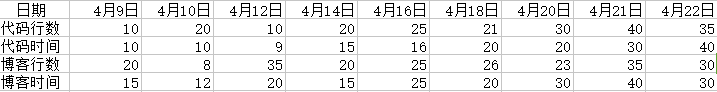
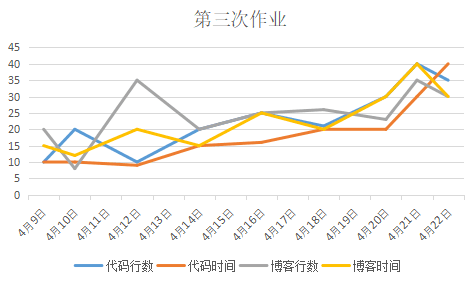
第三次作业
题目6-1 输出月份英文名
1.设计思路
(1)本次题目的算法
第一步:阅读题目 理解主函数与函数声明
第二步:定义调用函数*getmonth
第三步:使用witch函数
第四步:最终回到null
(2)流程图
2.实验代码
char *getmonth(int n)
{
switch(n)
{
case 1:return "January";
case 2:return "February";
case 3:return "March";
case 4:return "April";
case 5:return "May";
case 6:return "June";
case 7:return "July";
case 8:return "August";
case 9:return "September";
case 10:return "October";
case 11:return "November";
case 12:return "December";
default:return NULL;
}
}
3.调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
错误信息1:月份用了简写
错误原因:未能及时理解题意
改正方法:仔细阅读,理解题意
题目6-2 查找星期
1.设计思路
(1)本次题目的算法
第一步:阅读题目 理解主函数与函数声明
第二步:使用调用函数,定义变量j
第三步:使用数组标记星期,使用if函数和for函数
第四步:回归j或-1
(2)流程图
2.实验代码
int getindex(char *s)
{
int i;
int j=-1;
char *week[7]={"Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"};
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
{
if(strcmp(s,week[i])==0)
{
j=i;
}
else;
}
return j;
}
3.调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
错误信息1:无

题目6-3 计算最长的字符串长度
1.设计思路
(1)本次题目的算法
第一步:阅读题目 理解主函数与函数声明
第二步:使用调用函数,定义变量i,a,count
第三步:使用for函数和if函数
第四步:回归count
(2)流程图
2.实验代码
int max_len(char *s[],int n)
{
int i,a;
int count=0;
int q[20]={0};
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(a=0;*(*(s+i)+a)!='\0';a++)
{}
q[i]=a;
}
count =q[0];
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(q[i]>count)
{
count=q[i];
}
}
return count;
}
3.调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
错误信息1:编译错误
错误原因:打代码时不仔细,有错误
改正方法:多次反复检查,找到错误并改正
题目6-4 指定位置输出字符串
1.设计思路
(1)本次题目的算法
第一步:阅读题目 理解主函数与函数声明
第二步:使用调用函数,定义变量i,b,q,定义数组s
第三步:使用if函数和for函数,使用指针
第四步:最终回归s+i
(2)流程图
2.实验代码
char *match(char *s, char ch1, char ch2)
{
int i,b;
char *q=NULL;
for(i=0;*(s+i)!='\0';i++)
{
if(*(s+i)==ch1)
{
char *a=&s[i];
for(b=i;(*(s+b)!=ch2)&&(*(s+b)!='\0');b++)
{
printf("%c",*(s+b));
}
if(*(s+b)!='\0')
printf("%c",*(s+b));
printf("\n");
return a;
}
}
printf("\n");
return s+i;
}
3.调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
错误信息1:编译错误
错误原因:代码没打仔细
改正方法:重新输入
错误信息2:指针与&&
错误原因:指针与&&连用时出错
改正方法:((s+b)!=ch2)&&((s+b)!='\0')

题目6-1 奇数值结点链表
1.设计思路
(1)本次题目的算法
第一步:阅读题目 理解主函数与函数声明
第二步:使用调用函数,定义变量data,使用指针head,指针p,指针q
第三步:使用while函数,if函数和for函数
第四步:第一次使用调用函数回归head,第二次使用调用函数回归head1
(2)流程图
2.实验代码
struct ListNode *readlist()
{
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*p=NULL,*q=NULL;
int data;
p=q=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
while(p->data!=-1)
{
if(head==NULL)
{
head=p;
}
else
{
q->next=p;
}
q=p;
p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
scanf("%d",&p->data);
}
q->next=NULL;
return(head);
}
struct ListNode *getodd( struct ListNode **L )
{
struct ListNode *head=NULL,*q=NULL,*p,*w=NULL,*head1=NULL;
if(*L!=NULL)
{
for(head=*L;head!=NULL;head=head->next)
{
if(head->data%2!=0)
{
if(head1==NULL)
{
head1=head;
}
else
{
p->next=head;
}
p=head;
}
else
{
if(q==NULL)
{
q=head;
}
else
{
w->next=head;
}
w=head;
}
}
p->next=NULL;
if(w!=NULL)
w->next=NULL;
*L=q;
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
return(head1);
}
3.调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
错误信息1:使用了两次调用函数
错误原因:两次调用函数链接的不好
改正方法:根据系统提示逐一改正

题目6-2 学生成绩链表处理
1.设计思路
(1)本次题目的算法
第一步:阅读题目 理解主函数与函数声明
第二步:使用调用函数,使用指针head,指针p,指针q,指针w,定义变量num,name,score
第三步:使用while函数,if函数和for函数,两次使用调用函数
第四步:第一次调用函数回归head,第二次调用函数再回归head
(2)流程图
2.实验代码
struct stud_node *createlist()
{
struct stud_node *head=NULL,*p=NULL,*q=NULL;
p=q=(struct stud_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
int num;
char name[20];
int score;
scanf("%d",&p->num);
while(p->num!=0)
{
scanf("%s %d",p->name,&p->score);
if(head==NULL)
{
head=p;
}
else
{
q->next=p;
}
q=p;
p=(struct stud_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct stud_node));
scanf("%d",&p->num);
}
q->next=NULL;
return (head);
}
struct stud_node *deletelist( struct stud_node *head, int min_score )
{
struct stud_node *p,*q,*w;
if(head!=NULL)
{
for(w=head;w!=NULL;w=w->next)
{
if(w->score<min_score)
{
for(p=head;min_score<=p->score&&p->next!=NULL;p=p->next)
{
q=p;
}
if(min_score>p->score)
{
if(p==head)
{
head=p->next;
}
else
{
q->next=p->next;
}
}
}
}
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
return (head);
}
3.调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
错误信息1:编译错误
错误原因:缺少正确的代码观念,经常少打代码,打错代码
改正方法:经常打代码
题目6-3 链表拼接
1.设计思路
(1)本次题目的算法
第一步:阅读题目 理解主函数与函数声明
第二步:使用调用函数,定义变量n,i,j,t,数组a,指针p,指针q,指针head,指针tail
第三步:使用for函数,与指针连用
第四步:回归head
(2)流程图
2.实验代码
struct ListNode *mergelists(struct ListNode *list1, struct ListNode *list2)
{
int n=0,a[99];
struct ListNode *p=list1;
for(n;p!=NULL;n++)
{
a[n]=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
p=list2;
for(n;p!=NULL;n++)
{
a[n]=p->data;
p=p->next;
}
int i,j,t;
for(j=0;j<n-1;j++)
{
for(i=0;i<n-1-j;i++)
{
if(a[i]>a[i+1])
{
t=a[i];
a[i]=a[i+1];
a[i+1]=t;
}
}
}
struct ListNode *q=NULL,*head=NULL,*tail=NULL;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
q=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
q->data=a[i];
q->next=NULL;
if(head==NULL)
{
head=q;
}else
{
tail->next=q;
}
tail=q;
}
return head;
}
3.调试过程碰到问题及解决办法
错误信息1:数组
错误原因:数组a不会定义
改正方法:根据提示改正
错误信息2:编译错误
错误原因:打代码时错误
改正方法:重新打印




学习总结和进度
数组可以是任何类型,如果数组的各个元素都是指针类型,用于存放内存地址,那么这个数组就是指针数组。
*数组名[数组长度]
二维数组是数组元素为一维数组的一维数组。
指针数组可以直接对数组元素进行引用操作,也可以间接访问操作数组元素所指向的单元内容。