[Stats385] Lecture 04: Convnets from Probabilistic Perspective
本篇围绕“深度渲染混合模型”展开。
- A Probabilistic Framework for Deep Learning
- Semi-Supervised Learning with the Deep Rendering Mixture Model
- A Probabilistic Theory of Deep Learning
13:49 / 1:30:37
GAN的统计意义:统计假设检验
GAN 一定意义上成为了classical statistical hypothesis testing,判断新产生的数据到底属于哪一个model。
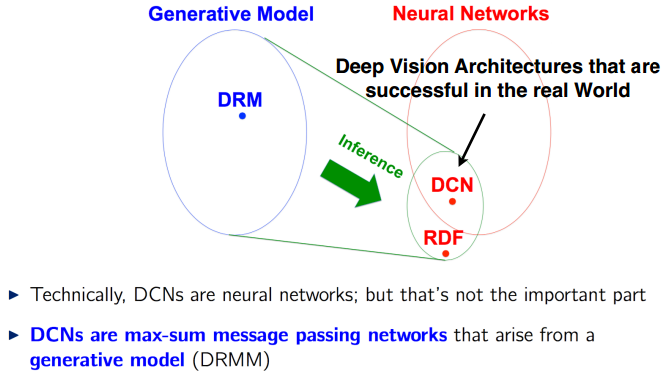
CNN vs DRM Model
Weight: dictionaries
Value: sparse coding
Dropout: missing at randam data em algorithm
Back-propagation: m step of generalized em algorithm
Batch normalization: curvature normalization
AutoEncoder: em algorithm with reconstruction
Skip connection: preconditioning
19:30 / 1:30:37
Lecture starts.
先从视觉神经系统找到深度学习的依据;
然后开始提及常见的卷积网络,以及一些缺陷,例如暴雨天识别效果差。
- 从概率生成式模型 Generative Model入手
提到了Deep Rendering Mixture Model,深度渲染混合模型;可通过该链接初步了解:http://www.sohu.com/a/121834092_465975
Each Layer of the DRMM is a Sparse Coding Model.
Inference in the DRMM yields Deep Convnets
作为一种Probabilistic Framework for Deep Learning,更一般化,貌似convNet成了它的特例?
如此,DRM的角色是为人们设计新的神经网络结构作为指导。
- 从动态规划的角度去认识
The Dynamic Programming Algorithm Interpretation of Convnets
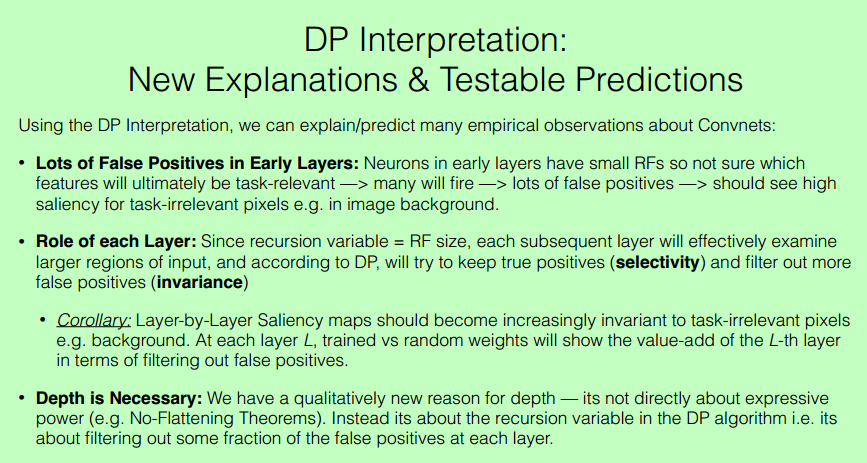
Saliency Maps show Selectivity and Invariance are Built up over Layers
Question: How do Convnets build up invariance to background?
Experiment: Visualize saliency maps for active neurons at each layer.
Observations:
• Neurons in early layers are selective for all detectable features in input, including background.
• Neurons in deeper layers are selective only for small subset of input pixels (those useful for discriminating class)
• Neurons in deep layers are invariant to (almost all) irrelevant pixels e.g. background and below the neck.
次要的特征逐渐被筛掉,相当于逐渐找到了更优路径。
说明关系的一张图,不错。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号