Tomcat源码分析——请求原理分析(中)
前言
在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中已经介绍了关于Tomcat7.0处理请求前作的初始化和准备工作,请读者在阅读本文前确保掌握《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中的相关知识以及HTTP协议和TCP协议的一些内容。本文重点讲解Tomcat7.0在准备好接受请求后,请求过程的原理分析。
请求处理架构
在正式开始之前,我们先来看看图1中的Tomcat请求处理架构。
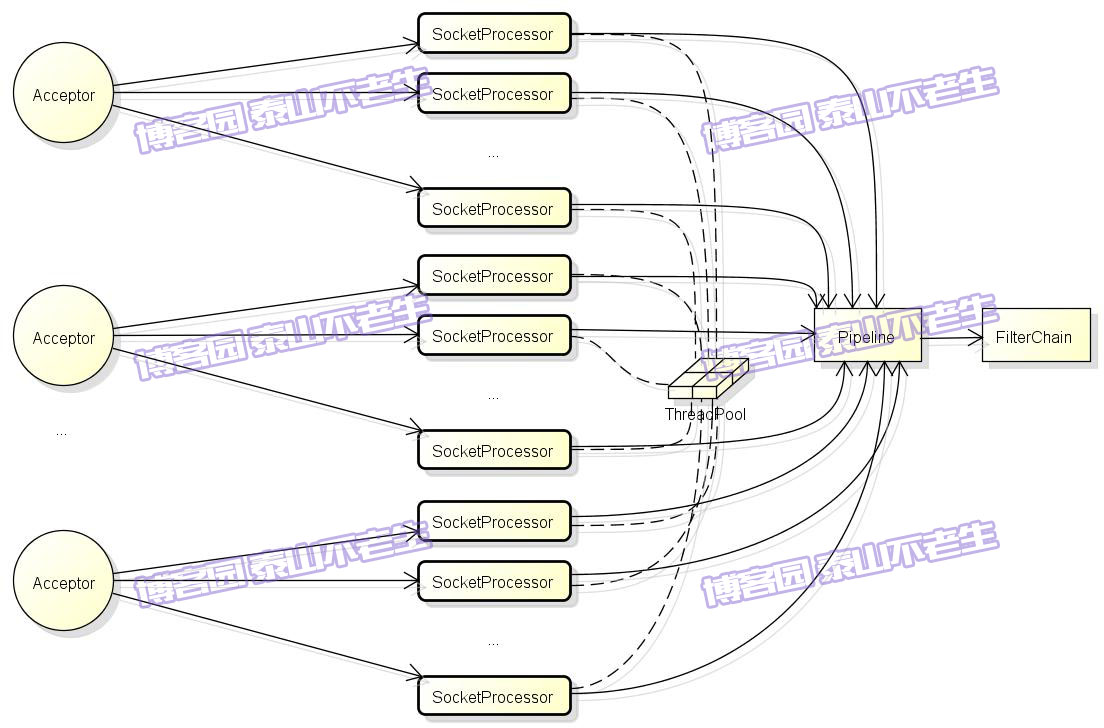
图1 Tomcat请求处理架构
图1列出了Tomcat请求处理架构中的主要组件,这里对它们做个简单介绍:
- Acceptor:负责从ServerSocket中接收新的连接,并将Socket转交给SocketProcessor处理。Acceptor是JIoEndpoint的内部类,其实现已在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中介绍。Acceptor线程的默认大小为1,我们可以在server.xml的Connector配置中增加acceptorThreadCount的大小。
- SocketProcessor:负责对Acceptor转交的Socket进行处理,包括给Socket设置属性、读取请求行和请求头等,最终将处理交给Engine的Pipeline处理。
- ThreadPool:执行SocketProcessor的线程来自《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中介绍的线程池,此线程池默认的最小线程数minSpareThreads等于10,最大线程数maxThreads等于200,我们可以在server.xml的Connector配置中调整它们的大小。
- Pipeline:SocketProcessor线程最后会将请求进一步交给Engine容器的Pipeline,管道Pipeline包括一系列的valve,如:StandardEngineValve、AccessLogValve、ErrorReportValve、StandardHostValve、 StandardContextValve、 StandardWrapperValve,它们就像地下水管中的一个个阀门,每一个都会对请求数据做不同的处理。
- FilterChain:管道Pipeline的最后一个valve是StandardWrapperValve,它会负责生成Servlet和Filter实例,并将它们组织成对请求处理的链条,这里正是Tomcat与J2EE规范相结合的部分。
默认情况下,Tomcat只有一个Acceptor线程,Acceptor不断循环从ServerSocket中获取Socket,当并发数大的情况下,这里会不会有性能问题?我想说的是,Acceptor的实现非常轻量级,它只负责两个动作:获取Socket和将Socket转交给SocketProcessor线程处理。另外,我们可以通过在server.xml的Connector配置中增加acceptorThreadCount的值,让我们同时可以拥有多个Acceptor线程。虽然我们可以修改maxThreads配置把SocketProcessor的线程数设置的很大,但是我们需要区别对待:
- 如果你部署在Tomcat上的Web服务主要用于计算,那么CPU的开销势必会很大,那么线程数不宜设置的过大,一般以CPU核数*2——CPU核数*3最佳。当然如果计算量非常大,就已经超出了Tomcat的使用范畴,我想此时,选择离线计算框架Hadoop或者实时计算框架Storm、Spark才是更好的选择。
- 如果部署在Tomcat上的Web服务主要是为了提供数据库访问,此时I/O的开销会很大,而CPU利用率反而低,此时应该将线程数设置的大一些,但是如果设置的过大,CPU为了给成百上千个线程分配时间片,造成CPU的精力都分散在线程切换上,反而造成性能下降。具体多大,需要对系统性能调优得出。
原理就讲这么多,下面具体分析下Tomcat处理请求的具体实现。
接收请求
在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中我们曾经介绍过JIoEndpoint的内部类Acceptor,Acceptor实现了Runnable接口。Acceptor作为后台线程不断循环,每次循环都会sleep大约1秒钟(由于是线程级别的,所以并不保证准确),然后接收来自浏览器的Socket连接(用户在浏览器输入HTTP请求地址后,浏览器底层实际使用Socket通信的),最后将Socket交给外部类JIoEndpoint的processSocket方法(见代码清单1)处理。
代码清单1
/** * Process given socket. */ protected boolean processSocket(Socket socket) { try { SocketWrapper<Socket> wrapper = new SocketWrapper<Socket>(socket); wrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); getExecutor().execute(new SocketProcessor(wrapper)); } catch (RejectedExecutionException x) { log.warn("Socket processing request was rejected for:"+socket,x); return false; } catch (Throwable t) { // This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that // the pool and its queue are full log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t); return false; } return true; }
根据代码清单1,JIoEndpoint的processSocket方法的处理步骤如下:
- 将Socket封装为SocketWrapper;
- 给SocketWrapper设置连接保持时间keepAliveLeft。这个值是通过调用父类AbstractEndpoint的getMaxKeepAliveRequests方法(见代码清单2)获得的;
- 创建SocketProcessor(此类也是JIoEndpoint的内部类,而且也实现了Runnable接口,见代码清单3),并使用线程池(此线程池已在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中启动PROTOCOLHANDLER一节介绍)执行。
代码清单2
/** * Max keep alive requests */ private int maxKeepAliveRequests=100; // as in Apache HTTPD server public int getMaxKeepAliveRequests() { return maxKeepAliveRequests; }
代码清单3
/** * This class is the equivalent of the Worker, but will simply use in an * external Executor thread pool. */ protected class SocketProcessor implements Runnable { protected SocketWrapper<Socket> socket = null; protected SocketStatus status = null; public SocketProcessor(SocketWrapper<Socket> socket) { if (socket==null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.socket = socket; } public SocketProcessor(SocketWrapper<Socket> socket, SocketStatus status) { this(socket); this.status = status; } public void run() { boolean launch = false; try { if (!socket.processing.compareAndSet(false, true)) { log.error("Unable to process socket. Invalid state."); return; } SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN; // Process the request from this socket if ( (!socket.isInitialized()) && (!setSocketOptions(socket.getSocket())) ) { state = SocketState.CLOSED; } socket.setInitialized(true); if ( (state != SocketState.CLOSED) ) { state = (status==null)?handler.process(socket):handler.process(socket,status); } if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) { // Close socket if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { log.trace("Closing socket:"+socket); } try { socket.getSocket().close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore } } else if (state == SocketState.OPEN){ socket.setKeptAlive(true); socket.access(); //keepalive connection //TODO - servlet3 check async status, we may just be in a hold pattern launch = true; } else if (state == SocketState.LONG) { socket.access(); waitingRequests.add(socket); } } finally { socket.processing.set(false); if (launch) getExecutor().execute(new SocketProcessor(socket)); socket = null; } // Finish up this request } }
SocketProcessor线程专门用于处理Acceptor转交的Socket,其执行步骤如下:
- 调用setSocketOptions方法(见代码清单4)给Socket设置属性,从中可以看到设置属性用到了SocketProperties的setProperties方法(见代码清单5),状态更改为初始化完毕;
- 调用handler的process方法处理请求。在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中我们讲过当处理Http11Protocol协议时,handler默认为Http11Protocol的内部类Http11ConnectionHandler;
- 请求处理完毕后,如果state等于SocketState.CLOSED,则关闭Socket;如果state等于SocketState.OPEN,则保持连接;如果state等于SocketState.LONG,则会作为长连接对待。
代码清单4
/** * Set the options for the current socket. */ protected boolean setSocketOptions(Socket socket) { // Process the connection try { // 1: Set socket options: timeout, linger, etc socketProperties.setProperties(socket); } catch (SocketException s) { //error here is common if the client has reset the connection if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.unexpected"), s); } // Close the socket return false; } catch (Throwable t) { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.err.unexpected"), t); // Close the socket return false; } try { // 2: SSL handshake serverSocketFactory.handshake(socket); } catch (Throwable t) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.handshake"), t); } // Tell to close the socket return false; } return true; }
代码清单5
public void setProperties(Socket socket) throws SocketException{ if (rxBufSize != null) socket.setReceiveBufferSize(rxBufSize.intValue()); if (txBufSize != null) socket.setSendBufferSize(txBufSize.intValue()); if (ooBInline !=null) socket.setOOBInline(ooBInline.booleanValue()); if (soKeepAlive != null) socket.setKeepAlive(soKeepAlive.booleanValue()); if (performanceConnectionTime != null && performanceLatency != null && performanceBandwidth != null) socket.setPerformancePreferences( performanceConnectionTime.intValue(), performanceLatency.intValue(), performanceBandwidth.intValue()); if (soReuseAddress != null) socket.setReuseAddress(soReuseAddress.booleanValue()); if (soLingerOn != null && soLingerTime != null) socket.setSoLinger(soLingerOn.booleanValue(), soLingerTime.intValue()); if (soTimeout != null && soTimeout.intValue() >= 0) socket.setSoTimeout(soTimeout.intValue()); if (tcpNoDelay != null) socket.setTcpNoDelay(tcpNoDelay.booleanValue()); if (soTrafficClass != null) socket.setTrafficClass(soTrafficClass.intValue()); }
以Http11ConnectionHandler为例,我们重点分析它是如何进一步处理Socket的。Http11ConnectionHandler的process方法,见代码清单6。
代码清单6
public SocketState process(SocketWrapper<Socket> socket) { return process(socket,SocketStatus.OPEN); } public SocketState process(SocketWrapper<Socket> socket, SocketStatus status) { Http11Processor processor = connections.remove(socket); boolean recycle = true; try { if (processor == null) { processor = recycledProcessors.poll(); } if (processor == null) { processor = createProcessor(); } processor.action(ActionCode.ACTION_START, null); if (proto.isSSLEnabled() && (proto.sslImplementation != null)) { processor.setSSLSupport (proto.sslImplementation.getSSLSupport(socket.getSocket())); } else { processor.setSSLSupport(null); } SocketState state = socket.isAsync()?processor.asyncDispatch(status):processor.process(socket); if (state == SocketState.LONG) { connections.put(socket, processor); socket.setAsync(true); recycle = false; } else { connections.remove(socket); socket.setAsync(false); } return state; } catch(java.net.SocketException e) { // SocketExceptions are normal Http11Protocol.log.debug (sm.getString ("http11protocol.proto.socketexception.debug"), e); } catch (java.io.IOException e) { // IOExceptions are normal Http11Protocol.log.debug (sm.getString ("http11protocol.proto.ioexception.debug"), e); } // Future developers: if you discover any other // rare-but-nonfatal exceptions, catch them here, and log as // above. catch (Throwable e) { // any other exception or error is odd. Here we log it // with "ERROR" level, so it will show up even on // less-than-verbose logs. Http11Protocol.log.error (sm.getString("http11protocol.proto.error"), e); } finally { // if(proto.adapter != null) proto.adapter.recycle(); // processor.recycle(); if (recycle) { processor.action(ActionCode.ACTION_STOP, null); recycledProcessors.offer(processor); } } return SocketState.CLOSED; }
根据代码清单6,可见Http11ConnectionHandler的process方法的处理步骤如下:
- 从Socket的连接缓存connections中获取依然Socket对应的Http11Processor;如果连接缓存connections中不存在Socket对应的Http11Processor,则从可以循环使用的recycledProcessors(类型为ConcurrentLinkedQueue)中获取;如果recycledProcessors中也没有可以使用的Http11Processor,则调用createProcessor方法(见代码清单7)创建Http11Processor;
- 如果当前Connector配置了指定了SSLEnabled="true",那么还需要给Http11Processor设置SSL相关的属性;
- 如果Socket是异步的,则调用Http11Processor的asyncDispatch方法,否则调用Http11Processor的process方法;
- 请求处理完毕,如果Socket是长连接的,则将Socket和Http11Processor一起放入connections缓存,否则从connections缓存中移除Socket和Http11Processor。
代码清单7
protected Http11Processor createProcessor() { Http11Processor processor = new Http11Processor(proto.getMaxHttpHeaderSize(), (JIoEndpoint)proto.endpoint); processor.setAdapter(proto.adapter); processor.setMaxKeepAliveRequests(proto.getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); processor.setKeepAliveTimeout(proto.getKeepAliveTimeout()); processor.setTimeout(proto.getTimeout()); processor.setDisableUploadTimeout(proto.getDisableUploadTimeout()); processor.setCompressionMinSize(proto.getCompressionMinSize()); processor.setCompression(proto.getCompression()); processor.setNoCompressionUserAgents(proto.getNoCompressionUserAgents()); processor.setCompressableMimeTypes(proto.getCompressableMimeTypes()); processor.setRestrictedUserAgents(proto.getRestrictedUserAgents()); processor.setSocketBuffer(proto.getSocketBuffer()); processor.setMaxSavePostSize(proto.getMaxSavePostSize()); processor.setServer(proto.getServer()); register(processor); return processor; }
根据之前的分析,我们知道Socket的处理方式有异步和同步两种,分别调用Http11Processor的asyncDispatch方法或process方法,我们以同步处理为例,来看看接下来的处理逻辑。
同步处理
Http11Processor的process方法(见代码清单8)用于同步处理,由于其代码很多,所以此处在代码后面追加一些注释,便于读者理解。这里面有一些关键方法重点拿出来解释下:
- InternalInputBuffer的parseRequestLine方法用于读取请求行;
- InternalInputBuffer的parseHeaders方法用于读取请求头;
- prepareRequest用于在正式处理请求之前,做一些准备工作,如根据请求头获取请求的版本号是HTTP/1.1还是HTTP/0.9、keepAlive是否为true等,还会设置一些输入过滤器用于标记请求、压缩等;
- 调用CoyoteAdapter的service方法处理请求。
代码清单8
RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor(); rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE); this.socket = socketWrapper; inputBuffer.setInputStream(socket.getSocket().getInputStream());//设置输入流 outputBuffer.setOutputStream(socket.getSocket().getOutputStream());//设置输出流 int keepAliveLeft = maxKeepAliveRequests>0?socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive():-1;//保持连接递减 int soTimeout = endpoint.getSoTimeout();//socket超时时间 socket.getSocket().setSoTimeout(soTimeout);//设置超时时间 boolean keptAlive = socketWrapper.isKeptAlive();//是否保持连接 while (started && !error && keepAlive) { // Parsing the request header try { //TODO - calculate timeout based on length in queue (System.currentTimeMills() - wrapper.getLastAccess() is the time in queue) if (keptAlive) {//是否保持连接 if (keepAliveTimeout > 0) { socket.getSocket().setSoTimeout(keepAliveTimeout); } else if (soTimeout > 0) { socket.getSocket().setSoTimeout(soTimeout); } } inputBuffer.parseRequestLine(false);//读取请求行 request.setStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); keptAlive = true; if (disableUploadTimeout) { socket.getSocket().setSoTimeout(soTimeout); } else { socket.getSocket().setSoTimeout(timeout); } inputBuffer.parseHeaders();//解析请求头 } catch (IOException e) { error = true; break; } catch (Throwable t) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), t); } // 400 - Bad Request response.setStatus(400); adapter.log(request, response, 0); error = true; } if (!error) { // Setting up filters, and parse some request headers rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED); try { prepareRequest();//对请求内容增加过滤器——协议、方法、请求头、host等 } catch (Throwable t) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.request.prepare"), t); } // 400 - Internal Server Error response.setStatus(400); adapter.log(request, response, 0); error = true; } } if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 && keepAliveLeft == 0) keepAlive = false; // Process the request in the adapter if (!error) { try { rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE); adapter.service(request, response); //将进一步处理交给CoyoteAdapter // Handle when the response was committed before a serious // error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both // set the status to 500 and set the errorException. // If we fail here, then the response is likely already // committed, so we can't try and set headers. if(keepAlive && !error) { // Avoid checking twice. error = response.getErrorException() != null || statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus()); } } catch (InterruptedIOException e) { error = true; } catch (Throwable t) { log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t); // 500 - Internal Server Error response.setStatus(500); adapter.log(request, response, 0); error = true; } } // Finish the handling of the request try { rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT); // If we know we are closing the connection, don't drain input. // This way uploading a 100GB file doesn't tie up the thread // if the servlet has rejected it. if(error && !async) inputBuffer.setSwallowInput(false); if (!async) endRequest(); } catch (Throwable t) { log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.finish"), t); // 500 - Internal Server Error response.setStatus(500); adapter.log(request, response, 0); error = true; } try { rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT); } catch (Throwable t) { log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.response.finish"), t); error = true; } // If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as // and error, and update the statistics counter if (error) { response.setStatus(500); } request.updateCounters(); rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE); // Don't reset the param - we'll see it as ended. Next request // will reset it // thrA.setParam(null); // Next request if (!async || error) { inputBuffer.nextRequest(); outputBuffer.nextRequest(); } //hack keep alive behavior break; } rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED); if (error) { recycle(); return SocketState.CLOSED; } else if (async) { return SocketState.LONG; } else { if (!keepAlive) { recycle(); return SocketState.CLOSED; } else { return SocketState.OPEN; } }
从代码清单8可以看出,最后的请求处理交给了CoyoteAdapter,CoyoteAdapter的service方法(见代码清单9)用于真正处理请求。
代码清单9
/** * Service method. */ public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res) throws Exception { Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES); if (request == null) { // Create objects request = connector.createRequest(); request.setCoyoteRequest(req); response = connector.createResponse(); response.setCoyoteResponse(res); // Link objects request.setResponse(response); response.setRequest(request); // Set as notes req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request); res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response); // Set query string encoding req.getParameters().setQueryStringEncoding (connector.getURIEncoding()); } if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) { response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY); } boolean comet = false; boolean async = false; try { // Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific // request parameters req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(Thread.currentThread().getName()); if (postParseRequest(req, request, res, response)) { //check valves if we support async request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); // Calling the container connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response); if (request.isComet()) { if (!response.isClosed() && !response.isError()) { if (request.getAvailable() || (request.getContentLength() > 0 && (!request.isParametersParsed()))) { // Invoke a read event right away if there are available bytes if (event(req, res, SocketStatus.OPEN)) { comet = true; res.action(ActionCode.ACTION_COMET_BEGIN, null); } } else { comet = true; res.action(ActionCode.ACTION_COMET_BEGIN, null); } } else { // Clear the filter chain, as otherwise it will not be reset elsewhere // since this is a Comet request request.setFilterChain(null); } } } AsyncContextImpl asyncConImpl = (AsyncContextImpl)request.getAsyncContext(); if (asyncConImpl!=null && asyncConImpl.getState()==AsyncContextImpl.AsyncState.STARTED) { res.action(ActionCode.ACTION_ASYNC_START, request.getAsyncContext()); async = true; } else if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) { asyncDispatch(req, res, SocketStatus.OPEN); if (request.isAsyncStarted()) { async = true; res.action(ActionCode.ACTION_ASYNC_START, request.getAsyncContext()); } } else if (!comet) { response.finishResponse(); req.action(ActionCode.ACTION_POST_REQUEST , null); } } catch (IOException e) { // Ignore } catch (Throwable t) { log.error(sm.getString("coyoteAdapter.service"), t); } finally { req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null); // Recycle the wrapper request and response if (!comet && !async) { request.recycle(); response.recycle(); } else { // Clear converters so that the minimum amount of memory // is used by this processor request.clearEncoders(); response.clearEncoders(); } } }
从代码清单9可以看出,CoyoteAdapter的service方法的执行步骤如下:
- 创建Request与Response对象并且关联起来;
- 调用postParseRequest方法(见代码清单10)对请求进行解析;
-
将真正的请求处理交给Engine的Pipeline去处理,代码:connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
代码清单10
/** * Parse additional request parameters. */ protected boolean postParseRequest(org.apache.coyote.Request req, Request request, org.apache.coyote.Response res, Response response) throws Exception { // 省略前边的次要代码 parsePathParameters(req, request); // URI decoding // %xx decoding of the URL try { req.getURLDecoder().convert(decodedURI, false); } catch (IOException ioe) { res.setStatus(400); res.setMessage("Invalid URI: " + ioe.getMessage()); connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess( request, response, 0, true); return false; } // Normalization if (!normalize(req.decodedURI())) { res.setStatus(400); res.setMessage("Invalid URI"); connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess( request, response, 0, true); return false; } // Character decoding convertURI(decodedURI, request); // Check that the URI is still normalized if (!checkNormalize(req.decodedURI())) { res.setStatus(400); res.setMessage("Invalid URI character encoding"); connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess( request, response, 0, true); return false; } // Set the remote principal String principal = req.getRemoteUser().toString(); if (principal != null) { request.setUserPrincipal(new CoyotePrincipal(principal)); } // Set the authorization type String authtype = req.getAuthType().toString(); if (authtype != null) { request.setAuthType(authtype); } // Request mapping. MessageBytes serverName; if (connector.getUseIPVHosts()) { serverName = req.localName(); if (serverName.isNull()) { // well, they did ask for it res.action(ActionCode.ACTION_REQ_LOCAL_NAME_ATTRIBUTE, null); } } else { serverName = req.serverName(); } if (request.isAsyncStarted()) { //TODO SERVLET3 - async //reset mapping data, should prolly be done elsewhere request.getMappingData().recycle(); } connector.getMapper().map(serverName, decodedURI, request.getMappingData()); request.setContext((Context) request.getMappingData().context); request.setWrapper((Wrapper) request.getMappingData().wrapper); // Filter trace method if (!connector.getAllowTrace() && req.method().equalsIgnoreCase("TRACE")) { Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper(); String header = null; if (wrapper != null) { String[] methods = wrapper.getServletMethods(); if (methods != null) { for (int i=0; i<methods.length; i++) { if ("TRACE".equals(methods[i])) { continue; } if (header == null) { header = methods[i]; } else { header += ", " + methods[i]; } } } } res.setStatus(405); res.addHeader("Allow", header); res.setMessage("TRACE method is not allowed"); request.getContext().logAccess(request, response, 0, true); return false; } // Now we have the context, we can parse the session ID from the URL // (if any). Need to do this before we redirect in case we need to // include the session id in the redirect if (request.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes() .contains(SessionTrackingMode.URL)) { // Get the session ID if there was one String sessionID = request.getPathParameter( ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.getSessionUriParamName( request.getContext())); if (sessionID != null) { request.setRequestedSessionId(sessionID); request.setRequestedSessionURL(true); } } // Possible redirect MessageBytes redirectPathMB = request.getMappingData().redirectPath; if (!redirectPathMB.isNull()) { String redirectPath = urlEncoder.encode(redirectPathMB.toString()); String query = request.getQueryString(); if (request.isRequestedSessionIdFromURL()) { // This is not optimal, but as this is not very common, it // shouldn't matter redirectPath = redirectPath + ";" + ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.getSessionUriParamName( request.getContext()) + "=" + request.getRequestedSessionId(); } if (query != null) { // This is not optimal, but as this is not very common, it // shouldn't matter redirectPath = redirectPath + "?" + query; } response.sendRedirect(redirectPath); request.getContext().logAccess(request, response, 0, true); return false; } // Finally look for session ID in cookies and SSL session parseSessionCookiesId(req, request); parseSessionSslId(request); return true; }
从代码清单10可以看出,postParseRequest方法的执行步骤如下:
- 解析请求url中的参数;
- URI decoding的转换;
- 调用normalize方法判断请求路径中是否存在"\", "//", "/./"和"/../",如果存在则处理结束;
- 调用convertURI方法将字节转换为字符;
- 调用checkNormalize方法判断uri是否存在"\", "//", "/./"和"/../",如果存在则处理结束;
- 调用Connector的getMapper方法获取Mapper(已在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中介绍),然后调用Mapper的map方法(见代码清单11)对host和context进行匹配(比如http://localhost:8080/manager/status会匹配host:localhost,context:/manager),其实质是调用internalMap方法;
- 使用ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.getSessionUriParamName获取sessionid的key,然后获取sessionid;
- 调用parseSessionCookiesId和parseSessionSslId方法查找cookie或者SSL中的sessionid。
代码清单11
public void map(MessageBytes host, MessageBytes uri, MappingData mappingData) throws Exception { if (host.isNull()) { host.getCharChunk().append(defaultHostName); } host.toChars(); uri.toChars(); internalMap(host.getCharChunk(), uri.getCharChunk(), mappingData); }
CoyoteAdapter的service方法最后会将请求交给Engine的Pipeline去处理,我将在《Tomcat源码分析——请求原理分析(下)》一文中具体讲解。
如需转载,请标明本文作者及出处——作者:jiaan.gja,本文原创首发:博客园,原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/jiaan-geng/p/4894832.html



