『TensorFlow』网络操作API_中_损失函数及分类器



一、误差值
度量两个张量或者一个张量和零之间的损失误差,这个可用于在一个回归任务或者用于正则的目的(权重衰减)。
l2_loss
tf.nn.l2_loss(t, name=None)解释:这个函数的作用是利用 L2 范数来计算张量的误差值,但是没有开方并且只取 L2 范数的值的一半,具体如下:
output = sum(t ** 2) / 2输入参数:
t: 一个Tensor。数据类型必须是一下之一:float32,float64,int64,int32,uint8,int16,int8,complex64,qint8,quint8,qint32。虽然一般情况下,数据维度是二维的。但是,数据维度可以取任意维度。name: 为这个操作取个名字。输出参数:
一个
Tensor,数据类型和t相同,是一个标量。
使用例子
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
input_data = tf.Variable( np.random.rand(2, 3), dtype = tf.float32 )
output = tf.nn.l2_loss(input_data)
with tf.Session() as sess:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init)
print sess.run(input_data)
print sess.run(output)
print sess.run(tf.shape(output))
二、分类器
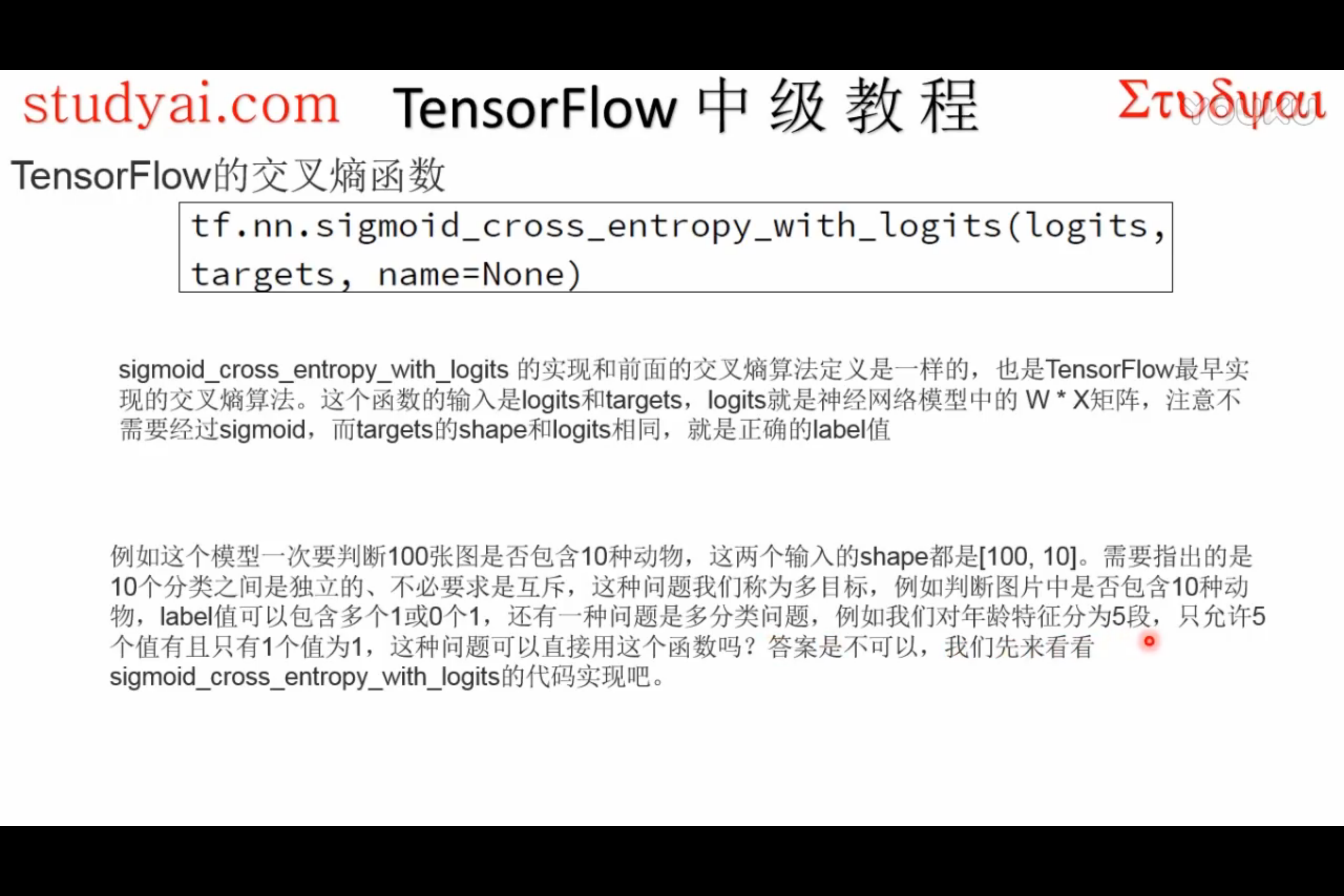
sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits
sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits
tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, targets, name=None)解释:这个函数的作用是计算
logits经 sigmoid 函数激活之后的交叉熵。对于一个不相互独立的离散分类任务,这个函数作用是去度量概率误差。比如,比如,在一张图片中,同时包含多个分类目标(大象和狗),那么就可以使用这个函数。
为了描述简洁,我们规定
x = logits,z = targets,那么 Logistic 损失值为:x - x * z + log( 1 + exp(-x) )为了确保计算稳定,避免溢出,真实的计算实现如下:
max(x, 0) - x * z + log(1 + exp(-abs(x)) )输入参数:
logits: 一个Tensor。数据类型是以下之一:float32或者float64。targets: 一个Tensor。数据类型和数据维度都和logits相同。name: 为这个操作取个名字。输出参数:
一个
Tensor,数据维度和logits相同。
使用例子:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
input_data = tf.Variable( np.random.rand(1,3), dtype = tf.float32 )
output = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(input_data, [[1.0,0.0,0.0]])
with tf.Session() as sess:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init)
print sess.run(input_data)
print sess.run(output)
print sess.run(tf.shape(output))
早期使用,后来多使用softmax。

softmax
tf.nn.softmax(logits, name=None)解释:这个函数的作用是计算 softmax 激活函数。
对于每个批
i和 分类j,我们可以得到:softmax[i, j] = exp(logits[i, j]) / sum(exp(logits[i]))输入参数:
logits: 一个Tensor。数据类型是以下之一:float32或者float64。数据维度是二维[batch_size, num_classes]。name: 为这个操作取个名字。输出参数:
一个
Tensor,数据维度和数据类型都和logits相同。
使用例子:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
input_data = tf.Variable( [[0.2, 0.1, 0.9]] , dtype = tf.float32 )
output = tf.nn.softmax(input_data)
with tf.Session() as sess:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init)
print sess.run(input_data)
print sess.run(output)
print sess.run(tf.shape(output))
log_softmax
tf.nn.log_softmax(logits, name=None)解释:这个函数的作用是计算 softmax 激活函数。
对于每个批
i和 分类j,我们可以得到:softmax[i, j] = log(exp(logits[i, j]) / sum(exp(logits[i])))输入参数:
logits: 一个Tensor。数据类型是以下之一:float32或者float64。数据维度是二维[batch_size, num_classes]。name: 为这个操作取个名字。输出参数:
一个
Tensor,数据维度和数据类型都和logits相同。
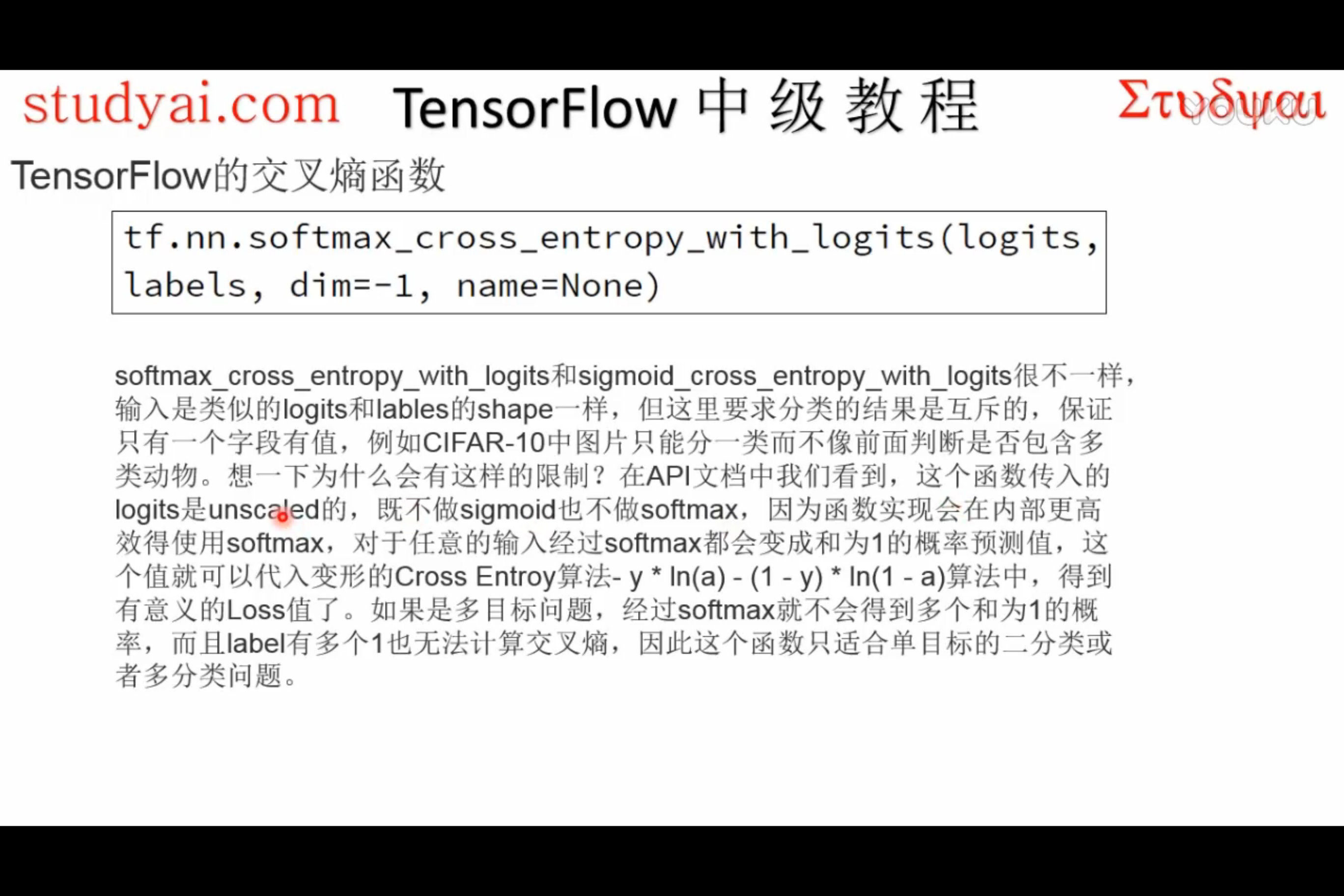
softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None)解释:这个函数的作用是计算
logits经 softmax 函数激活之后的交叉熵。对于每个独立的分类任务,这个函数是去度量概率误差。比如,在 CIFAR-10 数据集上面,每张图片只有唯一一个分类标签:一张图可能是一只狗或者一辆卡车,但绝对不可能两者都在一张图中。(这也是和
tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, targets, name=None)这个API的区别)警告:输入API的数据
logits不能进行缩放,因为在这个API的执行中会进行 softmax 计算,如果logits进行了缩放,那么会影响计算正确率。不要调用这个API区计算 softmax 的值,因为这个API最终输出的结果并不是经过 softmax 函数的值。
logits和labels必须有相同的数据维度[batch_size, num_classes],和相同的数据类型float32或者float64。
使用例子:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
input_data = tf.Variable( [[0.2, 0.1, 0.9]] , dtype = tf.float32 )
output = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(input_data, [[1,0,0]])
with tf.Session() as sess:
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init)
print sess.run(input_data)
print sess.run(output)
print sess.run(tf.shape(output))

sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits, labels, name=None)解释:这个函数的作用是计算
logits经 softmax 函数激活之后的交叉熵,同softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits,只是logits的shape是[batch, class], label的shape是[batch],不用人为one_hot编码。
weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits





