[Model] AlexNet
CaffeNet - a variant of AlexNet
Ref: Classification: Instant Recognition with Caffe
This is caffeNet
区别:https://github.com/BVLC/caffe/issues/4202
This is AlexNet.
单机版:http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~guerzhoy/tf_alexnet/myalexnet_forward_newtf.py

################################################################################ #Michael Guerzhoy and Davi Frossard, 2016 #AlexNet implementation in TensorFlow, with weights #Details: #http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~guerzhoy/tf_alexnet/ # #With code from https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow #Model from https://github.com/BVLC/caffe/tree/master/models/bvlc_alexnet #Weights from Caffe converted using https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow # # ################################################################################ from numpy import * import os #from pylab import * import numpy as np #import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #import matplotlib.cbook as cbook import time from scipy.misc import imread from scipy.misc import imresize import matplotlib.image as mpimg from scipy.ndimage import filters import urllib from numpy import random import tensorflow as tf from caffe_classes import class_names train_x = zeros((1, 227,227,3)).astype(float32) train_y = zeros((1, 1000)) xdim = train_x.shape[1:] ydim = train_y.shape[1] ################################################################################ #Read Image, and change to BGR im1 = (imread("laska.png")[:,:,:3]).astype(float32) im1 = im1 - mean(im1) im1[:, :, 0], im1[:, :, 2] = im1[:, :, 2], im1[:, :, 0] im2 = (imread("poodle.png")[:,:,:3]).astype(float32) im2[:, :, 0], im2[:, :, 2] = im2[:, :, 2], im2[:, :, 0] ################################################################################ # (self.feed('data') # .conv(11, 11, 96, 4, 4, padding='VALID', name='conv1') # .lrn(2, 2e-05, 0.75, name='norm1') # .max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool1') # .conv(5, 5, 256, 1, 1, group=2, name='conv2') # .lrn(2, 2e-05, 0.75, name='norm2') # .max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool2') # .conv(3, 3, 384, 1, 1, name='conv3') # .conv(3, 3, 384, 1, 1, group=2, name='conv4') # .conv(3, 3, 256, 1, 1, group=2, name='conv5') # .fc(4096, name='fc6') # .fc(4096, name='fc7') # .fc(1000, relu=False, name='fc8') # .softmax(name='prob')) #In Python 3.5, change this to: net_data = load(open("bvlc_alexnet.npy", "rb"), encoding="latin1").item() #net_data = load("bvlc_alexnet.npy").item() def conv(input, kernel, biases, k_h, k_w, c_o, s_h, s_w, padding="VALID", group=1): '''From https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow ''' c_i = input.get_shape()[-1] assert c_i%group==0 assert c_o%group==0 convolve = lambda i, k: tf.nn.conv2d(i, k, [1, s_h, s_w, 1], padding=padding) if group==1: conv = convolve(input, kernel) else: input_groups = tf.split(input, group, 3) #tf.split(3, group, input) kernel_groups = tf.split(kernel, group, 3) #tf.split(3, group, kernel) output_groups = [convolve(i, k) for i,k in zip(input_groups, kernel_groups)] conv = tf.concat(output_groups, 3) #tf.concat(3, output_groups) return tf.reshape(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases), [-1]+conv.get_shape().as_list()[1:]) x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None,) + xdim) #conv1 #conv(11, 11, 96, 4, 4, padding='VALID', name='conv1') k_h = 11; k_w = 11; c_o = 96; s_h = 4; s_w = 4 conv1W = tf.Variable(net_data["conv1"][0]) conv1b = tf.Variable(net_data["conv1"][1]) conv1_in = conv(x, conv1W, conv1b, k_h, k_w, c_o, s_h, s_w, padding="SAME", group=1) conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv1_in) #lrn1 #lrn(2, 2e-05, 0.75, name='norm1') radius = 2; alpha = 2e-05; beta = 0.75; bias = 1.0 lrn1 = tf.nn.local_response_normalization(conv1, depth_radius=radius, alpha=alpha, beta=beta, bias=bias) #maxpool1 #max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool1') k_h = 3; k_w = 3; s_h = 2; s_w = 2; padding = 'VALID' maxpool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1, ksize=[1, k_h, k_w, 1], strides=[1, s_h, s_w, 1], padding=padding) #conv2 #conv(5, 5, 256, 1, 1, group=2, name='conv2') k_h = 5; k_w = 5; c_o = 256; s_h = 1; s_w = 1; group = 2 conv2W = tf.Variable(net_data["conv2"][0]) conv2b = tf.Variable(net_data["conv2"][1]) conv2_in = conv(maxpool1, conv2W, conv2b, k_h, k_w, c_o, s_h, s_w, padding="SAME", group=group) conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2_in) #lrn2 #lrn(2, 2e-05, 0.75, name='norm2') radius = 2; alpha = 2e-05; beta = 0.75; bias = 1.0 lrn2 = tf.nn.local_response_normalization(conv2, depth_radius=radius, alpha=alpha, beta=beta, bias=bias) #maxpool2 #max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool2') k_h = 3; k_w = 3; s_h = 2; s_w = 2; padding = 'VALID' maxpool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn2, ksize=[1, k_h, k_w, 1], strides=[1, s_h, s_w, 1], padding=padding) #conv3 #conv(3, 3, 384, 1, 1, name='conv3') k_h = 3; k_w = 3; c_o = 384; s_h = 1; s_w = 1; group = 1 conv3W = tf.Variable(net_data["conv3"][0]) conv3b = tf.Variable(net_data["conv3"][1]) conv3_in = conv(maxpool2, conv3W, conv3b, k_h, k_w, c_o, s_h, s_w, padding="SAME", group=group) conv3 = tf.nn.relu(conv3_in) #conv4 #conv(3, 3, 384, 1, 1, group=2, name='conv4') k_h = 3; k_w = 3; c_o = 384; s_h = 1; s_w = 1; group = 2 conv4W = tf.Variable(net_data["conv4"][0]) conv4b = tf.Variable(net_data["conv4"][1]) conv4_in = conv(conv3, conv4W, conv4b, k_h, k_w, c_o, s_h, s_w, padding="SAME", group=group) conv4 = tf.nn.relu(conv4_in) #conv5 #conv(3, 3, 256, 1, 1, group=2, name='conv5') k_h = 3; k_w = 3; c_o = 256; s_h = 1; s_w = 1; group = 2 conv5W = tf.Variable(net_data["conv5"][0]) conv5b = tf.Variable(net_data["conv5"][1]) conv5_in = conv(conv4, conv5W, conv5b, k_h, k_w, c_o, s_h, s_w, padding="SAME", group=group) conv5 = tf.nn.relu(conv5_in) #maxpool5 #max_pool(3, 3, 2, 2, padding='VALID', name='pool5') k_h = 3; k_w = 3; s_h = 2; s_w = 2; padding = 'VALID' maxpool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1, k_h, k_w, 1], strides=[1, s_h, s_w, 1], padding=padding) #fc6 #fc(4096, name='fc6') fc6W = tf.Variable(net_data["fc6"][0]) fc6b = tf.Variable(net_data["fc6"][1]) fc6 = tf.nn.relu_layer(tf.reshape(maxpool5, [-1, int(prod(maxpool5.get_shape()[1:]))]), fc6W, fc6b) #fc7 #fc(4096, name='fc7') fc7W = tf.Variable(net_data["fc7"][0]) fc7b = tf.Variable(net_data["fc7"][1]) fc7 = tf.nn.relu_layer(fc6, fc7W, fc7b) #fc8 #fc(1000, relu=False, name='fc8') fc8W = tf.Variable(net_data["fc8"][0]) fc8b = tf.Variable(net_data["fc8"][1]) fc8 = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(fc7, fc8W, fc8b) #prob #softmax(name='prob')) prob = tf.nn.softmax(fc8) init = tf.initialize_all_variables() sess = tf.Session() sess.run(init) t = time.time() output = sess.run(prob, feed_dict = {x:[im1,im2]}) ################################################################################ #Output: for input_im_ind in range(output.shape[0]): inds = argsort(output)[input_im_ind,:] print("Image", input_im_ind) for i in range(5): print(class_names[inds[-1-i]], output[input_im_ind, inds[-1-i]]) print(time.time()-t)
################################################################################ #Michael Guerzhoy and Davi Frossard, 2016 #AlexNet implementation in TensorFlow, with weights #Details: #http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~guerzhoy/tf_alexnet/ # #With code from https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow #Model from https://github.com/BVLC/caffe/tree/master/models/bvlc_alexnet #Weights from Caffe converted using https://github.com/ethereon/caffe-tensorflow # # ################################################################################
此处推荐了将caffe model自动转为tensorflow的。
模型:
From: https://github.com/BVLC/caffe/tree/master/models/bvlc_alexnet

1. train_val.prototxt首先,train_val.prototxt文件是network配置文件。该文件是在训练的时候用的。2.deploy.prototxt该文件是在测试时使用的文件。
区别:首先deploy.prototxt文件都是在train_val.prototxt文件的基础上删除了一些东西,所形成的。由于两个文件的性质,train_val.prototxt文件里面训练的部分都会在deploy.prototxt文件中删除。
参数
- bvlc_alexnet.npy -- the weights; they need to be in the working directory [link]
Train: https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/alexnet.py
Test : https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/alexnet_test.py
# Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved. # # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. # You may obtain a copy of the License at # # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 # # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and # limitations under the License. # ============================================================================== """Contains a model definition for AlexNet. This work was first described in: ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever and Geoffrey E. Hinton and later refined in: One weird trick for parallelizing convolutional neural networks Alex Krizhevsky, 2014 Here we provide the implementation proposed in "One weird trick" and not "ImageNet Classification", as per the paper, the LRN layers have been removed. Usage: with slim.arg_scope(alexnet.alexnet_v2_arg_scope()): outputs, end_points = alexnet.alexnet_v2(inputs) @@alexnet_v2 """ from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import division from __future__ import print_function import tensorflow as tf slim = tf.contrib.slim trunc_normal = lambda stddev: tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.0, stddev) def alexnet_v2_arg_scope(weight_decay=0.0005): with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected], activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, biases_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1), weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay)): with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], padding='SAME'): with slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d], padding='VALID') as arg_sc: return arg_sc def alexnet_v2(inputs, num_classes=1000, is_training=True, dropout_keep_prob=0.5, spatial_squeeze=True, scope='alexnet_v2'): """AlexNet version 2. Described in: http://arxiv.org/pdf/1404.5997v2.pdf Parameters from: github.com/akrizhevsky/cuda-convnet2/blob/master/layers/ layers-imagenet-1gpu.cfg Note: All the fully_connected layers have been transformed to conv2d layers. To use in classification mode, resize input to 224x224. To use in fully convolutional mode, set spatial_squeeze to false. The LRN layers have been removed and change the initializers from random_normal_initializer to xavier_initializer. Args: inputs: a tensor of size [batch_size, height, width, channels]. num_classes: number of predicted classes. is_training: whether or not the model is being trained. dropout_keep_prob: the probability that activations are kept in the dropout layers during training. spatial_squeeze: whether or not should squeeze the spatial dimensions of the outputs. Useful to remove unnecessary dimensions for classification. scope: Optional scope for the variables. Returns: the last op containing the log predictions and end_points dict. """ with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'alexnet_v2', [inputs]) as sc: end_points_collection = sc.name + '_end_points' # Collect outputs for conv2d, fully_connected and max_pool2d. with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected, slim.max_pool2d], outputs_collections=[end_points_collection]):
net = slim.conv2d(inputs, 64, [11, 11], 4, padding='VALID', scope='conv1') net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], 2, scope='pool1') net = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [5, 5], scope='conv2') net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], 2, scope='pool2') net = slim.conv2d(net, 384, [3, 3], scope='conv3') net = slim.conv2d(net, 384, [3, 3], scope='conv4') net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv5') net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], 2, scope='pool5') # Use conv2d instead of fully_connected layers. with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d], weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.005), biases_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1)): net = slim.conv2d(net, 4096, [5, 5], padding='VALID', scope='fc6') net = slim.dropout(net, dropout_keep_prob, is_training=is_training, scope='dropout6') net = slim.conv2d(net, 4096, [1, 1], scope='fc7') net = slim.dropout(net, dropout_keep_prob, is_training=is_training, scope='dropout7') net = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, normalizer_fn=None, biases_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), scope='fc8') # Convert end_points_collection into a end_point dict. end_points = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(end_points_collection) if spatial_squeeze: net = tf.squeeze(net, [1, 2], name='fc8/squeezed') end_points[sc.name + '/fc8'] = net return net, end_points alexnet_v2.default_image_size = 224
From: http://vision.stanford.edu/teaching/cs231b_spring1415/slides/alexnet_tugce_kyunghee.pdf

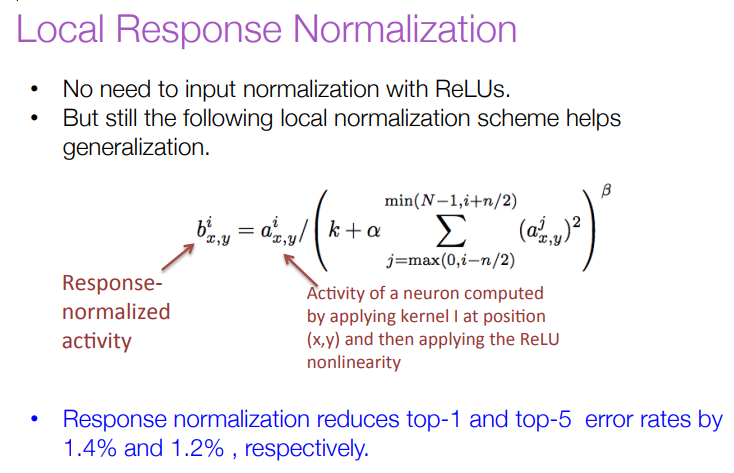
LCN: 使用价值不大的结构
其中这个LRN层真是让人百思不得其解,搜索了下,给出的介绍比较少。为什么会比较少呢,搜索到最后我得出的结论是,这货似乎没什么多少卵用。
但似乎,在后来的设计中,这一层已经被其它种的Regularization技术,如drop out, batch normalization取代了。知道了这些,似乎也可以不那么纠结这个LRN了。
Batch normalization参见:http://www.cnblogs.com/hansjorn/p/6298576.html
单独列出来学习:
SqueezeNet
http://www.jianshu.com/p/8e269451795d
http://blog.csdn.net/xbinworld/article/details/50897870
以上貌似是与AlexNet有关的两个网络设计,需要细看。




