第一章:Python基础の快速认识基本语法
本課主題
- 第一个 Hello World 程序实战
- 用户输入实战
- 模块介紹
- 变量介绍
- 格式化介紹
- 条件判断介紹和操作实战
- for 循环介紹和操作实战
- 作业需求
Python 第一个 Hello World 程序实战
Python是一门动态解释性的强类型定义语言,在 Python 的世界裡,打印出 Hello World 是一種很簡單的語法
print(x, y, z, sep='...', end='!\n')
print (最简单例子)
print("Hello World")
#Hello World
print (有参数例子)
x = 'apple' y = 'orange' z = 'waterlemon' print(x,y,z,sep='...',end='!\n') #apple...orange...waterlemon!
把打印结果输出到文件中
print(x, y, file=afile) #Send text to afile.write, not to sys.stdout.write
print (打印输出结果到文件中)
print(x, y, z, sep='...', file=open('data.txt', 'w'))
Python 用户输入实战
这个练习会来要求用户输入信息,然后会把用户输入的结果存储在一个变量中,然后在打印这个变量!在 Python 2.0 和 3.0 中对要求用户输入信息的语句有些不同。 2.0 和 3.0 都有 input( ),但它表达的意义有些不同。
- 在 Python 2.0,如果你用 input( ) 来要求用户输入信息,当输入信息后它会报错,因为这个函数只接受数字或者是变量,而不是接受字符串,在下面情况下就没有报错;
但如果直接输入字符串信息,它就会以为你是输入一个叫 Janice 的变量,这个变量在之前没有声明,然后直接调用,Python 在找这个变量的过程中发现找不到,它就会报错age = input("How old are you?") #How old are you?21 print age #21
所以在 Python 2.0 里如果想接受字符串的輸入,請務必用 raw_input ( ) 函数 Python2.0 input()
Python2.0 input()>>> user_input = input("What is your name? ") What is your name? Janice Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> File "<string>", line 1, in <module> NameError: name 'Janice' is not defined # Janice 变量在之前没有声明便直接调用
 Python2.0 raw_input()
Python2.0 raw_input()>>> user_name = raw_input("What is your name? ") What is your name? Janice >>> print user_name Janice
- 在 Python 3.0,就沒有 raw_input( ) 這個函数,統一用 input( ),但這個 Input( ) 的函数默應返回類型是 String
 Python3.0 input()
Python3.0 input()>>> user_name = input("What is your name? ") What is your name? Janice >>> print(user_name) Janice
- Python 可以在把 Input 存儲在一個變量裡,然後打印出來的時候配合一些格式。
 打印信息
打印信息>>> name = input("What is your name? ") What is your name? Janice >>> age = int(input("What is your age? ")) #Convert String to Integer What is your age? 20 >>> occupation = input("What is your occupation? ") What is your occupation? Sales >>> msg = """ ... Information of user %s: ... ------------------------ ... Name: %s ... Age: %d ... Job: %s ... -----------End---------- ... """ % (name,name,age,occupation) >>> print(msg) Information of user Janice: ------------------------ Name: Janice Age: 20 Job: Sales -----------End----------
Python 模块介紹
介紹幾個常用模块:
- import os
import os os.getcwd() # 打印当前目录位置 os.mkdir('/Users/DirA') # 在指定位置创建新目录 os.rename('DirA','RDirA') # 把当前目录称从 testDir 改成 renameTestDir os.remove("/Users/DirA/a.py") # 删除指定文件 os.listdir() # 返回一个列表 os.chdir("/Users/DirB") # 返回一个列表 os.system("ls -a") # 执行 Linux Shell Command os.getenv("SPARK_HOME") # echo $SPARK_HOME os.path.isfile('/etc/passwd') # 判断当前输入是不是文件 os.path.isdir('/etc/passwd') # 判断当前输入是不是文件夹 os.path.islink('/usr/local/bin/python3') # 判断当前输入是不是LINK os.path.getsize('/etc/passwd') # 获取文件的大小 os.path.getmtime('/etc/passwd') # 获取文件创建时的时间戳 - import sys
- import getpass
getpass.getpass() #获取用户输入密码 getpass.getpass(prompt='Input Password: ') #获取用户输入密码并且打印输入信息 getpass.getuser() #获取当前用户名称
- import 自定義的模块
Python 变量介绍
- 变量很重要的概念是变量取名字的意义,要容易明白,可以用下划线分开,变量就像一个容器一样:比如是 sonoftwinsbrotherage = 2 和 son_of_twins_brother_age = 2
- 可以一次同时赋值给多个变量
 同时赋值多个变量
同时赋值多个变量>>> x,y,z = 1,2,3 >>> x 1 >>> y 2 >>> z 3
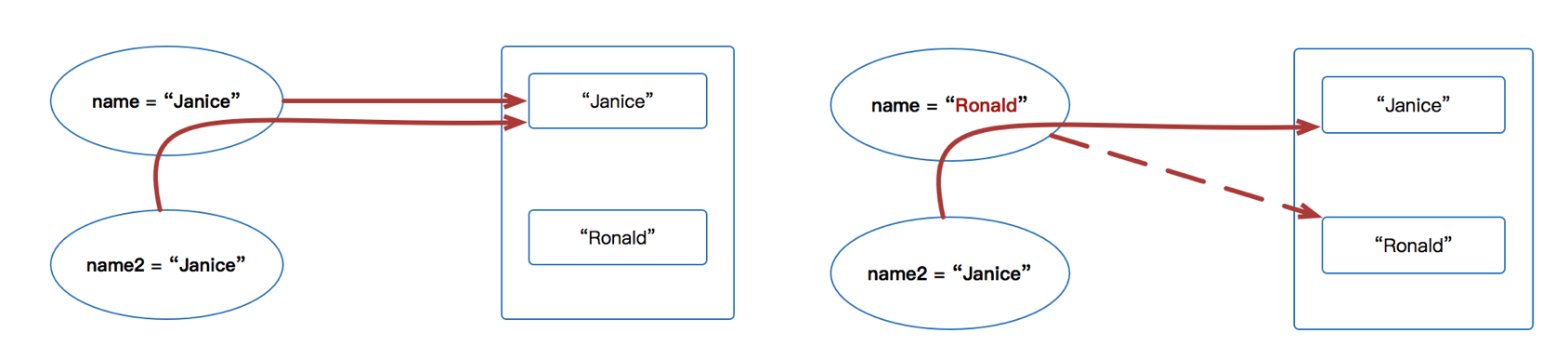
- 注意:变量可以赋值给变量,一旦赋值了,它会指向变量存储的对象,如下图:有一个name = “Janice” ,然后有一个name2 = name 的时候,name2 是指向name 实际存储的对象e.g. “Janice" ,所以在图左這两个变量的name 都是“Janice”;然后当name 这个变量改变了变成Ronald 的时候,它也不会影响name2 里面的值,因为它们实际指向对象本身,而不是指向name 的Reference。
运行程序后的结果:
 name指向同一个变量例子
name指向同一个变量例子# 首先赋值 name 变量 # 然后把 name 变量里的赋值给 name2 >>> name = "Janice" >>> name2 = name >>> id(name) #内存地址是一样的 4343794576 >>> id(name2) #内存地址是一样的 4343794576 >>> print("Part1: ",name, name2) Part1: Janice Janice
 重新赋值 name 变量
重新赋值 name 变量# 然后重新赋值 name 变量 >>> name = "Ronald" >>> id(name) 4343794856 >>> id(name2) 4343794576 >>> print("Part2: ",name, name2) Part2: Ronald Janice
Python 条件判断介紹和操作实战
if True: # 条件为真时的操作 else: # 条件为假时的操作
- if 表達式的基本語法是以下:if else 的如果别的的流程判斷,永遠只會有一種流程結果,如果第一條滿足了條件,他就不會往下走啦,如果沒有else 呢,其實他不會出錯
 条件判断例子之猜年龄游戏
条件判断例子之猜年龄游戏>>> age = int(input("What is your age? ")) What is your age? 20 >>> if age < 18: # Execute the next line if the condition is True ... print("You are still a teenagers") ... else: # Execute the next line if the condition is False ... print("You are an adult now!") ... You are an adult now!
- 下面是一个 number guessing game 的例子,也是用了 if-then-else 的逻辑判断来完成的
 条件判断例子之猜数字游戏
条件判断例子之猜数字游戏>>> secret_number = 8 #Define a secret_number >>> guess_number = int(input("Guess a number: ")) #Getting the user input Guess a number: 3 >>> if guess_number == secret_number: #Comparing the user_input with the secret number ... print("Congratulations! You got it!") ... elif guess_number >= secret_number: ... print("You guess a higher number! Try again") ... else: ... print("You guess a lower number! Try again") ... You guess a lower number! Try again
- 三元运算
 条件判断例子之三元运算
条件判断例子之三元运算>>> if 1 == 1: ... fruit = "apple" ... else: ... fruit = "orange" ... >>> name = "apple" if 1 == 1 else "orange" >>> >>> name 'apple'
Python for 循环介紹和操作实战
for i in iterable: #iterable可以是列表、字典、元组、集合、字符串 print(i)
- 表达式 for 循环基本語法如下:
 for循环基本語法
for循环基本語法1 for i in range(10): 2 print("Value of i: ",i) 3 4 #Value of i: 0 5 #Value of i: 1 6 #Value of i: 2 7 #Value of i: 3 8 #Value of i: 4
- 根据上面猜数字游戏的逻辑判断,这个游戏只可以玩一次;现在就结合 For-loop,让游戏可以在特定时间里循环,然後至少玩3次。
 猜数字游戏:进阶版
猜数字游戏:进阶版1 secret_number = 8 2 3 for i in range(10): 4 if i < 3: 5 guess_number = int(input("Guess a number: ")) 6 if guess_number == secret_number: 7 print("Congratulations! You got it!") 8 break 9 elif guess_number > secret_number: 10 print("You guess a higher number! Try again") 11 else: 12 print("You guess a lower number! Try again") 13 else: 14 print("too many attempts....Bye!") 15 break
 猜数字游戏:进阶版(运行结果)
猜数字游戏:进阶版(运行结果)#python3 numebr_guessing_game_v2.py Guess a number: 4 You guess a lower number! Try again Guess a number: 2 You guess a lower number! Try again Guess a number: 3 You guess a lower number! Try again too many attempts....Bye! #python3 numebr_guessing_game_v2.py Guess a number: 7 You guess a lower number! Try again Guess a number: 8 Congratulations! You got it!
- 这个程序优化了一点点,我们就可以玩多于一次,现在再多加一些需求,就是可以让玩家输入 yes 重覆游戏
 猜数字游戏:优化进阶版
猜数字游戏:优化进阶版1 secret_number = 8 2 counter = 0 3 4 for i in range(10): 5 print("Counter ->",counter) 6 if counter < 3: 7 guess_number = int(input("Guess a number: ")) 8 if guess_number == secret_number: 9 print("Congratulations! You got it!") 10 break 11 elif guess_number > secret_number: 12 print("You guess a higher number! Try again") 13 else: 14 print("You guess a lower number! Try again") 15 else: 16 play_again = input("Do you want to play again? y/n ") 17 # Ask if want to play again? 18 if play_again == 'y': 19 counter = 0 20 continue #continue the for loop 21 else: 22 print("Bye! See you again!") 23 break 24 # Increase one for the counter 25 counter += 1
 猜数字游戏:优化进阶版(运行结果)
猜数字游戏:优化进阶版(运行结果)#python3 numebr_guessing_game_v5.py Counter -> 0 Guess a number: 1 You guess a lower number! Try again Counter -> 1 Guess a number: 3 You guess a lower number! Try again Counter -> 2 Guess a number: 5 You guess a lower number! Try again Counter -> 3 Do you want to play again? y/n y Counter -> 0 Guess a number: 3 You guess a lower number! Try again Counter -> 1 Guess a number: 7 You guess a lower number! Try again Counter -> 2 Guess a number: 8 Congratulations! You got it!
作业需求
编写登陆接口
- 输入用户名密码
- 认证成功后显示欢迎信息
- 输错三次后锁定
多级菜单
- 三级菜单
- 可依次选择进入各子菜单
[所需新知识点:列表、字典]
程序运行结果
- 认证成功后显示欢迎信息
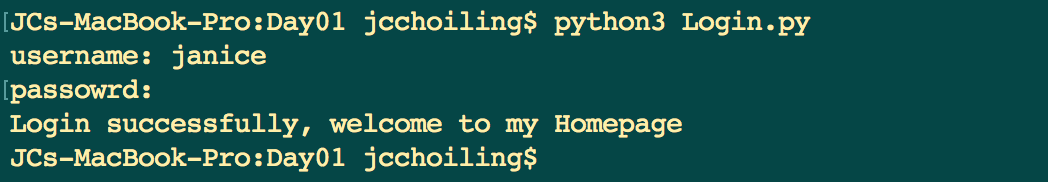
- 输错三次后锁定

参考资料
金角大王:[Python之路,Day1 - Python基础1]
銀角大王:[Python开发【第二篇】:初识Python]





