)){ 25 ans = ans * 10 + c - '0'; 26 c = getchar(); 27 } 28 return ans * f; 29 } 30 inline void addedge(int x,int y,int z){ 31 edge[++tot].pre = last[x]; 32 edge[tot].to = y; 33 edge[tot].cost = z; 34 last[x] = tot; 35 } 36 bool bfs(){ 37 while (!q.empty()) q.pop(); 38 clr(d,-1); d[s] = 0; q.push(s); 39 while (!q.empty()){ 40 now = q.front(); q.pop(); 41 travel(now){ 42 if (d[edge[i].to] == -1 && edge[i].cost > 0){ 43 d[edge[i].to] = d[now] + 1; 44 q.push(edge[i].to); 45 if (edge[i].to == t) return 1; 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 return 0; 50 } 51 int dfs(int x,int flow){ 52 if (x == t || (!flow)) return flow; int w = 0; 53 for (int i=cur[x]; i!=-1 && w<flow; i=edge[i].pre){ 54 if (d[edge[i].to] == d[x] + 1 && edge[i].cost > 0){ 55 int delta = dfs(edge[i].to,min(flow-w,edge[i].cost)); 56 edge[i].cost -= delta; 57 edge[i^1].cost += delta; 58 w += delta; 59 if (edge[i].cost) cur[x] = i; 60 } 61 } 62 if (w < flow) d[x] = -1; 63 return w; 64 } 65 int main(){ 66 n = read(); m = read(); clr(last,-1); 67 s = 0; t = n + m + 1; 68 rep(i,1,n){ 69 x = read(); 70 addedge(s,i,x); addedge(i,s,0); 71 } 72 rep(i,1,m){ 73 x = read(); y = read(); z = read(); 74 total += z; 75 addedge(i+n,t,z); addedge(t,i+n,0); 76 addedge(x,i+n,INF); addedge(i+n,x,0); 77 addedge(y,i+n,INF); addedge(i+n,y,0); 78 } 79 while (bfs()){ 80 rep(i,0,n+m+1) cur[i] = last[i]; 81 int tans = dfs(s,INF); 82 ans += tans; 83 } 84 printf("%d\n",total-ans); 85 return 0; 86 }




