- 学习目的:
通过进一步学习Nhibernate基础知识,掌握用Nhiberate实现多对多的业务逻辑
- 开发环境+必要准备
开发环境: windows 2003,Visual studio .Net 2005,Sql server 2005 developer edition
前期准备: 学习上两篇单表操作和many-to-one篇
3.对上篇文章的部分解释
1)bag节点:用于定义System.Collection.IList类型的集合元素。
|
属性
|
用法
|
举例
|
|
name
|
映射的属性(必须)
|
name=”SalaryList”
|
|
table
|
映射的数据表(可选) |
table=”Salary” |
| lazy |
延迟加载(可选) |
Lazy=true|false |
| cascade |
指示级联操作方式(可选) |
Cascade=all |
| inverse |
关联由谁负责维护 |
Inverse=”true” |
当lazy=”true”,父类初始化的时候不会自动加载子类集合
Cascade为级联操作方式,包括:
| 属性 |
用法说明 |
| none |
默认值,不进行级联操作 |
| save-update |
save和update级联 |
| delete |
删除级联 |
| delete-orphan |
删除不相关的父对象的子对象 |
| all |
save/update/delete级联 |
| all-delete-orphan |
all+delete-arphan |
 当inverse=”true”的时候代表由子类维护级联关系。这时候如果只往父类中添加子类,但不设定子类的父类,是不能保存子类的
当inverse=”true”的时候代表由子类维护级联关系。这时候如果只往父类中添加子类,但不设定子类的父类,是不能保存子类的。
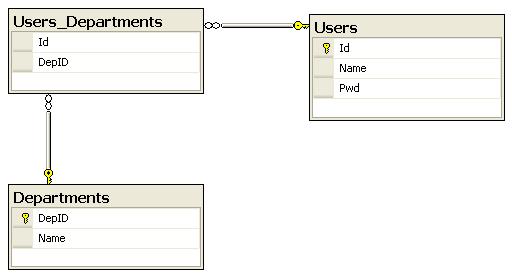
4.多对多业务模型
还是用户系统,1个用户职员隶属于多个部门,同时1个部门有多个不同的职员
用户和部门之间的数据关系图为:
5. 实现步骤:
1)User.cs

 User.cs
User.cs
 using System;
using System;
 using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic;
 using System.Text;
using System.Text;

 namespace NhibernateSample1
namespace NhibernateSample1


 {
{
 public class User
public class User


 {
{
 private int _id;
private int _id;
 private string _name;
private string _name;
 private string _pwd;
private string _pwd;
 private System.Collections.IList _departmentsList;
private System.Collections.IList _departmentsList;

 /**//// <summary>
/**//// <summary>
 /// 编号
/// 编号
 /// </summary>
/// </summary>
 public virtual int Id
public virtual int Id


 {
{
 get
get


 {
{
 return _id;
return _id;
 }
}
 set
set


 {
{
 _id = value;
_id = value;
 }
}
 }
}


 /**//// <summary>
/**//// <summary>
 /// 名称
/// 名称
 /// </summary>
/// </summary>
 public virtual string Name
public virtual string Name


 {
{
 get
get


 {
{
 return _name;
return _name;
 }
}
 set
set


 {
{
 _name = value;
_name = value;
 }
}
 }
}


 /**//// <summary>
/**//// <summary>
 /// 密码
/// 密码
 /// </summary>
/// </summary>
 public virtual string Pwd
public virtual string Pwd


 {
{
 get
get


 {
{
 return _pwd;
return _pwd;
 }
}
 set
set


 {
{
 _pwd = value;
_pwd = value;
 }
}
 }
}

 /**//// <summary>
/**//// <summary>
 /// 工资列表
/// 工资列表
 /// </summary>
/// </summary>
 public System.Collections.IList DepartmentsList
public System.Collections.IList DepartmentsList


 {
{
 get
get


 {
{
 return _departmentsList;
return _departmentsList;
 }
}
 set
set


 {
{
 _departmentsList = value;
_departmentsList = value;
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}

2)User.hbm.xml

 User.hbm.xml
User.hbm.xml
 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
 <hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2">
<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2">
 <class name="NhibernateSample1.User,NhibernateSample1" table="Users" lazy="false">
<class name="NhibernateSample1.User,NhibernateSample1" table="Users" lazy="false">
 <id name="Id" column="Id" unsaved-value="0">
<id name="Id" column="Id" unsaved-value="0">
 <generator class="native" />
<generator class="native" />
 </id>
</id>
 <property name="Name" column="Name" type="string" length="64" not-null="true" unique="true"></property>
<property name="Name" column="Name" type="string" length="64" not-null="true" unique="true"></property>
 <property name="Pwd" column="Pwd" type="string" length="64" not-null="true"></property>
<property name="Pwd" column="Pwd" type="string" length="64" not-null="true"></property>
 <bag name="DepartmentsList" table="Users_Departments" inverse="true" lazy="false" cascade="all">
<bag name="DepartmentsList" table="Users_Departments" inverse="true" lazy="false" cascade="all">
 <key column="Id"/>
<key column="Id"/>
 <many-to-many class="NhibernateSample1.Departments,NhibernateSample1" column="DepID"></many-to-many>
<many-to-many class="NhibernateSample1.Departments,NhibernateSample1" column="DepID"></many-to-many>
 </bag>
</bag>
 </class>
</class>
 </hibernate-mapping>
</hibernate-mapping>
3) Departments.cs

 Departments
Departments
 using System;
using System;
 using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic;
 using System.Text;
using System.Text;
 using System.Collections;
using System.Collections;

 namespace NhibernateSample1
namespace NhibernateSample1


 {
{
 public class Departments
public class Departments


 {
{
 int _depID;
int _depID;
 string _name;
string _name;
 IList _usersList= new ArrayList();
IList _usersList= new ArrayList();
 public virtual int DepID
public virtual int DepID


 {
{
 get
get


 {
{
 return _depID;
return _depID;
 }
}
 set
set


 {
{
 _depID = value;
_depID = value;
 }
}
 }
}
 public virtual string Name
public virtual string Name


 {
{
 get
get


 {
{
 return _name;
return _name;
 }
}
 set
set


 {
{
 _name = value;
_name = value;
 }
}
 }
}
 public virtual IList UsersList
public virtual IList UsersList


 {
{
 get
get


 {
{
 return _usersList;
return _usersList;
 }
}
 set
set


 {
{
 _usersList = value;
_usersList = value;
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}
 }
}

4) Departments.hbm.xml

 Departments.hbm.xml
Departments.hbm.xml
 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
 <hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2">
<hibernate-mapping xmlns="urn:nhibernate-mapping-2.2">
 <class name="NhibernateSample1.Departments,NhibernateSample1" table="Departments" lazy="false">
<class name="NhibernateSample1.Departments,NhibernateSample1" table="Departments" lazy="false">
 <id name="DepID" column="DepID" unsaved-value="0">
<id name="DepID" column="DepID" unsaved-value="0">
 <generator class="native" />
<generator class="native" />
 </id>
</id>
 <property name="Name" column="Name" type="string" length="64" not-null="true" unique="true"></property>
<property name="Name" column="Name" type="string" length="64" not-null="true" unique="true"></property>
 <bag name="UsersList" table="Users_Departments" lazy="true" >
<bag name="UsersList" table="Users_Departments" lazy="true" >
 <key column="DepID"/>
<key column="DepID"/>
 <many-to-many class="NhibernateSample1.User,NhibernateSample1" column="Id"></many-to-many>
<many-to-many class="NhibernateSample1.User,NhibernateSample1" column="Id"></many-to-many>
 </bag>
</bag>
 </class>
</class>
 </hibernate-mapping>
</hibernate-mapping>
5) 数据操作类

 UserDepartmentFixure.cs
UserDepartmentFixure.cs
 using System;
using System;
 using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic;
 using System.Text;
using System.Text;
 using System.Collections;
using System.Collections;
 using NHibernate;
using NHibernate;
 using NHibernate.Cfg;
using NHibernate.Cfg;
 using NHibernate.Tool.hbm2ddl;
using NHibernate.Tool.hbm2ddl;

 namespace NhibernateSample1
namespace NhibernateSample1


 {
{
 public class UserDepartmentFixure
public class UserDepartmentFixure


 {
{
 private ISessionFactory _sessions;
private ISessionFactory _sessions;
 public void Configure()
public void Configure()


 {
{
 Configuration cfg = GetConfiguration();
Configuration cfg = GetConfiguration();
 _sessions = cfg.BuildSessionFactory();
_sessions = cfg.BuildSessionFactory();
 }
}
 Configuration GetConfiguration()
Configuration GetConfiguration()


 {
{
 string cfgPath = @"E:\my project\nhibernate study\simle 1\NHibernateStudy1\NhibernateSample1\hibernate.cfg.xml";
string cfgPath = @"E:\my project\nhibernate study\simle 1\NHibernateStudy1\NhibernateSample1\hibernate.cfg.xml";
 Configuration cfg = new Configuration().Configure(cfgPath);
Configuration cfg = new Configuration().Configure(cfgPath);
 return cfg;
return cfg;
 }
}
 public void ExportTables()
public void ExportTables()


 {
{
 Configuration cfg = GetConfiguration();
Configuration cfg = GetConfiguration();
 new SchemaExport(cfg).Create(true, true);
new SchemaExport(cfg).Create(true, true);
 }
}
 public User CreateUser(String name,string pwd)
public User CreateUser(String name,string pwd)


 {
{
 User u = new User();
User u = new User();
 u.Name = name;
u.Name = name;
 u.Pwd = pwd;
u.Pwd = pwd;
 u.DepartmentsList = new ArrayList();
u.DepartmentsList = new ArrayList();

 ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();

 ITransaction tx = null;
ITransaction tx = null;

 try
try


 {
{
 tx = session.BeginTransaction();
tx = session.BeginTransaction();
 session.Save(u);
session.Save(u);
 tx.Commit();
tx.Commit();
 }
}
 catch (HibernateException e)
catch (HibernateException e)


 {
{
 if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
 throw e;
throw e;
 }
}
 finally
finally


 {
{
 session.Close();
session.Close();
 }
}

 return u;
return u;
 }
}
 public Departments CreateDepartments(User u, string name)
public Departments CreateDepartments(User u, string name)


 {
{
 Departments item = new Departments();
Departments item = new Departments();
 item.Name=name;
item.Name=name;
 u.DepartmentsList.Add(item);
u.DepartmentsList.Add(item);
 item.UsersList.Add(u);
item.UsersList.Add(u);
 ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
 ITransaction tx = null;
ITransaction tx = null;

 try
try


 {
{
 tx = session.BeginTransaction();
tx = session.BeginTransaction();
 session.Save(item);
session.Save(item);
 tx.Commit();
tx.Commit();
 }
}
 catch (HibernateException e)
catch (HibernateException e)


 {
{
 if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
 throw e;
throw e;
 }
}
 finally
finally


 {
{
 session.Close();
session.Close();
 }
}
 return item;
return item;
 }
}
 public Departments GetDepartments(int depID)
public Departments GetDepartments(int depID)


 {
{
 ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
 ITransaction tx = null;
ITransaction tx = null;
 try
try


 {
{
 tx = session.BeginTransaction();
tx = session.BeginTransaction();
 Departments item = (Departments)session.Load(typeof(Departments),
Departments item = (Departments)session.Load(typeof(Departments),
 depID);
depID);
 tx.Commit();
tx.Commit();
 return item;
return item;
 }
}
 catch (HibernateException e)
catch (HibernateException e)


 {
{
 if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
 return null;
return null;
 }
}
 finally
finally


 {
{
 session.Close();
session.Close();
 }
}
 return null;
return null;
 }
}
 public User GetUser(int uid)
public User GetUser(int uid)


 {
{
 ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
 ITransaction tx = null;
ITransaction tx = null;
 try
try


 {
{
 tx = session.BeginTransaction();
tx = session.BeginTransaction();
 User item = (User)session.Load(typeof(User),
User item = (User)session.Load(typeof(User),
 uid);
uid);
 tx.Commit();
tx.Commit();
 return item;
return item;
 }
}
 catch (HibernateException e)
catch (HibernateException e)


 {
{
 if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
 return null;
return null;
 }
}
 finally
finally


 {
{
 session.Close();
session.Close();
 }
}
 return null;
return null;
 }
}

 public void Delete(int uid)
public void Delete(int uid)


 {
{
 ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
ISession session = _sessions.OpenSession();
 ITransaction tx = null;
ITransaction tx = null;
 try
try


 {
{
 tx = session.BeginTransaction();
tx = session.BeginTransaction();
 Departments item = session.Load(typeof(Departments), uid) as Departments;
Departments item = session.Load(typeof(Departments), uid) as Departments;
 session.Delete(item);
session.Delete(item);
 tx.Commit();
tx.Commit();
 }
}
 catch (HibernateException e)
catch (HibernateException e)


 {
{
 if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
if (tx != null) tx.Rollback();
 throw e;
throw e;
 }
}
 finally
finally


 {
{
 session.Close();
session.Close();
 }
}
 }
}

 }
}
 }
}

6)单元测试类

 UnitTest1.cs
UnitTest1.cs
 using System;
using System;
 using System.Text;
using System.Text;
 using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.Generic;
 using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
 using NhibernateSample1;
using NhibernateSample1;

 namespace TestProject1
namespace TestProject1


 {
{

 /**//// <summary>
/**//// <summary>
 /// UnitTest1 的摘要说明
/// UnitTest1 的摘要说明
 /// </summary>
/// </summary>
 [TestClass]
[TestClass]
 public class UnitTest1
public class UnitTest1


 {
{
 public UnitTest1()
public UnitTest1()


 {
{
 //
//
 // TODO: 在此处添加构造函数逻辑
// TODO: 在此处添加构造函数逻辑
 //
//
 }
}
 NhibernateSample1.UserDepartmentFixure usf = new UserDepartmentFixure();
NhibernateSample1.UserDepartmentFixure usf = new UserDepartmentFixure();

 其他测试属性#region 其他测试属性
其他测试属性#region 其他测试属性
 //
//
 // 您可以在编写测试时使用下列其他属性:
// 您可以在编写测试时使用下列其他属性:
 //
//
 // 在运行类中的第一个测试之前使用 ClassInitialize 运行代码
// 在运行类中的第一个测试之前使用 ClassInitialize 运行代码
 // [ClassInitialize()]
// [ClassInitialize()]
 // public static void MyClassInitialize(TestContext testContext) { }
// public static void MyClassInitialize(TestContext testContext) { }
 //
//
 // 在类中的所有测试都已运行之后使用 ClassCleanup 运行代码
// 在类中的所有测试都已运行之后使用 ClassCleanup 运行代码
 // [ClassCleanup()]
// [ClassCleanup()]
 // public static void MyClassCleanup() { }
// public static void MyClassCleanup() { }
 //
//
 // 在运行每个测试之前使用 TestInitialize 运行代码
// 在运行每个测试之前使用 TestInitialize 运行代码
 // [TestInitialize()]
// [TestInitialize()]
 // public void MyTestInitialize() { }
// public void MyTestInitialize() { }
 //
//
 // 在运行每个测试之后使用 TestCleanup 运行代码
// 在运行每个测试之后使用 TestCleanup 运行代码
 // [TestCleanup()]
// [TestCleanup()]
 // public void MyTestCleanup() { }
// public void MyTestCleanup() { }
 //
//
 #endregion
#endregion

 [TestMethod]
[TestMethod]
 public void Test1()
public void Test1()


 {
{
 usf.Configure();
usf.Configure();
 usf.ExportTables();
usf.ExportTables();
 User u = usf.CreateUser(Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), "ds");
User u = usf.CreateUser(Guid.NewGuid().ToString(), "ds");
 Assert.IsTrue(u.Id>0);
Assert.IsTrue(u.Id>0);
 Departments s = usf.CreateDepartments(u, "政治部");
Departments s = usf.CreateDepartments(u, "政治部");
 Assert.IsTrue(s.DepID > 0);
Assert.IsTrue(s.DepID > 0);
 Departments s1 = usf.CreateDepartments(u, "事业部");
Departments s1 = usf.CreateDepartments(u, "事业部");
 Assert.IsTrue(s1.DepID > 0);
Assert.IsTrue(s1.DepID > 0);
 usf.Delete(s1.DepID);
usf.Delete(s1.DepID);
 s1 = usf.GetDepartments(s1.DepID);
s1 = usf.GetDepartments(s1.DepID);
 Assert.IsNull(s1);
Assert.IsNull(s1);
 User u1 = usf.GetUser(1);
User u1 = usf.GetUser(1);
 Assert.IsTrue(u1.DepartmentsList.Count>0);
Assert.IsTrue(u1.DepartmentsList.Count>0);
 }
}

 }
}
 }
}

到现在为止,终于更加体会到nhibernate的强大了。继续努力,fight!
files:
/Files/jillzhang/simple3.rar 上几篇文章:
Nhibernate学习之起步篇-1 Nhibernate分析之华山论剑篇 Nhibernate学习起步之many-to-one篇










 }
}