Java四种线程池
线程池的好处
1、线程的创建需要消耗的,用完了马上就扔了比较可惜,所以把它缓存起来,以后还能再用;
2、可以根据实际情况调整线程池的大小,防止线程太多;
3、有些场合可以用线程池来做同步(比如多个线程使用同一文件系统时,可以用SingleThreadExecutor来保持同步);
可缓存(可变大小)的线程池 CachedThreadPool
这是一种很宽松的线程池,当任务来了之后,如果没有可用的线程那么就新建一个,如果有空闲的线程,则直接使用现有的线程。
可以根据实际的处理需求动态变化线程的数量。如果实际处理需求没那么多了,就会把部分线程回收掉。反之,如果实际处理需求又上来了,就会重新创建线程。
比如下面的代码,模拟每隔2秒才有一个新任务,而这个任务每次只需要1秒就能执行完:
public class CachedThreadPool { static Random random = new Random(); static int taskId = 0; static ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); public static void main(String[] args) { while(true) { service.execute(new MyThread()); try { //新增任务速度 Thread.sleep(new Long(2*1000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } static class MyThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running for task:" + (taskId++)); try { //任务线程执行所需时间 Thread.sleep(new Long(1*1000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
这种情况下,线程池只需要一个线程就够用了:
thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:0 thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:1 thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:2 thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:3 thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:4 thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:5
如果把任务执行时间增加到3秒,则会产生3个线程:
thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:0 thread pool-1-thread-2 is running for task:1 thread pool-1-thread-3 is running for task:2 thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:3 thread pool-1-thread-2 is running for task:4 thread pool-1-thread-3 is running for task:5 thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:6 thread pool-1-thread-2 is running for task:7 thread pool-1-thread-3 is running for task:8 thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:9
如果刚开始新增任务速度很快,后来变慢了,之前新增的线程会被回收掉:
public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; while(true) { service.execute(new MyThread()); long sleep = i>=5 ? 2000 : 50; #<---------------- 前五个任务新增得很快故意让线程池多创建任务,之后变慢,让增加速度比任务执行速度还慢 try { //新增任务速度 Thread.sleep(sleep); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } i++; } } static class MyThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is running for task:" + (taskId++)); try { //任务线程执行所需时间 Thread.sleep(new Long(1*1000)); #<-------------------- 执行速度是1秒,新增速度的一半 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
输出结果如下:
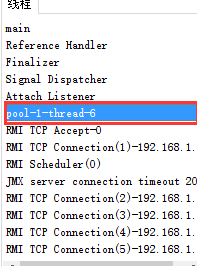
thread pool-1-thread-1 is running for task:0 thread pool-1-thread-2 is running for task:1 thread pool-1-thread-3 is running for task:2 thread pool-1-thread-4 is running for task:3 thread pool-1-thread-5 is running for task:4 thread pool-1-thread-6 is running for task:5 thread pool-1-thread-6 is running for task:6 thread pool-1-thread-6 is running for task:7 thread pool-1-thread-6 is running for task:8 thread pool-1-thread-6 is running for task:9 thread pool-1-thread-6 is running for task:10 thread pool-1-thread-6 is running for task:11 thread pool-1-thread-6 is running for task:12 ...
后面只有thread-6在跑了,打开jconsole,会发现其他的thread-1-threac-X已经不见了。
固定大小的线程池 FixedThreadPool
这个好理解了,我就这么几个线程,你任务再多也没用。
定时执行线程池 ScheduledThreadPool
定时任务线程池要注意的是,在线程资源稀缺的时候(就是线程数量设置的很小,比增加的定时任务还少,不够用),任务的执行时间会影响任务的执行周期。简单来说就是不要把线程数量设置的太少了。
单线程的线程池 SingleThreadExecutor
它创建单个工作者来执行任务,如果工作者线程异常退出了会重新创建一个来替换。它可以确保任务在队列中依次串行执行,例如FIFO、LIFO、优先级。另外固定大小的线程池还提供了大量同步机制,从而是一个任务写入到内存的结果对于后续的任务是可见的。

