Shiro踩坑记(二):使用RequiresXXX的注解后,访问对应请求返回404
问题描述:
我在项目中的某个Controller上添加了@RequirePermissions注解,希望在执行该请求前,可以先进行权限验证。但是当我请求该Controller时,返回的确是404错误。
首先我怀疑的是因为权限不足而抛出了404错误。但是我发现我在AController的请求方法1上加了@RequiresPermession注释,但是请求方法2同样也报了404错误。所以应该不是shiro对权限进行了拦截,更像是整个controller的请求映射都没被Spring正常解析。
哪个步骤产生了404错误
我们知道SpringMVC处理请求转发的地方是在DispatchServlet的doDispatch方法中。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//如果是Multipart请求,则先处理
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//根据请求找到对应HandlerMapping,在通过HandlerMapping返回对应的处理器执行链HandlerExecuteChain
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
//找不到对应的映射,则抛出404异常
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
//GET 和 HEAD请求 如果资源没更新,则直接返回
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//请求的预处理,其实就是应用拦截器的preHandle方法
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//正式由Controller处理请求,
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//根据Controller返回的视图名,解析视图
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//后置处理,应用拦截器的后置处理方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//处理异常或是渲染视图
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
一种怀疑是在getHandler时,找不到对应的executeHandlerChain,所以产生了404错误。但是在断点中我们发现依旧可以获取到相应的executeHandlerChain。

貌似没有问题(其实如果够细心且了解MappingHandler的话,此时应该已经能看出问题了)。
继续往下,直到过了前置处理依旧没有问题(说明基本上不是拦截器造成的404错误)。
而再往下发现经过ha.handle()方法后,返回的mv对象为null,而此时看response对象已经出现了404的错误。
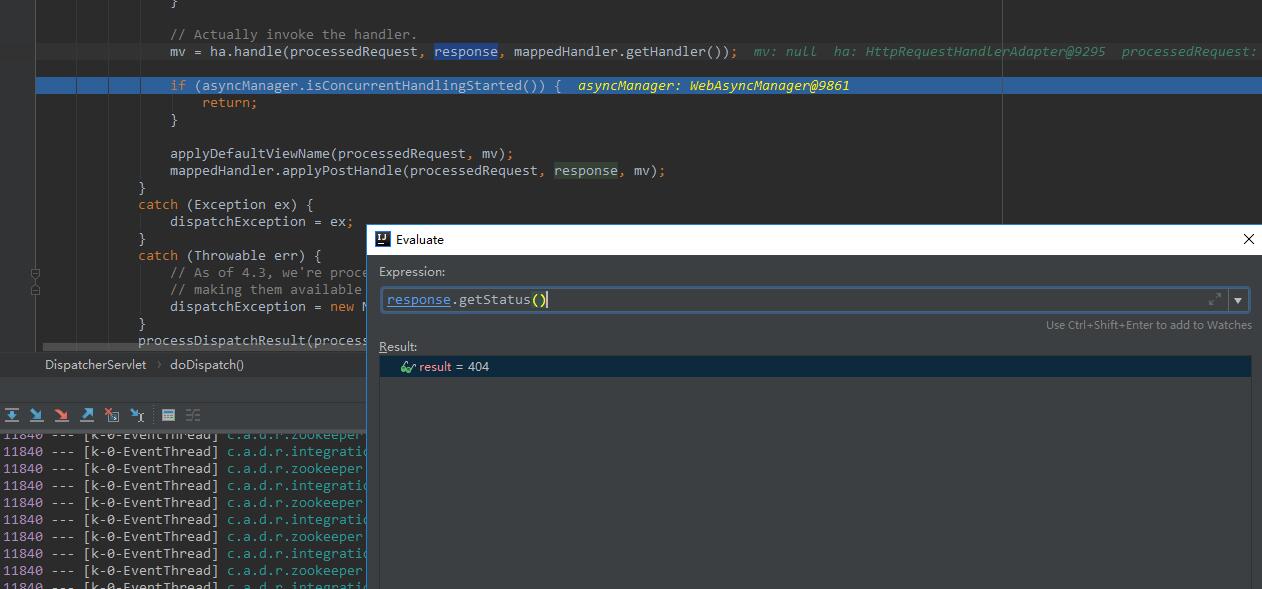
因此我们将关注点放在handle的执行顺序上。
我们得到的ha是HttpRequestHandlerAdapter对象。它的handle方法如下:
@Override
@Nullable
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
return null;
}
HandlerAdapter是一个处理器适配器。主要是适配不同类型的处理器。而此时的Handler类型是ResourceHttpRequestHandler。
其中handleRequest方法如下:
@Override
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// For very general mappings (e.g. "/") we need to check 404 first
//根据请求路径,解析对应的静态资源
Resource resource = getResource(request);
//如果找不到对应资源,则抛出404错误
if (resource == null) {
logger.trace("No matching resource found - returning 404");
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND);
return;
}
if (HttpMethod.OPTIONS.matches(request.getMethod())) {
response.setHeader("Allow", getAllowHeader());
return;
}
// Supported methods and required session
checkRequest(request);
// Header phase
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(resource.lastModified())) {
logger.trace("Resource not modified - returning 304");
return;
}
// Apply cache settings, if any
prepareResponse(response);
// Check the media type for the resource
MediaType mediaType = getMediaType(request, resource);
if (mediaType != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Determined media type '" + mediaType + "' for " + resource);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No media type found for " + resource + " - not sending a content-type header");
}
}
// Content phase
if (METHOD_HEAD.equals(request.getMethod())) {
setHeaders(response, resource, mediaType);
logger.trace("HEAD request - skipping content");
return;
}
ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage = new ServletServerHttpResponse(response);
if (request.getHeader(HttpHeaders.RANGE) == null) {
Assert.state(this.resourceHttpMessageConverter != null, "Not initialized");
setHeaders(response, resource, mediaType);
this.resourceHttpMessageConverter.write(resource, mediaType, outputMessage);
}
else {
Assert.state(this.resourceRegionHttpMessageConverter != null, "Not initialized");
response.setHeader(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT_RANGES, "bytes");
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = new ServletServerHttpRequest(request);
try {
List<HttpRange> httpRanges = inputMessage.getHeaders().getRange();
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_PARTIAL_CONTENT);
this.resourceRegionHttpMessageConverter.write(
HttpRange.toResourceRegions(httpRanges, resource), mediaType, outputMessage);
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
response.setHeader("Content-Range", "bytes */" + resource.contentLength());
response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE);
}
}
}
其中需要关系的部分是getResource方法,因为找不到对应的Resource,而产生了404错误。我们也找到了404错误的原因。
找到404的原因后,继续分析。ResourceHttpRequestHandler是负责处理静态资源的。正常情况下,我们到控制器的请求不应该是由ResourceHttpRequestHandler处理。因此,我们得到的Handler并非是我们期望的。
getHandler解析的Handler为什么不对
首先看DispatchServlet的getHandler方法。
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
//遍历内部的HandlerMapping(内置处理器),返回该请求映射的处理器
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
//返回处理器,并形成处理器链
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
DispatcherServlet在初始化时会创建内置的一些HandlerMapping。常见的有SimpleUrlHandlerMapping(映射请求和静态资源),RequestMappingHandlerMapping(映射请求和@RequestMapping注解的Controller中的方法),BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping(映射请求和处理器bean,映射关系由bean Name确定)等。
为什么RequestMappingHandlerMapping没能够为我们对应的处理器?了解下RequestMappingHandlerMapping的getHandler方法:
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//调用内部获取处理器的方法(模板模式)
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
//如果处理器为空 则使用默认的处理器
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
//如果返回的处理器是bean Name,则获取bean对象
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//形成处理器执行链(主要是添加拦截器)
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
//如果是跨域请求,则设置跨域的配置
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
查找处理器的逻辑主要是是在getHandlerInternal方法中:
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//根据请求解析路径
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
}
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
//获取对应的处理器方法
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (handlerMethod != null) {
logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
}
else {
logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
}
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
而lookupHandlerMethod方法则是从MappingRegistry中获取匹配url的方法。在根据URL匹配的精度确认最后的方法。ReqeustMappingHandlerMapping找不到处理器,说明MappingRegistry并没有解析到对应的处理器方法。
RequstMappingHandlerMapping的初始化过程
RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现了InitializingBean接口。在其afterPropertiesSet方法中实现了将
处理器映射方法mappingRegistry的逻辑。具体实现在其父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中。
//初始化时检测处理器方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
//扫描上下文中的bean,注册对应的处理器方法
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
//获取上下文中的bean name
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
//遍历bean names
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
//是否为标准处理器(RequestMappingHandlerMapping的实现根据类上是否有@Controller或是@RequestMapping注释)
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
//筛选对应的方法并注册
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
接下来就是在RequestMappingHandlerMapping初始化的过程中断点调试,看看是什么问题:
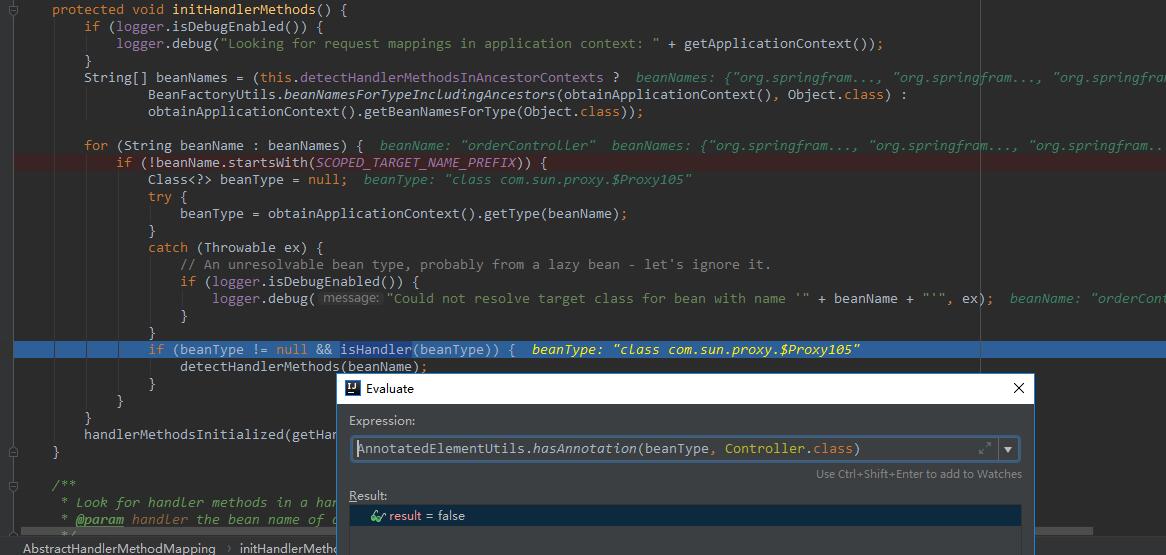
可以看到相应的控制器被代理过后丢失了注释。而这里的代理并非是AspectJ的创建的,而是com.sun.Proxy对象。
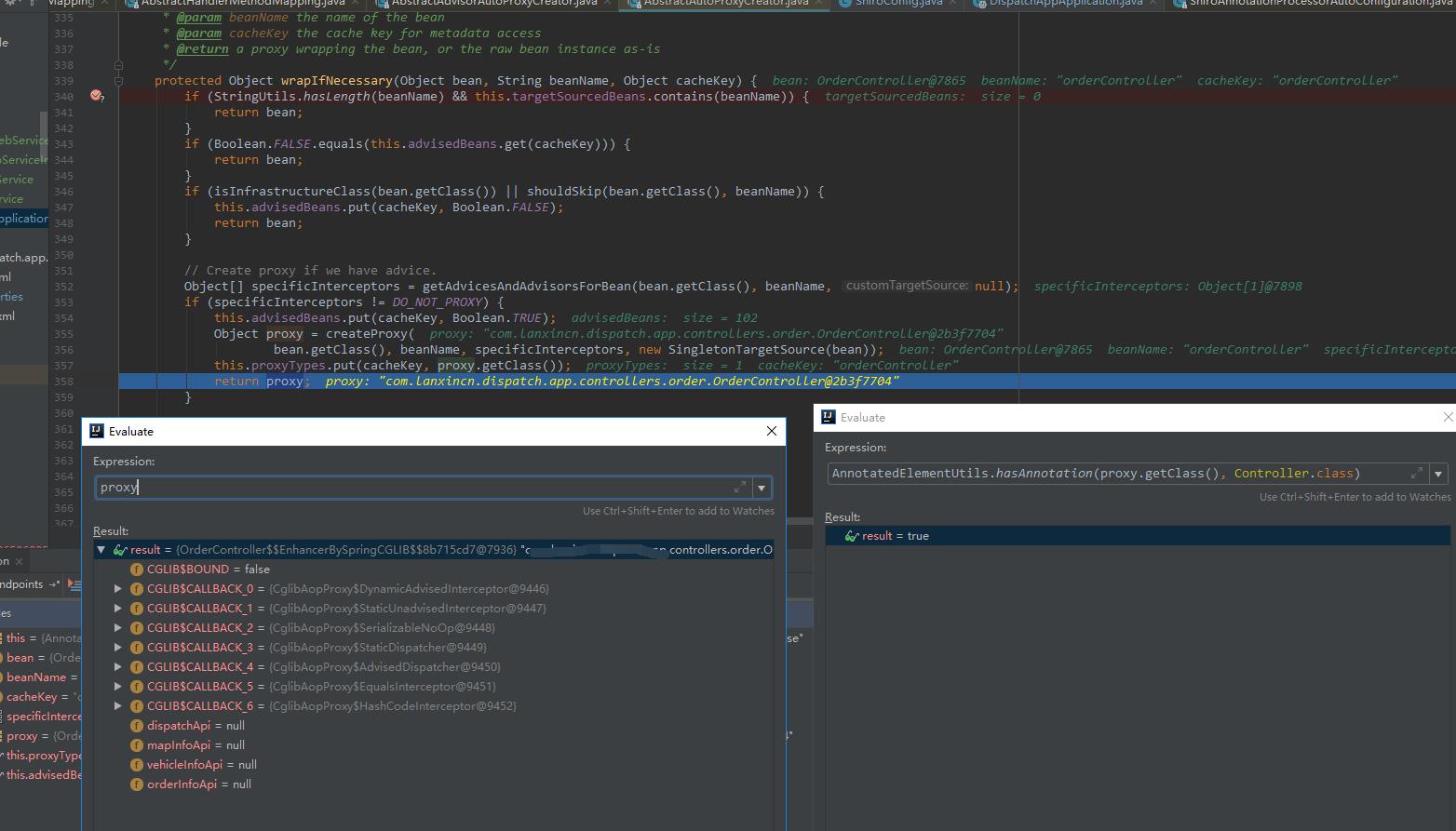
如果在启动时观察对应控制器的bean的创建情况,可以发现这个bean被增强了两次:
第一次增强:
第二次增强:
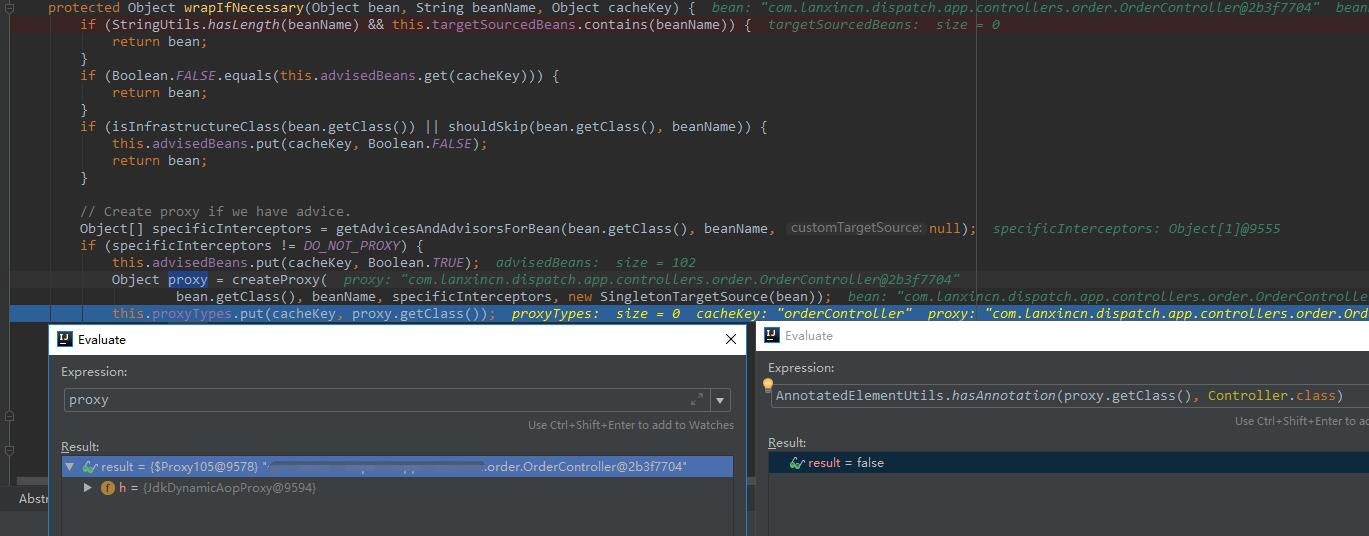
可以看到第二次增强过后bean丢失了@Controller的注释。
解决方案
我们已经知道造成404的真正原因是Controller初始化时被增强了两次。并在第二次增强时丢掉了注释。导致了该Controller无法被正常映射。因此我们只需要关闭一次增强过程即可。事实上,由于已经存在了ProxyCreator,因此ShiroAnnotationProcessorAutoConfiguration中的DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator就不再需要了。
所以可以通过在配置文件中将shiro.annotations.enabled属性设置为false。或者是直接在项目的配置中exclude掉ShiroAnnotationProcessorAutoConfiguration。然后再声明AuthorizationAttributeSourceAdvisor即可。


