Spring笔记
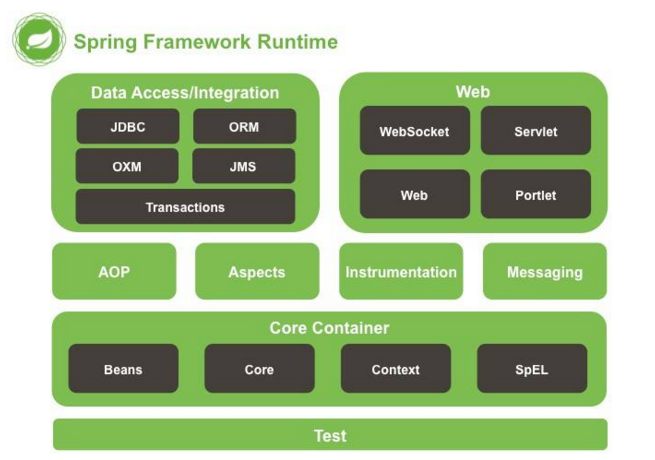
Spring的框架组成:它是对web层、业务层、数据访问层的每层都有解决方案;web层:Spring MVC;持久层:JDBC Template ;
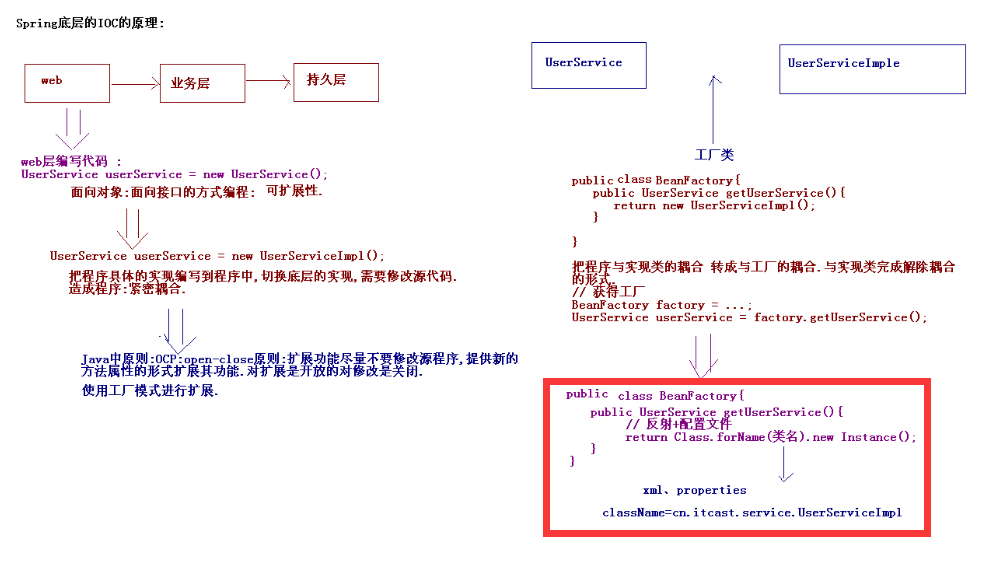
业务层:Spring的Bean管理(类的实例化托管给Spring,即Ioc,Spring利用动态代理给类进行增强,即AOP;从另一个角色看,对象都是你Spring管理的,那将来对这些对象进行修改,你Spring部应该负责到底吗?);
首先知道,实现AOP的方法有很多,Spring默认使用JDK动态代理,在需要代理类而不是代理接口的时候,Spring会自动切换为使用CGLIB代理,不过现在的项目都是面向接口编程,所以JDK动态代理相对来说用的还是多一些。
一、核心部分之IOC
1.1 相关概念 IOC:控制反转:将对象的创建权由Spring管理。 DI:依赖注入:在Spring创建对象的过程中,把对象依赖的属性注入到类中。
ApplicationContext 应用上下文,加载Spring 框架配置文件; ApplicationContext类继承了BeanFactory;BeanFactory在使用到这个类的时候,getBean()方法的时候才会加载这个类而ApplicationContext类加载配置文件的时候,创建所有的类;ApplicationContext对BeanFactory提供了扩展: 国际化处理、事件传递、Bean自动装配、各种不同应用层的Context实现;早期开发使用BeanFactory。
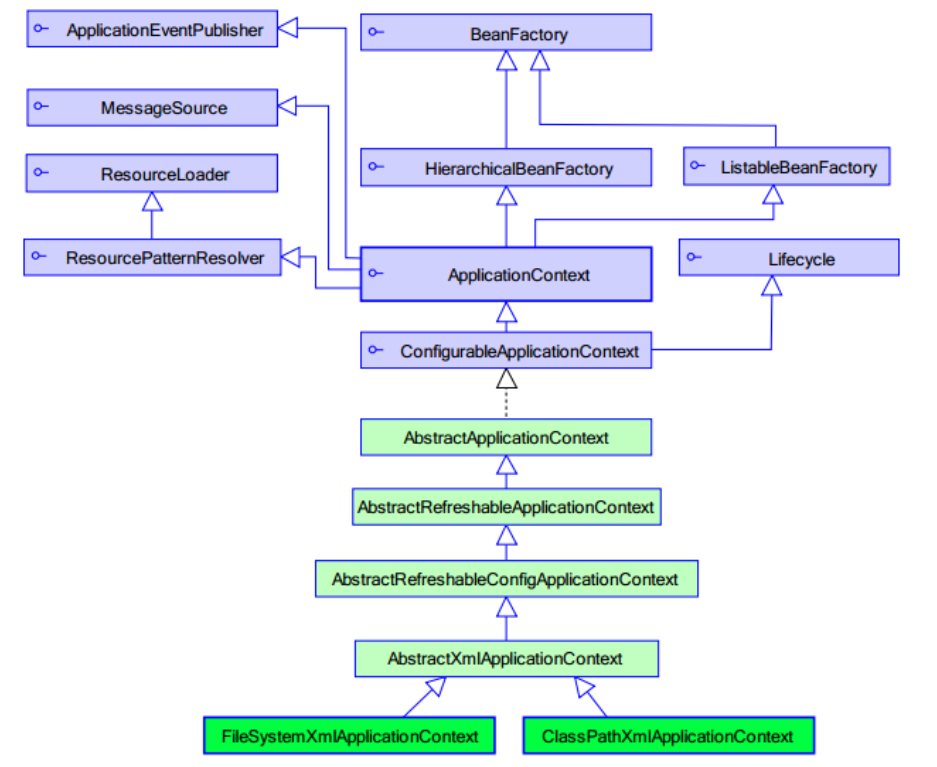
下面为ApplicationContext加载配置文件的两个子类:

new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");加载classpath下面配置文件。 new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");加载磁盘下配置文件。
1.2 IOC实例;前提,导入相关jar包。接口:HelloService.java

public interface HelloService { public void sayHello(); }
接口实现类:HelloServiceImpl.java

public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService { private String info; public void setInfo(String info) { this.info = info; } public void sayHello() { System.out.println("Hello Spring..."+info); } }
配置文件:applicationContext.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 通过一个<bean>标签设置类的信息,通过id属性为类起个标识. --> <bean id="userService" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.HelloServiceImpl"> <!-- 使用<property>标签注入属性 --> <property name="info" value="传智播客"/> </bean> </beans>
测试: SpringTest1.java

public class SpringTest1 { @Test // 传统方式 public void demo1() { // 造成程序紧密耦合. HelloService helloService = new HelloServiceImpl(); helloService.sayHello(); } @Test // Spring开发 public void demo2() { // 创建一个工厂类. ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( "applicationContext.xml"); HelloService helloService = (HelloService) applicationContext .getBean("userService"); helloService.sayHello(); } @Test // 加载磁盘路径下的配置文件: public void demo3() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( "applicationContext.xml"); HelloService helloService = (HelloService) applicationContext .getBean("userService"); helloService.sayHello(); } @Test public void demo4(){ // ClassPathResource FileSystemResource BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource("applicationContext.xml")); HelloService helloService = (HelloService) beanFactory.getBean("userService"); helloService.sayHello(); } }
1.3 IOC装配Bean
1- Spring提供三种装配Bean的方法:构造方法实例化(默认无参数)、静态工厂实例化、实例工厂实例化

<!-- 默认情况下使用的就是无参数的构造方法. --> <bean id="bean1" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.Bean1"></bean> <!-- 第二种使用静态工厂实例化 --> <bean id="bean2" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.Bean2Factory" factory-method="getBean2"></bean> <!-- 第三种使用实例工厂实例化 --> <bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="getBean3"></bean> <bean id="bean3Factory" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.Bean3Factory"/>
2- Bean的配置

1- id和name的区别: id遵守XML约束的id的约束.id约束保证这个属性的值是唯一的,而且必须以字母开始,可以使用字母、数字、连字符、下划线、句话、冒号 name没有这些要求 ***** 如果bean标签上没有配置id,那么name可以作为id. ***** 开发中Spring和Struts1整合的时候, /login. <bean name=”/login” class=””> 现在的开发中都使用id属性即可. 2-类的作用范围: scope属性 : * singleton :单例的.(默认的值.) * prototype :多例的. * request :web开发中.创建了一个对象,将这个对象存入request范围,request.setAttribute(); * session :web开发中.创建了一个对象,将这个对象存入session范围,session.setAttribute(); * globalSession :一般用于Porlet应用环境.指的是分布式开发.不是porlet环境,globalSession等同于session; 实际开发中主要使用singleton,prototype 3-Bean的生命周期: 配置Bean的初始化和销毁的方法: 配置初始化和销毁的方法: * init-method=”setup” * destroy-method=”teardown” 执行销毁的时候,必须手动关闭工厂,而且只对scope=”singleton”有效. Bean的生命周期的11个步骤: 1.instantiate bean对象实例化 2.populate properties 封装属性 3.如果Bean实现BeanNameAware 执行 setBeanName 4.如果Bean实现BeanFactoryAware 或者 ApplicationContextAware 设置工厂 setBeanFactory 或者上下文对象 setApplicationContext 5.如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean) ,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization 6.如果Bean实现InitializingBean 执行 afterPropertiesSet 7.调用<bean init-method="init"> 指定初始化方法 init 8.如果存在类实现 BeanPostProcessor(处理Bean) ,执行postProcessAfterInitialization 9.执行业务处理 10.如果Bean实现 DisposableBean 执行 destroy 11.调用<bean destroy-method="customerDestroy"> 指定销毁方法 customerDestroy 在CustomerService类的add方法之前进行权限校验?
Spring生命周期 示例:接口CustomerService.java

public interface CustomerService { public void add(); public void find(); }
CustomerServiceImpl.java

import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService, BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean { private String name; public void setName(String name) { System.out.println("第二步:属性的注入."); this.name = name; } public CustomerServiceImpl() { super(); System.out.println("第一步:实例化类."); } public void add(){ System.out.println("添加客户..."); } public void find(){ System.out.println("查询客户..."); } public void setBeanName(String name) { System.out.println("第三步:注入配置的类的名称"+name); } public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("第四步:注入applicationContext"+applicationContext); } public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("第六步:属性设置后执行..."); } public void setup(){ System.out.println("第七步:调用手动设置的初始化方法..."); } public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("第十步:调用销毁的方法..."); } public void teardown(){ System.out.println("第十一步:调用手动销毁方法..."); } }
MyBeanPostProcessor.java

import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor{ /** * bean:实例对象 * beanName:在配置文件中配置的类的标识. */ public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("第五步:初始化之前执行..."); return bean; } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(final Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("第八步:初始化后执行..."); // 动态代理: if(beanName.equals("customerService")){ Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(bean.getClass().getClassLoader(), bean.getClass().getInterfaces() , new InvocationHandler() { // 调用目标方法的时候,调用invoke方法. public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if("add".equals(method.getName())){ System.out.println("权限校验..."); Object result = method.invoke(bean, args); //System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); return result; } return method.invoke(bean, args); } }); return proxy; } return bean; } }
配置文件:applicationContext.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="customerService" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.CustomerServiceImpl" init-method="setup" destroy-method="teardown"> <property name="name" value="itcast"></property> </bean> <bean class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean> </beans>
测试SpringTest4.java

import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class SpringTest4 { @Test // Bean完整的生命周期 public void demo1() { ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( "applicationContext.xml"); CustomerService customerService = (CustomerService) applicationContext.getBean("customerService"); customerService.add(); customerService.find(); applicationContext.close(); } }
结果示例: 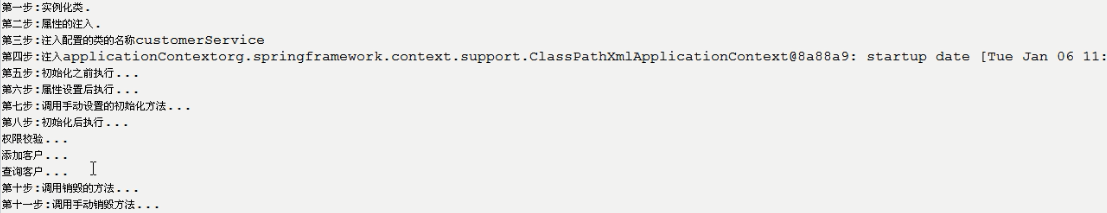
3- Bean属性注入

使用配置文件注入:

1-Bean中属性注入:Spring支持构造方法注入和setter方法注入: * 构造器注入: <bean id="car" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Car"> <!-- <constructor-arg name="name" value="宝马"/> <constructor-arg name="price" value="1000000"/> --> <constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="奔驰"/> <constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.Double" value="2000000"/> </bean> * setter方法注入: <bean id="car2" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Car2"> <!-- <property>标签中name就是属性名称,value是普通属性的值,ref:引用其他的对象 --> <property name="name" value="保时捷"/> <property name="price" value="5000000"/> </bean> * setter方法注入对象属性:<property name="car2" ref="car2"/> * 名称空间p:注入属性: Spring2.5版本引入了名称空间p. p:<属性名>="xxx" 引入常量值 p:<属性名>-ref="xxx" 引用其它Bean对象.引入名称空间: <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car2" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Car2" p:name="宝马" p:price="400000"/> <bean id="person" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Person" p:name="童童" p:car2-ref="car2"/> * SpEL:属性的注入: Spring3.0提供注入属性方式:语法:#{表达式}<bean id="" value="#{表达式}"> <bean id="car2" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Car2"> <property name="name" value="#{'大众'}"></property> <property name="price" value="#{'120000'}"></property> </bean> <bean id="person" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.Person"> <!--<property name="name" value="#{personInfo.name}"/>--> <property name="name" value="#{personInfo.showName()}"/> <property name="car2" value="#{car2}"/> </bean> <bean id="personInfo" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo5.PersonInfo"> <property name="name" value="张三"/> </bean> 2-集合属性的注入: <bean id="collectionBean" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo6.CollectionBean"> <!-- 注入List集合 --> <property name="list"> <list> <value>童童</value> <value>小凤</value> </list> </property> <!-- 注入set集合 --> <property name="set"> <set> <value>杜宏</value> <value>如花</value> </set> </property> <!-- 注入map集合 --> <property name="map"> <map> <entry key="刚刚" value="111"/> <entry key="娇娇" value="333"/> </map> </property> <property name="properties"> <props> <prop key="username">root</prop> <prop key="password">123</prop> </props> </property> </bean>
4-加载配置文件

第一种写法:ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml",”bean2.xml”); 第二种方法: <import resource="applicationContext2.xml"/>
5- 使用注解装配Bean spring使用JavaConfig进行配置

pring的注解装配Bean:
Spring2.5 引入使用注解去定义Bean;@Component 描述Spring框架中Bean
Spring的框架中提供了与@Component注解等效的三个注解:
@Repository 用于对DAO实现类进行标注
@Service 用于对Service实现类进行标注
@Controller 用于对Controller实现类进行标注
***** 三个注解为了后续版本进行增强的.
Bean的属性注入:
普通属性;
@Value(value="itcast")
private String info;
对象属性:
@Autowired:自动装配默认使用类型注入.
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userDao") --- 按名称进行注入.
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userDao")
private UserDao userDao;
等价于
@Resource(name="userDao")
private UserDao userDao;
Bean其他的属性的配置
配置Bean初始化方法和销毁方法:
* init-method 和 destroy-method.
@PostConstruct 初始化
@PreDestroy 销毁
配置Bean的作用范围: @Scope
Spring3.0提供使用Java类定义Bean信息的方法
@Configuration
public class BeanConfig {
@Bean(name="car")
public Car showCar(){
Car car = new Car();
car.setName("长安");
car.setPrice(40000d);
return car;
}
@Bean(name="product")
public Product initProduct(){
Product product = new Product();
product.setName("空调");
product.setPrice(3000d);
return product;
}
}
两种方式结合;一般使用XML注册Bean,使用注解进行属性的注入.
6- Spring整合Servlet

正常整合Servlet和Spring没有问题的但是每次执行Servlet的时候加载Spring配置,加载Spring环境. * 解决办法:在Servlet的init方法中加载Spring配置文件? * 当前这个Servlet可以使用,但是其他的Servlet的用不了了!!! * 将加载的信息内容放到ServletContext中.ServletContext对象时全局的对象.服务器启动的时候创建的.在创建ServletContext的时候就加载Spring的环境. * ServletContextListener:用于监听ServletContext对象的创建和销毁的. 导入;spring-web-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar 在web.xml中配置: <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> 修改程序的代码: WebApplicationContext applicationContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext applicationContext = (WebApplicationContext) getServletContext().getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
二、核心部分之AOP
1.1 相关概念
AOP Aspect Oriented Programing 面向切面编程; AOP采取横向抽取机制,取代了传统纵向继承体系重复性代码(性能监视、事务管理、安全检查、缓存); Spring AOP使用纯Java实现,不需要专门的编译过程和类加载器,在运行期通过代理方式向目标类织入增强代码; AspecJ是一个基于Java语言的AOP框架,Spring2.0开始,Spring AOP引入对Aspect的支持,AspectJ扩展了Java语言,提供了一个专门的编译器,在编译时提供横向代码的织入。
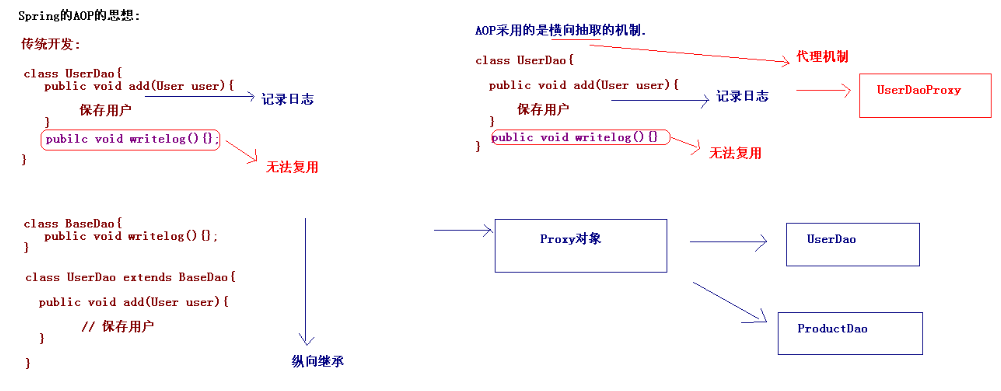
AOP底层原理:就是代理机制; 动态代理:(JDK中使用); JDK的动态代理对实现了接口的类生成代理。 Spring的AOP代理:JDK动态代理:对实现了接口的类生成代理;CGLib代理机制:对类生成代理。Spring框架,如果类实现了接口,就使用JDK的动态代理生成代理对象,如果这个类没有实现任何接口,使用CGLIB生成代理对象。
JDK动态代理:

public class JDKProxy implements InvocationHandler{ private UserDao userDao; public JDKProxy(UserDao userDao) { super(); this.userDao = userDao; } public UserDao createProxy() { UserDao proxy = (UserDao) Proxy.newProxyInstance(userDao.getClass() .getClassLoader(), userDao.getClass().getInterfaces(), this); return proxy; } // 调用目标对象的任何一个方法 都相当于调用invoke(); public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if("add".equals(method.getName())){ // 记录日志: System.out.println("日志记录================="); Object result = method.invoke(userDao, args); return result; } return method.invoke(userDao, args); } }
CGLIB代理:

CGLIB(Code Generation Library)是一个开源项目!是一个强大的,高性能,高质量的Code生成类库,它可以在运行期扩展Java类与实现Java接口。 Hibernate支持它来实现PO(Persistent Object 持久化对象)字节码的动态生成Hibernate生成持久化类的javassist. CGLIB生成代理机制:其实生成了一个真实对象的子类. 下载cglib的jar包. * 现在做cglib的开发,可以不用直接引入cglib的包.已经在spring的核心中集成cglib. public class CGLibProxy implements MethodInterceptor{ private ProductDao productDao; public CGLibProxy(ProductDao productDao) { super(); this.productDao = productDao; } public ProductDao createProxy(){ // 使用CGLIB生成代理: // 1.创建核心类: Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); // 2.为其设置父类: enhancer.setSuperclass(productDao.getClass()); // 3.设置回调: enhancer.setCallback(this); // 4.创建代理: return (ProductDao) enhancer.create(); } public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { if("add".equals(method.getName())){ System.out.println("日志记录=============="); Object obj = methodProxy.invokeSuper(proxy, args); return obj; } return methodProxy.invokeSuper(proxy, args); } }
下面打个比方来记忆AOP中的术语:铠甲勇士,有4个人(均可变身,称为Joinpoint:连接点),现在有张三和李四(Target,目标对象)选择对手臂(Pointcut,切入点)变身;;他俩拿着变身器(其实就是代理机制)变身,张三和李四都变成了手臂有盔甲,盔甲就是(Advice,通知);此时,他俩的手臂(Pointcut)+盔甲(Advice)=切面(Aspect)是个组合;其中在给手臂增加盔甲的过程,就是变身也叫织入(Weaving);如果变身改变了他俩的本身属性的话就称做引介(Introduct),比如变成了三头六臂;变身后的他俩就改了一个高逼格的名字叫铠甲勇士(Proxy,代理对象);
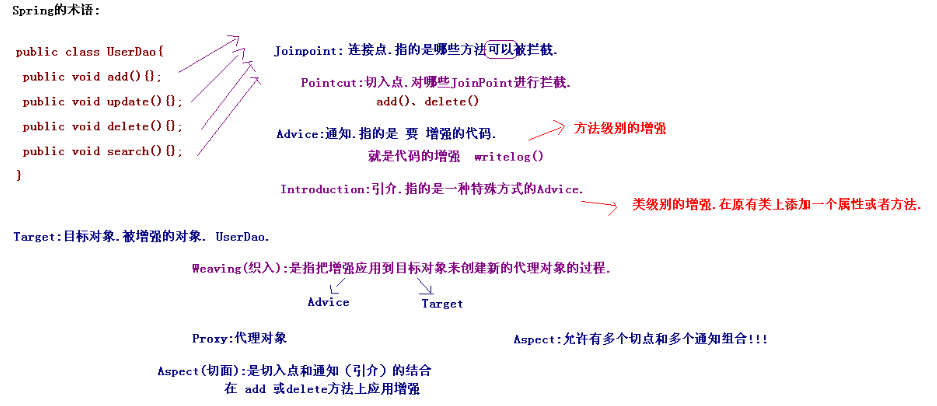
1.2 Spring中的AOP
1- Spring的传统AOP:

AOP:不是由Spring定义.AOP联盟的组织定义. Spring中的通知:(增强代码) 前置通知 org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice * 在目标方法执行前实施增强 后置通知 org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice * 在目标方法执行后实施增强 环绕通知 org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor * 在目标方法执行前后实施增强 异常抛出通知 org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice * 在方法抛出异常后实施增强 引介通知 org.springframework.aop.IntroductionInterceptor(课程不讲.) * 在目标类中添加一些新的方法和属性 Spring中的切面类型: Advisor : Spring中传统切面. * Advisor:都是有一个切点和一个通知组合. * Aspect:多个切点和多个通知组合. Advisor : 代表一般切面,Advice本身就是一个切面,对目标类所有方法进行拦截(* 不带有切点的切面.针对所有方法进行拦截) PointcutAdvisor : 代表具有切点的切面,可以指定拦截目标类哪些方法(带有切点的切面,针对某个方法进行拦截) IntroductionAdvisor : 代表引介切面,针对引介通知而使用切面(不要求掌握)
1.1 针对所有方法的增强:(不带有切点的切面)

第一步:导入相应jar包. * spring-aop-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar * com.springsource.org.aopalliance-1.0.0.jar 第二步:编写被代理对象: * CustomerDao接口 * CustoemrDaoImpl实现类 第三步:编写增强的代码: public class MyBeforeAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice{ /** * method:执行的方法 * args:参数 * target:目标对象 */ public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("前置增强..."); } } 第四步:生成代理:(配置生成代理:) * 生成代理Spring基于ProxyFactoryBean类.底层自动选择使用JDK的动态代理还是CGLIB的代理. * 属性: target : 代理的目标对象 proxyInterfaces : 代理要实现的接口 如果多个接口可以使用以下格式赋值 <list> <value></value> .... </list> proxyTargetClass : 是否对类代理而不是接口,设置为true时,使用CGLib代理 interceptorNames : 需要织入目标的Advice singleton : 返回代理是否为单实例,默认为单例 optimize : 当设置为true时,强制使用CGLib <!-- 定义目标对象 --> <bean id="customerDao" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.CustomerDaoImpl"></bean> <!-- 定义增强 --> <bean id="beforeAdvice" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.MyBeforeAdvice"></bean> <!-- Spring支持配置生成代理: --> <bean id="customerDaoProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean"> <!-- 设置目标对象 --> <property name="target" ref="customerDao"/> <!-- 设置实现的接口 ,value中写接口的全路径 --> <property name="proxyInterfaces" value="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.CustomerDao"/> <!-- 需要使用value:要的名称 --> <property name="interceptorNames" value="beforeAdvice"/> </bean> ***** 注入的时候要注入代理对象: @Autowired // @Qualifier("customerDao")// 注入是真实的对象,必须注入代理对象. @Qualifier("customerDaoProxy") private CustomerDao customerDao;
1.2 带有切点的切面:(针对目标对象的某些方法进行增强)

PointcutAdvisor 接口: DefaultPointcutAdvisor 最常用的切面类型,它可以通过任意Pointcut和Advice 组合定义切面 RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor 构造正则表达式切点切面 第一步:创建被代理对象. * OrderDao 第二步:编写增强的类: public class MyAroundAdvice implements MethodInterceptor{ public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕前增强..."); Object result = methodInvocation.proceed();// 执行目标对象的方法 System.out.println("环绕后增强..."); return result; } } 第三步:生成代理: <!-- 带有切点的切面 --> <!-- 定义目标对象 --> <bean id="orderDao" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.OrderDao"></bean> <!-- 定义增强 --> <bean id="aroundAdvice" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.MyAroundAdvice"></bean> <!-- 定义切点切面: --> <bean id="myPointcutAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor"> <!-- 定义表达式,规定哪些方法执行拦截 --> <!-- . 任意字符 * 任意个 --> <!-- <property name="pattern" value=".*"/> --> <!-- <property name="pattern" value="cn\.itcast\.spring3\.demo4\.OrderDao\.add.*"/> --> <!-- <property name="pattern" value=".*add.*"></property> --> <property name="patterns" value=".*add.*,.*find.*"></property> <!-- 应用增强 --> <property name="advice" ref="aroundAdvice"/> </bean> <!-- 定义生成代理对象 --> <bean id="orderDaoProxy" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean"> <!-- 配置目标 --> <property name="target" ref="orderDao"></property> <!-- 针对类的代理 --> <property name="proxyTargetClass" value="true"></property> <!-- 在目标上应用增强 --> <property name="interceptorNames" value="myPointcutAdvisor"></property> </bean>
1.3 自动代理
前面的案例中,每个代理都是通过ProxyFactoryBean织入切面代理,在实际开发中,非常多的Bean每个都配置ProxyFactoryBean开发维护量巨大; 自动创建代理(基于后处理Bean。在Bean创建的过程中完成的增强;生成Bean就是代理)。
1- BeanNameAutoProxyCreator 根据Bean名称创建代理

<!-- 定义目标对象 --> <bean id="customerDao" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.CustomerDaoImpl"></bean> <bean id="orderDao" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.OrderDao"></bean> <!-- 定义增强 --> <bean id="beforeAdvice" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.MyBeforeAdvice"></bean> <bean id="aroundAdvice" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.MyAroundAdvice"></bean> <!-- 自动代理:按名称的代理 基于后处理Bean,后处理Bean不需要配置ID--> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator"> <property name="beanNames" value="*Dao"/> <property name="interceptorNames" value="beforeAdvice"/> </bean>
2- DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 根据Advisor本身包含信息创建代理

<!-- 定义目标对象 --> <bean id="customerDao" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.CustomerDaoImpl"></bean> <bean id="orderDao" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.OrderDao"></bean> <!-- 定义增强 --> <bean id="beforeAdvice" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.MyBeforeAdvice"></bean> <bean id="aroundAdvice" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo4.MyAroundAdvice"></bean> <!-- 定义一个带有切点的切面 --> <bean id="myPointcutAdvisor" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor"> <property name="pattern" value=".*add.*"/> <property name="advice" ref="aroundAdvice"/> </bean> <!-- 自动生成代理 --> <bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator"></bean> 区分基于ProxyFattoryBean的代理与自动代理区别? ***** ProxyFactoryBean:先有被代理对象,将被代理对象传入到代理类中生成代理. 自动代理基于后处理Bean.在Bean的生成过程中,就产生了代理对象,把代理对象返回.生成Bean已经是代理对象.
3- AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 基于Bean中的AspectJ 注解进行自动代理
2- Spring的AspectJ的AOP https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43468667/article/details/88831441

AspectJ是一个面向切面的框架,它扩展了Java语言。AspectJ定义了AOP语法所以它有一个专门的编译器用来生成遵守Java字节编码规范的Class文件。 AspectJ是一个基于Java语言的AOP框架 Spring2.0以后新增了对AspectJ切点表达式支持 @AspectJ 是AspectJ1.5新增功能,通过JDK5注解技术,允许直接在Bean类中定义切面 新版本Spring框架,建议使用AspectJ方式来开发AOP AspectJ表达式: * 语法:execution(表达式) execution(<访问修饰符>?<返回类型><方法名>(<参数>)<异常>) * execution(“* cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.dao.*(..)”) ---只检索当前包 * execution(“* cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.dao..*(..)”) ---检索包及当前包的子包. * execution(* cn.itcast.dao.GenericDAO+.*(..)) ---检索GenericDAO及子类 AspectJ的通知类型: @Before 前置通知,相当于BeforeAdvice * 就在方法之前执行.没有办法阻止目标方法执行的. @AfterReturning 后置通知,相当于AfterReturningAdvice * 后置通知,获得方法返回值. @Around 环绕通知,相当于MethodInterceptor * 在可以方法之前和之后来执行的,而且可以阻止目标方法的执行. @AfterThrowing抛出通知,相当于ThrowAdvice @After 最终final通知,不管是否异常,该通知都会执行 @DeclareParents 引介通知,相当于IntroductionInterceptor (不要求掌握) 切点的定义: @Pointcut("execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.UserDao.find(..))") private void myPointcut(){} 面试: * Advisor和Aspect的区别? * Advisor:Spring传统意义上的切面:支持一个切点和一个通知的组合. * Aspect:可以支持多个切点和多个通知的组合.
2.1 基于注解

第一步:引入相应jar包. * aspectj依赖aop环境. * spring-aspects-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar * com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar 第二步:编写被增强的类: * UserDao 第三步:使用AspectJ注解形式: @Aspect public class MyAspect { @Before("execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.UserDao.add(..))") public void before(){ System.out.println("前置增强...."); } } 第四步:创建applicationContext.xml * 引入aop的约束: * <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> --- 自动生成代理: * 底层就是AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator <aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> <bean id="userDao" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.UserDao"></bean> <bean id="myAspect" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.MyAspect"></bean>
2.2 基于XML

第一步:编写被增强的类: * ProductDao 第二步:定义切面 第三步:配置applicationContext.xmll 前置通知: * 代码: public void before(){ System.out.println("前置通知..."); } * 配置: <aop:config> <!-- 定义切点: --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.ProductDao.add(..))" id="mypointcut"/> <aop:aspect ref="myAspectXML"> <!-- 前置通知 --> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> 后置通知: * 代码: public void afterReturing(Object returnVal){ System.out.println("后置通知...返回值:"+returnVal); } * 配置: <aop:config> <!-- 定义切点: --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.ProductDao.add(..))" id="mypointcut"/> <aop:aspect ref="myAspectXML"> <!-- 后置通知 --> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturing" pointcut-ref="mypointcut" returning="returnVal"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> 环绕通知: * 代码: public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable{ System.out.println("环绕前增强...."); Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕后增强...."); return result; } * 配置: <aop:config> <!-- 定义切点: --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.ProductDao.add(..))" id="mypointcut"/> <aop:aspect ref="myAspectXML"> <!-- 前置通知 --> <!-- <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"/> --> <!-- 后置通知 --> <!-- <aop:after-returning method="afterReturing" pointcut-ref="mypointcut" returning="returnVal"/> --> <!-- 环绕通知 --> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> 异常通知: * 代码; public void afterThrowing(Throwable e){ System.out.println("异常通知..."+e.getMessage()); } * 配置; <aop:config> <!-- 定义切点: --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.ProductDao.add(..))" id="mypointcut"/> <aop:aspect ref="myAspectXML"> <!-- 异常通知 --> <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="mypointcut" throwing="e"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> 最终通知: * 代码: public void after(){ System.out.println("最终通知...."); } * 配置: <aop:config> <!-- 定义切点: --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo2.ProductDao.add(..))" id="mypointcut"/> <aop:aspect ref="myAspectXML"> <!-- 最终通知 --> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
三、核心部分之数据访问
JdbcTemplate模板与DbUtils工具类比较类似。Spring对持久层技术支持:

JDBC:org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate Hibernate3.0:org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate IBatis(MyBatis):org.springframework.orm.ibatis.SqlMapClientTemplate JPA:org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTemplate
1、JDBCTemplate
1.1 配置连接池

1-Spring默认的连接池: <!-- 配置Spring默认的连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring3_day02"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="123"/> </bean> 2-DBCP连接池: 导入jar包: * com.springsource.org.apache.commons.dbcp-1.2.2.osgi.jar * com.springsource.org.apache.commons.pool-1.5.3.jar <!-- 配置DBCP连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring3_day02"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="123"/> </bean> 3- C3P0连接池: 导入jar包: * com.springsource.com.mchange.v2.c3p0-0.9.1.2.jar <!-- 配置c3p0连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring3_day02"/> <property name="user" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="123"/> </bean> 参数设置到属性文件中 在src下创建jdbc.properties jdbc.driver = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql:///spring3_day02 jdbc.user = root jdbc.password = 123 需要在applicationContext.xml 中使用属性文件配置的内容. * 第一种写法: <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties"></property> </bean> * 第二种写法: <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
1.2 JdbcTemplate的CRUD

Spring框架中提供了对持久层技术支持的类: JDBC : org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport Hibernate 3.0 : org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.HibernateDaoSupport iBatis : org.springframework.orm.ibatis.support.SqlMapClientDaoSupport 编写DAO的时候: Public class UserDao extends JdbcDaoSupport{ } 进行CRUD的操作; * 保存:update(String sql,Object... args) * 修改:update(String sql,Object... args) * 删除:update(String sql,Object... args) 查询: * 简单查询: * select count(*) from user; --- queryForInt(String sql); * select name from user where id = ?; --- queryForObject(String sql,Class clazz,Object... args); * 复杂查询:(返回对象,和对象集合) * select * from user where id = ? --- queryForObjectString sql,RowMapper<T> rowMapper,Object... args); * select * from user; --- query(String sql,RowMapper<T> rowMapper,Object... args);
2、Spring事务管理
事务处在Service层.

Spring提供事务管理API: PlatformTransactionManager:平台事务管理器. commit(TransactionStatus status) getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) rollback(TransactionStatus status) TransactionDefinition:事务定义 ISOLation_XXX:事务隔离级别. PROPAGATION_XXX:事务的传播行为.(不是JDBC中有的,为了解决实际开发问题.) 过期时间: TransactionStatus:事务状态 是否有保存点 是否一个新的事务 事务是否已经提交 关系:PlatformTransactionManager通过TransactionDefinition设置事务相关信息管理事务,管理事务过程中,产生一些事务状态:状态由TransactionStatus记录. API详解: PlatformTransactionManager:接口. Spring为不同的持久化框架提供了不同PlatformTransactionManager接口实现 org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager : 使用Spring JDBC或iBatis 进行持久化数据时使用 org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager: 使用Hibernate3.0版本进行持久化数据时使用 org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager:使用JPA进行持久化时使用 org.springframework.jdo.JdoTransactionManager:当持久化机制是Jdo时使用 org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager:使用一个JTA实现来管理事务,在一个事务跨越多个资源时必须使用 TransactionDefinition: * ISOLATION_DEFAULT:默认级别. Mysql repeatable_read oracle read_commited ISOLATION_READ_UNCOMMITTED ISOLATION_READ_COMMITTED ISOLATION_REPEATABLE_READ ISOLATION_SERIALIZABLE * 事务的传播行为:(不是JDBC事务管理,用来解决实际开发的问题.)传播行为:解决业务层之间的调用的事务的关系. PROPAGATION_REQUIRED :支持当前事务,如果不存在 就新建一个 * A,B 如果A有事务,B使用A的事务,如果A没有事务,B就开启一个新的事务.(A,B是在一个事务中。) PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS :支持当前事务,如果不存在,就不使用事务 * A,B 如果A有事务,B使用A的事务,如果A没有事务,B就不使用事务. PROPAGATION_MANDATORY :支持当前事务,如果不存在,抛出异常 * A,B 如果A有事务,B使用A的事务,如果A没有事务,抛出异常. PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW 如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务,创建一个新的事务 * A,B 如果A有事务,B将A的事务挂起,重新创建一个新的事务.(A,B不在一个事务中.事务互不影响.) PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起当前事务 * A,B 非事务的方式运行,A有事务,就会挂起当前的事务. PROPAGATION_NEVER 以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常 PROPAGATION_NESTED 如果当前事务存在,则嵌套事务执行 * 基于SavePoint技术. * A,B A有事务,A执行之后,将A事务执行之后的内容保存到SavePoint.B事务有异常的话,用户需要自己设置事务提交还是回滚. * 常用:(重点) PROPAGATION_REQUIRED PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW PROPAGATION_NESTED
Spring的事务管理分成两类: * 编程式事务管理: 手动编写代码完成事务管理; * 声明式事务管理:不需要手动编写代码,配置。事务管理参考
2.1 事务操作的环境搭建

CREATE TABLE `account` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(20) NOT NULL, `money` double DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; INSERT INTO `account` VALUES ('1', 'aaa', '1000'); INSERT INTO `account` VALUES ('2', 'bbb', '1000'); INSERT INTO `account` VALUES ('3', 'ccc', '1000'); 创建一个web项目: * 导入相应jar包 * 引入配置文件: * applicationContext.xml、log4j.properties、jdbc.properties 创建类: * AccountService * AccountDao 在Spring中注册: <!-- 业务层类 --> <bean id="accountService" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.AccountServiceImpl"> <!-- 在业务层注入Dao --> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/> </bean> <!-- 持久层类 --> <bean id="accountDao" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.AccountDaoImpl"> <!-- 注入连接池的对象,通过连接池对象创建模板. --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> 编写一个测试类:
2.2 编程式事务

需要事务管理器:真正管理事务对象. * Spring提供了事务管理的模板(工具类.) 第一步:注册事务管理器: <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!-- 需要注入连接池,通过连接池获得连接 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> 第二步:注册事务模板类: <!-- 事务管理的模板 --> <bean id="transactionTemplate" class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate"> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/> </bean> 第三步:在业务层注入模板类:(模板类管理事务) <!-- 业务层类 --> <bean id="accountService" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.AccountServiceImpl"> <!-- 在业务层注入Dao --> <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/> <!-- 在业务层注入事务的管理模板 --> <property name="transactionTemplate" ref="transactionTemplate"/> </bean> 第四步:在业务层代码上使用模板: public void transfer(final String from, final String to, final Double money) { transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() { @Override protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status) { accountDao.out(from, money); int d = 1 / 0; accountDao.in(to, money); } }); } 手动编码方式缺点: * 代码量增加,代码有侵入性.
2.3 声明式事务-原始方式

基于TransactionProxyFactoryBean. 导入:aop相应jar包. 第一步:注册平台事务管理器: <!-- 事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!-- 注入连接池 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> 第二步:创建业务层代理对象: <!-- 配置生成代理对象 --> <bean id="accountServiceProxy" class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionProxyFactoryBean"> <!-- 目标对象 --> <property name="target" ref="accountService"/> <!-- 注入事务管理器 --> <property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager"/> <!-- 事务的属性设置 --> <property name="transactionAttributes"> <props> <prop key="transfer">PROPAGATION_REQUIRED</prop> </props> </property> </bean> 第三步:编写测试类: ***** 千万注意:注入代理对象 @Autowired @Qualifier("accountServiceProxy") private AccountService accountService; prop格式:PROPAGATION,ISOLATION,readOnly,-Exception,+Exception * 顺序:传播行为、隔离级别、事务是否只读、发生哪些异常可以回滚事务(所有的异常都回滚)、发生了哪些异常不回滚. ***** 缺点:就是需要为每一个管理事务的类生成代理.需要为每个类都需要进行配置.
2.4 声明式事务-自动代理

第一步:导入相应jar包. * aspectj 第二步:引入相应约束: * aop、tx约束. <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> 第三步:注册事务管理器; <!-- 事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> 第四步:定义增强(事务管理) <!-- 定义一个增强 --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <!-- 增强(事务)的属性的配置 --> <tx:attributes> <!-- isolation:DEFAULT :事务的隔离级别. propagation :事务的传播行为. read-only :false.不是只读 timeout :-1 no-rollback-for :发生哪些异常不回滚 rollback-for :发生哪些异常回滚事务 --> <tx:method name="transfer"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> 第五步:定义aop的配置(切点和通知的组合) <!-- aop配置定义切面和切点的信息 --> <aop:config> <!-- 定义切点:哪些类的哪些方法应用增强 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.itcast.spring3.demo3.AccountService+.*(..))" id="mypointcut"/> <!-- 定义切面: --> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="mypointcut"/> </aop:config> 第六步:编写测试类: * 注入Service对象,不需要注入代理对象(生成这个类的时候,已经是代理对象.)
2.5 基于注解的事务管理

第一步:事务管理器: <!-- 事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> 第二步:注解事务: <!-- 开启注解的事务管理 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> 第三步:在Service上使用注解 @Transactional * 注解中有属性值: * isolation * propagation * readOnly




