JDK8集合类源码解析 - HashMap
java为数据结构中的映射定义了一个接口java.util.Map,此接口主要有四个常用的实现类,分别是HashMap、Hashtable、LinkedHashMap和TreeMap
HashMap 比较常用,无序的,线程不安全的
Hashtable (不推荐使用)线程安全的,如果要确保线程安全,推荐使用ConcurrentHashMap
LinkedHashMap是HashMap的一个子类,保存了记录的插入顺序
TreeMap实现SortedMap接口,能够把它保存的记录根据键排序,默认是按键值的升序排序(比如在微信支付做签名的时候就可以使用TreeMap),也可以指定排序的比较器
考虑到使用情况 ,Hashmap的使用频率最高,这篇文章主要分析HashMap
接下来我将按照以下几个部分来介绍下
1核心数据结构
2相关方法解析
3其他补充
性能?
扩容因子?
线程安全性?
容量必须是2的n次幂?
4最佳实践
====================
1核心数据结构
Jdk8采用的是数组+链表+红黑树(当链表长度超过8的时候就会转化成红黑树,本文不对红黑树展开讨论,想了解更多红黑树数据结构的工作原理同学 可以点击 红黑树)
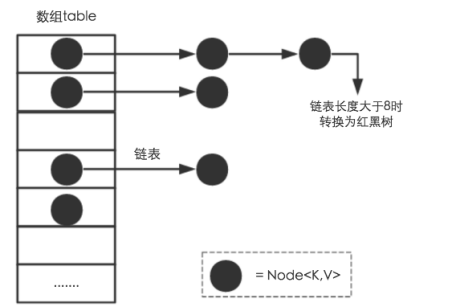
核心代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 | transient Node<K,V>[] table;static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; //用来定位数组索引位置 final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; //下一个Node Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; }static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links TreeNode<K,V> left; TreeNode<K,V> right; TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion boolean red; TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, val, next); } static class LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> { Entry<K,V> before, after; Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) { super(hash, key, value, next); } } |
可以看出Node是TreeNode的爷爷
2相关方法解析
put 方法解析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 | public V put(K key, V value) { //hash() 获取key在table里面的下标值 return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); }final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; //table为空 初始化table if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)//table当前下标的值为空直接插入 tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; //判断是否和已有的key重复,如果重复 把当前节点赋值给e 结束判断<br><br><br> if (p.hash == hash && ((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) e = p;//如果该节点 是TreeNode 进行红黑树的操作 else if (p instanceof TreeNode) e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else {//如果该链表元素不止一个 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); //链表长度超过8 转换为红黑树 if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } //在链表中找到相同的key 循环结束 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } //如果找到了相同的key的节点 进行value覆盖 if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; //如果超过最大容量 就执行扩容操作 if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; } |
resize方法解析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 | final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { //超过最大值就不再扩充了 if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return oldTab; }//容量扩大一倍 else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold } else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold newCap = oldThr; else { // 长度为0 初始化 newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0) { float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab;//如果原来的数组不为空 移动数据到扩容后的数组中 if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; //让原来的值为空 方便gc if (e.next == null) //如果该链只有一个数据 就放置到新的数组去//新的下标要么是原来的下标,要么是原来的+oldCap(后面会说道) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // 如果是该链后面还有数据 就遍历重新得到新的2条或者1条新的链 //新的低位的head,tail Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; //新的高位的head,tail Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; } |
注意:关于扩容后的下标计算
这里假如原来的大小为16,扩容后变成32
分别有两个元素 key1,key2
扩容前 [(n - 1) & hash] 长度16
长度(n-1) 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111
key1 1111 1111 1111 1111 0000 1111 0001 0010 --> 0 0010 2
key2 1111 1111 1111 1111 0000 1111 0000 0010 --> 0 0010 2
扩容后(e.hash & oldCap) 长度32
长度(n) 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000
key1 1111 1111 1111 1111 0000 1111 0001 0010 --> 1 0010 18
key2 1111 1111 1111 1111 0000 1111 0000 0010 --> 0 0010 2
于是乎只需要看看原来的hash值新增的那个bit是1还是0就好了,是0的话下标没变,是1的话下标变成 原下标+oldCap
3其他补充
性能?这里分2种情况,第一种,hash比较均匀的状况下,jdk8比jdk7提高了至少10%的性能
第二种,hash不均匀的状况下,jdk7的get方法花费的时间会随着长度的增加而线性增加,而jdk8中当链表长度过长会转成红黑树,get方法花费的时间呈现对数增长稳定。
扩容因子? 默认为0.75,这是综合时间和空间的利用率来考虑的,通常不要变,如果该值过大,可能会造成链表太长,导致get、put等操作缓慢;如果太小,空间利用率不足。
线程安全性?线程不安全,容易导致死循环(形成环形链表),多线程环境推荐使用ConcurrentHashMap
容量必须是2的n次幂?当数组长度为2的n次幂的时候,不同的key算得得index相同的几率较小,那么数据在数组上分布就比较均匀,也就是说碰撞的几率小,当然这我们指定大小的时候不需要指定为2的n次幂,jdk会调用tableSizeFor()返回大于当前值的最小的2的n次幂整数
4最佳实践
1 在使用hashmap的时候,如果能够预知需要使用的大小,最好指定其大小,较少因为扩容而导致的性能损失。
1 | HashMap<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(100); |
2 HashMap可以插入null的key 的value
3线程不安全,多线程环境推荐使用ConcurrentHashMap
4 JDK1.8引入红黑树很大程度提高了HashMap的性能,特别是在hash极不均衡的时候。
posted on 2017-07-03 17:52 一只小蜗牛12138 阅读(161) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报


【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步