day9-20180419笔记
笔记:Python的class类
pycharm下载github代码

pycharm提交代码到github
点击“File”,选择“Default Settings”
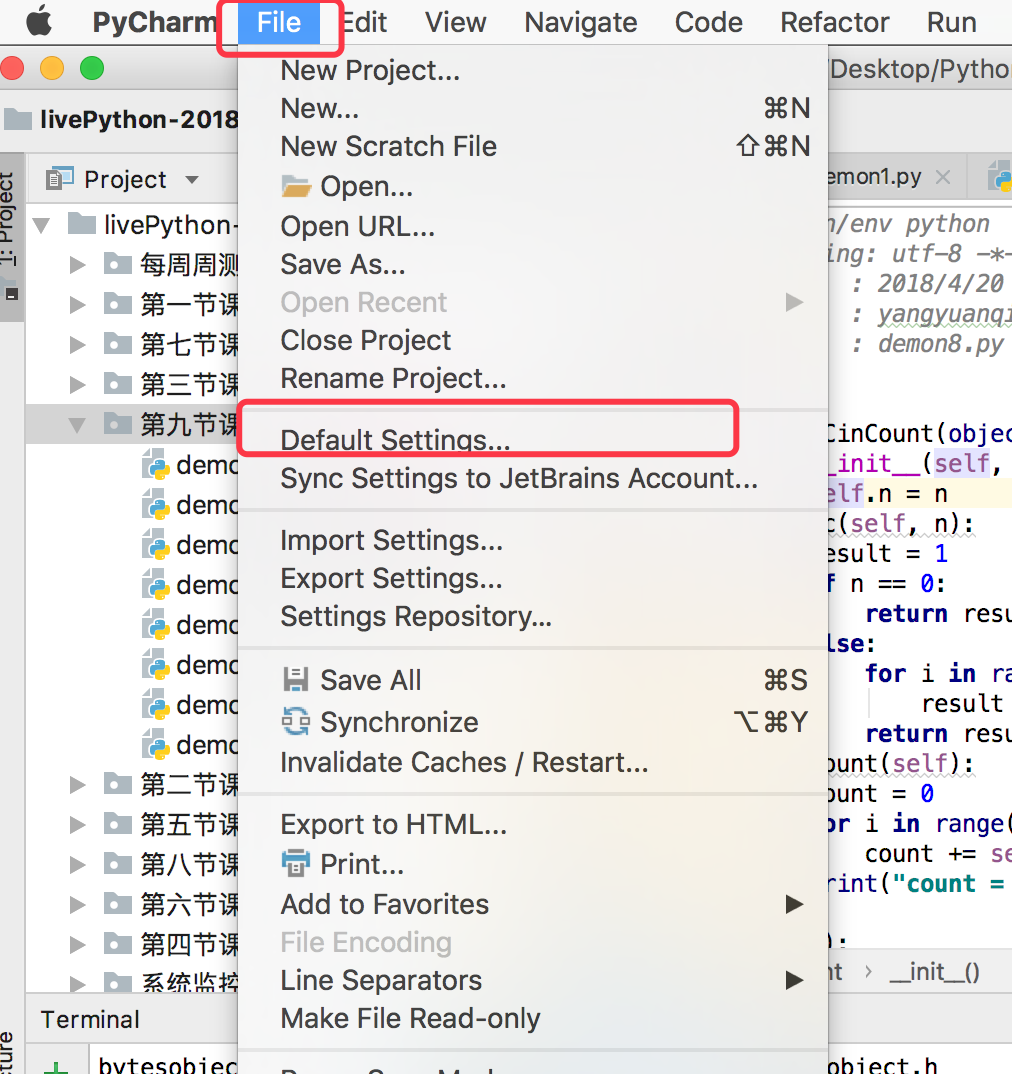
设置git
设置github
Host:填写github.com仓库地址
Auth Type:选择“Password”
Login:github登录账号
Password:github登录密码
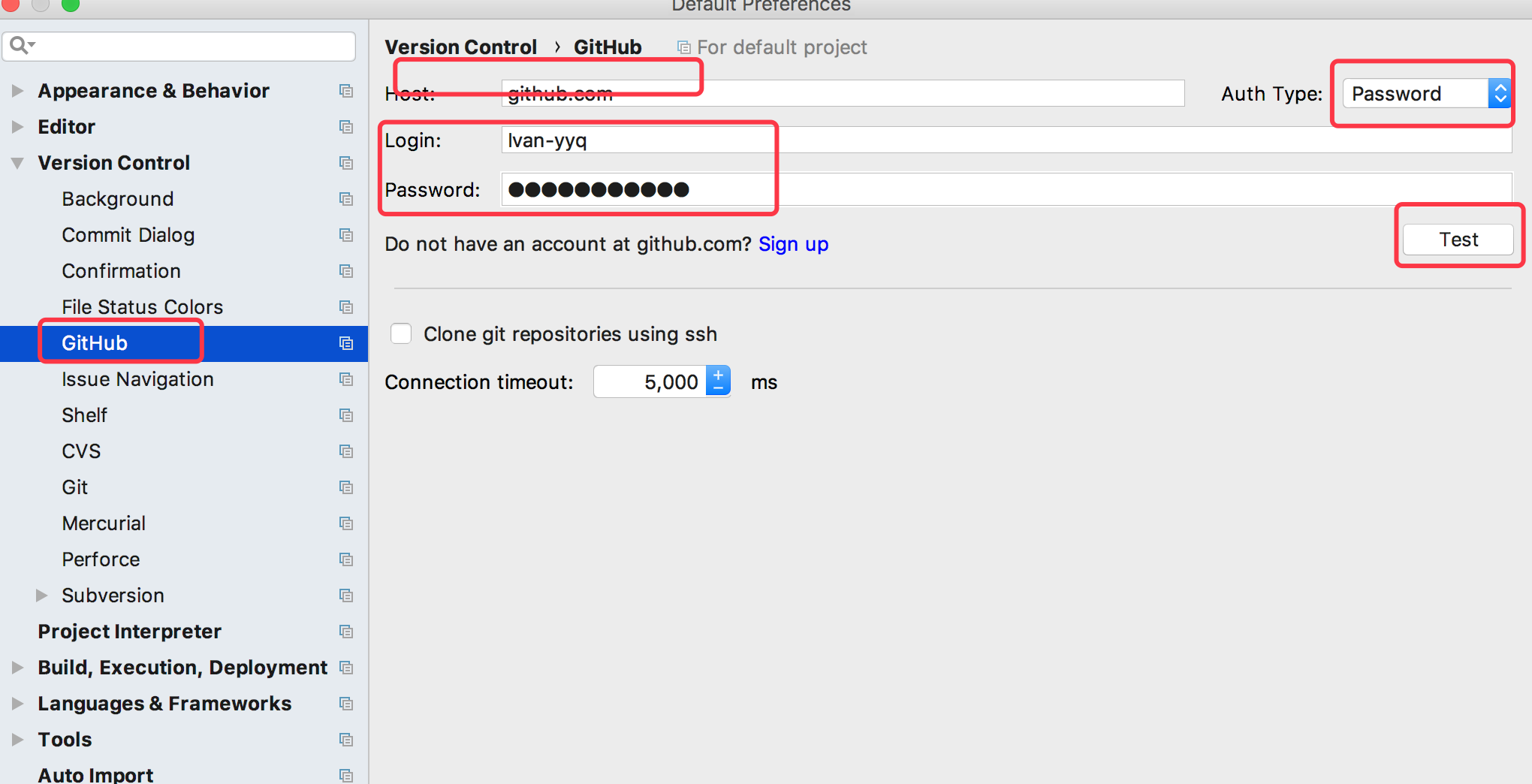
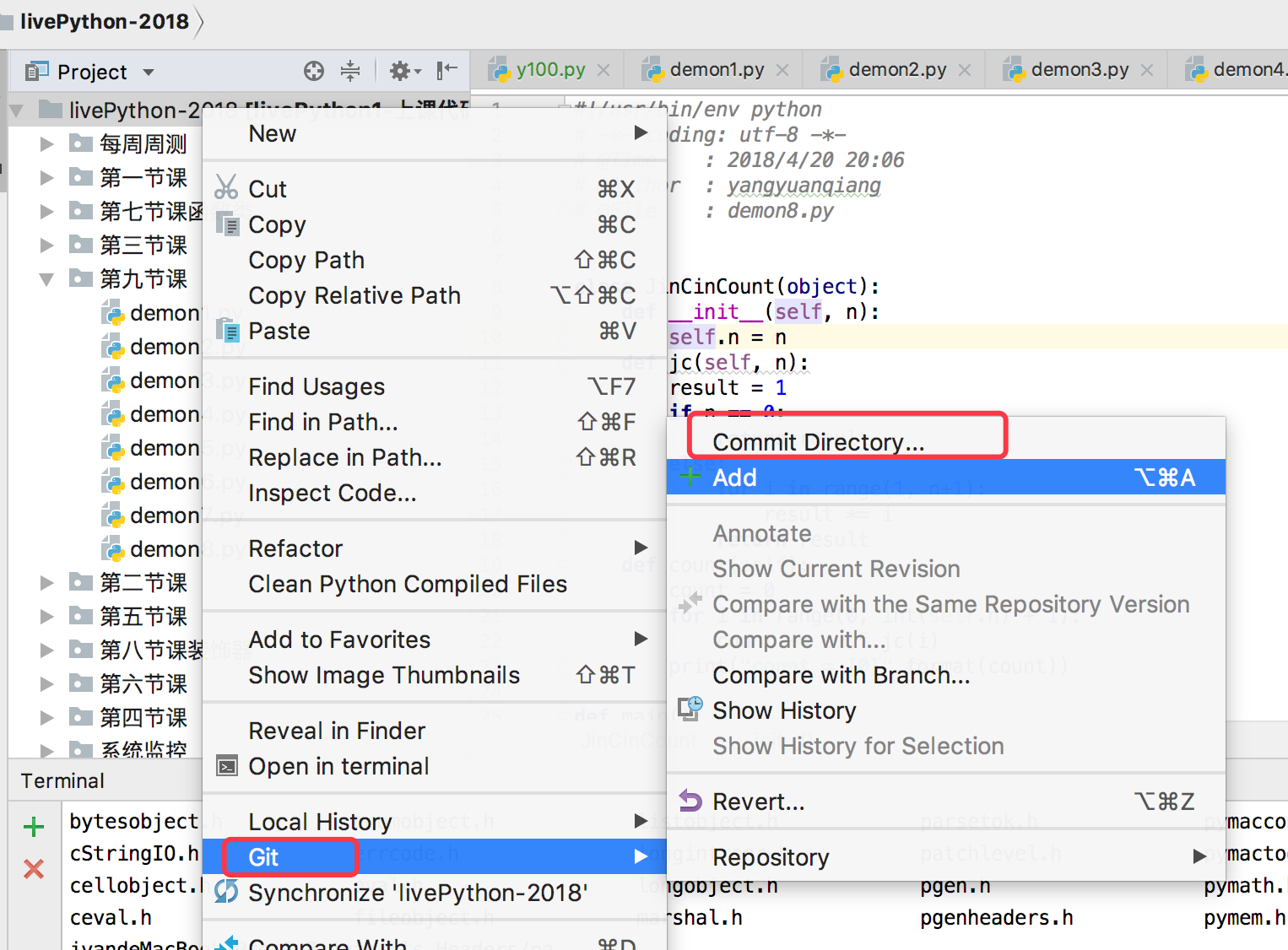
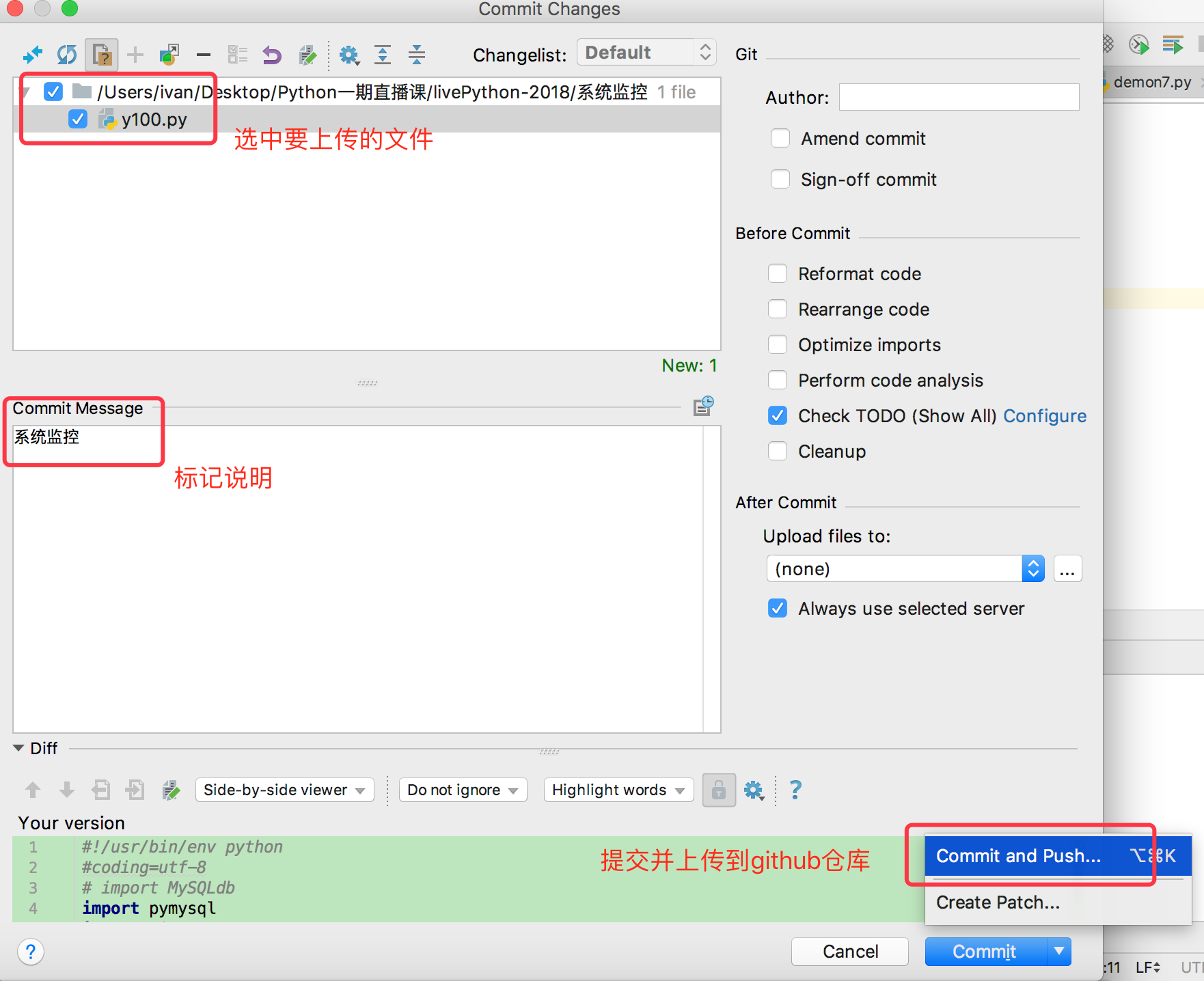

登录github.com,就可以找到提交的项目代码
一、Python的class类
类, 面向对象一个很重要的载体
1. 类的定义
class StuentName(object): #(object)是一个超级类,StuentName继承object的类
pass
2. 类里面一般都是由很多函数组成,函数的第一个参数默认都是self
如果需要全局变量,就在类的内部直接定义
3. 类的内部在调用函数或者调用变量的时候,必须使用self.变量 或者self.函数
self 代表的是类实例化以后的个体
4.类的实例化
实例化类的首字母小写作为实例,然后类实例化
studentName = StudentName();
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2018/4/20 20:04 # @Author : yangyuanqiang # @File : demon2.py class A(object): name = "ajing" def hello(self): print("hello {0}".format(self.name)) def test(self): self.hello() print("This is test.") a = A() b = A()
类的构造器
就是类在初始化的时候,首先,必须要执行的函数
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2018/4/20 20:05 # @Author : yangyuanqiang # @File : demon3.py class A(object): # def __init__(self, name): self.name = name print("init class A") def hello(self): print("hello {0}".format(self.name)) a = A("ajing") a.hello() #调用函数 hello(self)
以上实例输出的结果
init class A hello ajing
Python同样有限的支持多继承形式。多继承的类定义形如下例:
class DerivedClassName(Base1, Base2, Base3): <statement-1> . . . <statement-N>
需要注意圆括号中父类的顺序,若是父类中有相同的方法名,而在子类使用时未指定,python从左至右搜索 即方法在子类中未找到时,从左到右查找父类中是否包含方法。
继承 spuer
重写
调用: 先去找子类中的方法,如果子类中找不到对应的方法,就是父类中找
多继承:如果父类中都有该方法,那么先继承谁, 就用谁的方法。
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2018/4/20 20:05 # @Author : yangyuanqiang # @File : demon4.py class Animal(object): def __init__(self, name): #定义一个构造器 print("你现在正在初始化一个Animal") def run(self): #定义一个函数 print("Animal can run.") class Bird(Animal): #子类继承Animal父类的特性 def __init__(self): print("bird") def fly(self): print("Bird can fly.") class Cat(Animal): #子类继承Animal父类的特性 def __init__(self, name, sex): self.name = name self.sex = sex super(Cat, self).__init__(self.name) print("我是一只猫,啦啦啦啦") def jiao(self): print("miao miao miao miao") def run(self): print("我是一只猫,会上树来会跑路.") class BianYi(Cat, Bird): pass # animal = Animal() #继承 # cat = Cat() #重写 # cat.run() # bianYi = BianYi() cat = Cat("mao", "man")
以上实例输出的结果
你现在正在初始化一个Animal
我是一只猫,啦啦啦啦
java的思想
java 中的set和get方法
private host;
private port;
public getHost():
return host
public setHost(String host):
this.host = host
模拟,对数据库的操作
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2018/4/20 20:05 # @Author : yangyuanqiang # @File : demon5.py ''' host port username password dbname ''' class DbArgs(object): # 只有类本身才可以调用 __host = str("1.1.1.1") __port = str() __username = str() __password = str() __dbname = str() # 任何人可以调用 name = "ajing" # 只能实例自己调用 _host = "asdlfjasdl" def getHost(self): return self.__host def setHost(self, host): self.__host = host dbArgs = DbArgs() print(dbArgs.getHost()) dbArgs.name = "就是要改你,怎么的" print(dbArgs.name) print(dbArgs._host)
以上实例输出的结果
1.1.1.1
就是要改你,怎么的
asdlfjasdl
例子:
10学生
id
name
score
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2018/4/20 20:06 # @Author : yangyuanqiang # @File : demon7.py ''' 例子: 10学生 id name score ''' # class Student(object): # __id = int() # __name = str() # __score = int() # # def getId(self): # return self.__id # def setId(self, id): # self.__id = id # # def getName(self): # return self.__name # def setName(self, name): # self.__name = name # # def getScore(self): # return self.__score # def setScore(self, score): # self.__score = score import codecs class Student(object): def __init__(self, id, name, score): self.id = id self.name = name self.score = score class InitStduents(): def __init__(self): self.students = list() self.init() def init(self): self.students.append(Student(1001, "aaa", 59)) self.students.append(Student(1002, "bbb", 96)) self.students.append(Student(1003, "ccc", 87)) self.students.append(Student(1004, "ddd", 89)) self.students.append(Student(1005, "eee", 33)) self.students.append(Student(1006, "fff", 85)) self.students.append(Student(1007, "ggg", 78)) self.students.append(Student(1008, "hhh", 97)) self.students.append(Student(1009, "iii", 31)) self.students.append(Student(1010, "jjj", 93)) def sort(self): return sorted(self.students, key=lambda student: student.score) def writeFile(self, newStudents): with codecs.open("sortStudent.txt", "w")as f: for i in newStudents: f.write("id = {0}".format(i.id)) f.write("\t") f.write("name = {0}".format(i.name)) f.write("\t") f.write("score = {0}".format(i.score)) f.write("\n") def main(): students = InitStduents() newStudents = students.sort() students.writeFile(newStudents) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
以上实例输出的结果
id = 1009 name = iii score = 31 id = 1005 name = eee score = 33 id = 1001 name = aaa score = 59 id = 1007 name = ggg score = 78 id = 1006 name = fff score = 85 id = 1003 name = ccc score = 87 id = 1004 name = ddd score = 89 id = 1010 name = jjj score = 93 id = 1002 name = bbb score = 96 id = 1008 name = hhh score = 97
类的封装
python通过变量名命名来区分属性和方法的访问权限,默认权限相当于c++和java中的public
类的私有属性: __private_attrs:两个下划线开头,声明该属性为私有,不能在类地外部被使用或直接访问。在类内部的方法中使用时self.__private_attrs。
类的私有方法:__private_method:两个下划线开头,声明该方法为私有方法,不能在类地外部调用。在类的内部调用 self.__private_methods
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2018/4/20 20:06 # @Author : yangyuanqiang # @File : demon8.py # 阶乘的和 class JinCinCount(object): def __init__(self, n): self.n = n def jc(self, n): result = 1 if n == 0: return result else: for i in range(1, n+1): result *= i return result def count(self): count = 0 for i in range(0, int(self.n) + 1): count += self.jc(i) print("count = {0}".format(count)) def main(): n = input("Please inpurt a number: ") jinCinCount = JinCinCount(int(n)) jinCinCount.count() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
以上实例输出的结果
Please inpurt a number: 3
count = 10
总结:
1、重复看录播视频,加强练习类、继承、封装及方法的使用



