Java基础——枚举
一、使用枚举类之前是如何实现枚举的
在JDK1.5之前,我们定义常量都是:public static fianl....;定义枚举也可以通过如下的方式:
package com.jiangbei.test.enumtest;
/**
* 颜色枚举类
* 作者: Administrator
* 日期: 2017/9/23
**/
public class Color {
// 1.私有的final属性
private final String name; // 颜色名称
private final String desc; // 颜色描述
// 2.构造器私有化,防止外部创建变量;并通过构造器初始化属性
private Color(String name, String desc){
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
}
// 3.公有方法获取属性(final不提供setter)
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
// 4.通过枚举类创建对象
public static final Color RED = new Color("red", "这是红色");
public static final Color GREEN = new Color("green", "这是绿色");
public static final Color BLUE = new Color("blue", "这是蓝色");
// 5.其他普通方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Color{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", desc='" + desc + '\'' +
'}';
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("给你点颜色看看:");
}
}
可以看到,主要是通过私有化构造器,然后在内部创建对象实现对象可以枚举的(这也是一个普通的类,本质和平时写的类没根本区别)
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Color red = Color.RED;
Color green = Color.GREEN;
red.show();
System.out.println(red);
System.out.println(red.getName());
System.out.println(green);
System.out.println(green.getDesc());
}

二、使用JDK5新增的enum定义枚举类
1.定义一个无属性的Enum
public enum ColorEnum {
RED,GREEN,BLUE;
}
// 相当于定义了三个Color的枚举类,它们是经过Enum构造函数来创建的:

3个属性,相当于调用了3次构造方法(也就是我们没有枚举类的时候进行的3次的new的操作)
之后通过API来了解它的使用:
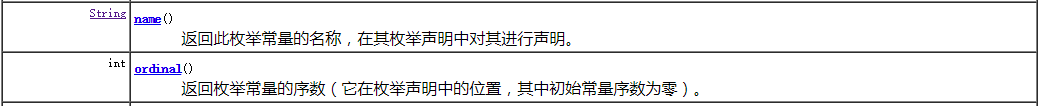
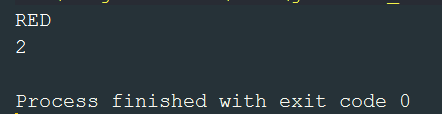
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorEnum red = ColorEnum.RED;
System.out.println(red.name());
ColorEnum blue = ColorEnum.BLUE;
System.out.println(blue.ordinal());
}
其他方法例如 valueOf(),以及可以用于switch等不再赘述
并且,枚举本质也是一个类,他也可以实现接口(但不能继承类,因为已经隐式继承了java.lang.Enum)
2.自定义属性的Enum
其实枚举类是不用给setter的,因为基本不会再去设置属性了

package com.jiangbei.test.enumtest; /** * 颜色枚举类 */ public enum ColorEnum { RED("red", "红色"),GREEN("green", "绿色"),BLUE("blue", "蓝色"); private String name; private String desc; ColorEnum(String name, String desc){ this.name = name; this.desc = desc; } public static String getDescByName(String name){ for (ColorEnum c : ColorEnum.values()) { if (c.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(name)) { return c.getDesc(); } } return null; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getDesc() { return desc; } public void setDesc(String desc) { this.desc = desc; } @Override public String toString() { return "ColorEnum{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", desc='" + desc + '\'' + '}'; } }
测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String red = ColorEnum.getDescByName("red");
System.out.println(red);
ColorEnum blue = ColorEnum.BLUE;
System.out.println(blue);
}

其他常见用法可以参见:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_27093465/article/details/52180865
http://www.cnblogs.com/linjiqin/archive/2011/02/11/1951632.html


